1 FORMULE TRIGONOMETRICHE
Formule trigonometriche - Archi notevoli
Marcello Colozzo - http://www.extrabyte.info
1
Formule trigonometriche
Dalla circonferenza trigonometica si ha:
P (cos x, sin x) ∈ Γ : ξ 2 + η 2 = 1,
cosicchè:
sin2 x + cos2 x = 1,
(1)
che è l’identità fondamentale della trigonometria piana. Altre formule notevoli di cui omettiamo
la dimostrazione sono:
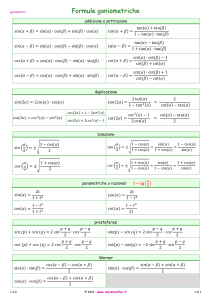
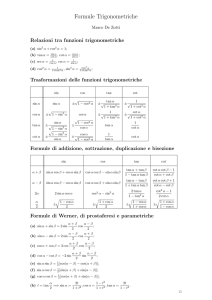
1. Formule di addizione e sottrazione
sin (x ± y) = sin x cos x ∓ cos x sin y
(2)
cos (x ± y) = cos x cos x ∓ sin x sin y
(3)
tan (x ± y) =
tan x ± tan y
1 ∓ tan x tan y
(4)
cot (x ± y) =
cot x cot y − 1
cot x ∓ cot y
(5)
2. Formule di duplicazione
sin 2x = 2 sin x cos x
(6)
cos 2x = cos2 x − sin2 x = 2 cos2 x − 1 = 1 − 2 sin2 x
(7)
tan 2x =
2 tan x
1 − tan2 x
(8)
cot 2x =
cot2 x − 1
2 cot x
(9)
3. Formule di bisezione
x
sin = ±
2
tan
x
2
cot
x
2
r
1 − cos x
2
r
1 + cos x
x
cos = ±
2
2
r
1 − cos x
sin x
1 − cos x
=±
=
=
1 + cos x
1 + cos x
sin x
r
1 + cos x
1 + cos x
sin x
=±
=
=
1 − cos x
sin x
1 − cos x
1
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
1 FORMULE TRIGONOMETRICHE
4. Formule di prostaferesi
sin x ± sin y = 2 sin
x±y
x∓y
cos
2
2
(14)
cos x + cos y = 2 cos
x−y
x+y
cos
2
2
(15)
x+y
x−y
sin
2
2
(16)
cos x − cos y = −2 sin
tan x ± tan y =
sin (x ± y)
π
, con x, y 6= (2k + 1) , ∀k ∈ Z
cos x cos y
2
(17)
sin (x ± y)
, con x, y 6= kπ, ∀k ∈ Z
sin x sin y
(18)
cot x ± cot y =
5. Formule di Werner
sin x cos y =
1
[sin (x + y) + sin (x − y)]
2
(19)
cos x cos y =
1
[cos (x + y) + cos (x − y)]
2
(20)
sin x sin y =
1
[cos (x − y) − cos (x + y)]
2
(21)
6. Altre formule notevoli che esprimono sin x, cos x, tan x, cot x, in funzione razionale di tan x2 :
sin x =
2 tan x2
1 + tan2
x
2
cos x =
1 − tan2
1 + tan2
x
2
x
2
tan x =
2 tan x2
1 − tan2
cot x =
1 − tan2
2 tan x2
2
x
2
x
2
(22)
(23)
(24)
(25)
1 FORMULE TRIGONOMETRICHE
1.0.1
Archi notevoli
π π
, 5 . Risulta:
Gli archi notevoli sono π6 , π3 , π4 , 10
√
√
r
π
1
π
π
π √
3
3
2 π
sin = =⇒ cos = 1 − sin
=
=⇒ tan =
=⇒ cot = 3
6
2
6
6
2
6
3
6
√
√
π
π
3
3
π
1
π √
sin =
=⇒ cos = =⇒ tan = 3 =⇒ cot =
3
3
2
3
3
3
√2
√
π
2
2
π
π
π
sin =
=⇒ cos =
=⇒ tan = 1 =⇒ cot = 1
4
2
4
2 s
4
4
p
√
2
√
√
5−1
5−1
10 + 2 5
π
π
sin
=
=⇒ cos
= 1−
=
10
4
10
16
4
p
√
√
π
π
5−1
10 + 2 5
=p
= √
=⇒ tan
√ =⇒ cot
10
10
5−1
10 + 2 5
p
√
π
10 − 2 5
sin =
=⇒
5
4
q
s
√ 2
p
p
√
√
√
√
1+ 5
6+2 5
1+2 5+5
1+ 5
π
10 − 2 5
=
=
=
=
cos = 1 −
5
16
4
4
4
4
Riassumiamo nella seguente tabella:
x
π
6
sin x
1
2
√
π
3
√
3
2
tan x
3
2
√
3
3
cot x
√
cos x
3
1
2
√
√
3
3
3
π
4
√
2
2
√
2
2
1
1
π
10
√
5−1
√4
√
10+2 5
4
√
5−1
√
√
√10+2√5
10+2 5
√
5−1
π
5
√
√
10−2 5
4
√
1+ 5
√4 √
10−2 5
√
1+ 5
√1+
√
5
√
10−2 5
Di seguito un esempio di equazione trigonometrica (o goniometrica).
3