2 aprile 2012
VB
Membrane specializzate e vita della cellula
(identità e dinamica)
• Tutte le membrane biologiche hanno ruolo di confinamento e generano identità
• Ogni membrana ha una sua specializzazione in particolari funzioni
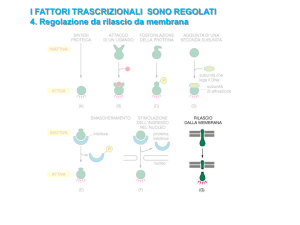
Funzione nel controllo trascrizionale di geni chiave del metabolismo ?
PDB code 1T02
Rudolf Schoenheimer.
1898-1941
Hitler’s gift and the era of Biosynthesis JBC Centennial November 16 2001
* * * HMG (controllo sul gene)
Sterol regulatory
element-binding protein
SREBP cleavage
activating protein
ER
Insulin induced gene
Golgi
Helix-Loop-HelixLeucine Zipper Domain
Lee et al Science 302, 1571-5, 2003
Lee et al Science 302, 1571-5, 2003
Cholesterol Scap interaction
COP II: coat protein complex
Mechanism of transport h1p://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4TGDPotbJV4 h1p://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kOeJwQ0OXc4&feature=related INSIG 1
mRNA controlled by insulin
Protein controlled by cholesterol (stabilization-destabilization
and ubiquitination) (reservoir effect when low cholesterol)
nSREBP control INSIG gene
INSULIN
Activate expression of SREBP
Activate the expression of INSIG1
Phosphorilation of SREBP
HMG reductase (controllo sulla proteina)
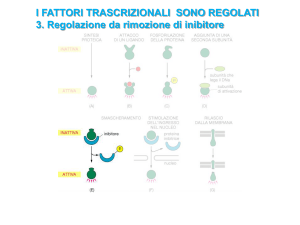
1. INSIG binding to SCAP SREBP = stabilization
2. INSIG binding to HMG= degradation
2 is mainly mediated by lanosterol (toxic for the cell)
(SREBP activating enzymes acting on the pathway lanosterol-cholesterol)
MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders.
Rottiers V, Näär AM
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Mar 22;13(4):239-50.
Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center, Charlestown, Massachusetts 02129,
USA. [2] Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts
02115, USA.
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have recently emerged as key regulators of metabolism. For
example, miR-33a and miR-33b have a crucial role in controlling cholesterol and lipid
metabolism in concert with their host genes, the sterol-regulatory element-binding
protein (SREBP) transcription factors. Other metabolic miRNAs, such as miR-103 and
miR-107, regulate insulin and glucose homeostasis, whereas miRNAs such as miR-34a
are emerging as key regulators of hepatic lipid homeostasis. The discovery of
circulating miRNAs has highlighted their potential as both endocrine signalling
molecules and disease markers. Dysregulation of miRNAs may contribute to metabolic
abnormalities, suggesting that miRNAs may potentially serve as therapeutic targets for
ameliorating cardiometabolic disorders.
Rudolf Schoenheimer.
1898-1941
:
“The dynamic state of body constituents”
1941 Dunham Lectures at Harvard Medical School