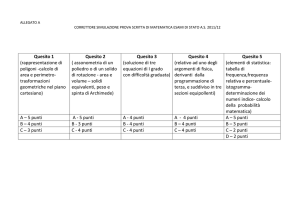
Scenari per la
determinazione
del valore di un
farmaco oncologico
(ASCO – ESMO).
Perché Ni
Giovanni L. Pappagallo
The wide array of treatment options, their attendant clinical
impact, and cost to the patient suggested the importance of
developing a framework with which to assess new therapies.
Two frameworks have been developed: one for advanced
disease and the other for potentially curative disease.
Essential domains in the assessment of an agent’s value were
clinical benefit, toxicity, and cost.
ASCO Framework for Assessing Value in Cancer Care
• Will serve as a tool in the process of shared decisionmaking between physician and patient:
designed to have the relative weights (importance) be modifiable according to patient preference
ASCO Framework for Assessing Value in Cancer Care
• Will serve as a tool in the process of shared decisionmaking between physician and patient:
designed to have the relative weights (importance) be modifiable according to patient preference
• The composite of the clinical benefit, bonus points,
and toxicity scores is tallied to generate a net health
benefit (NHB):
a measure of the relative improvement a new
regimen has yielded when compared with the
control therapy against which it was compared in
the clinical trial
ASCO Framework for Assessing Value in Cancer Care
This tool uses a rational, structured and consistent approach to
derive a relative ranking of the magnitude of clinically meaningful benefit that can be expected from a new anti-cancer treatment.
ESMO-MCBS
• To assign the highest grade to trials having adequate
power for a relevant magnitude of benefit, and to
make appropriate grade adjustment to reflect the
observed magnitude of benefit.
does not address the issue from the perspective of
communication between physician and patient
a policy tool, not a tool to be deployed at the
clinical interface
ESMO-MCBS
• To assign the highest grade to trials having adequate
power for a relevant magnitude of benefit, and to
make appropriate grade adjustment to reflect the
observed magnitude of benefit.
• Clinical benefit in either the advanced or potentially
curative settings is judged by both the hazard ratios
achieved and absolute improvement in the prespecified clinical endpoint defined for the trial in
question
ESMO-MCBS
What if non
proportional
hazards?
(metastatic disease,
no long-survivors;
plateau of longsurvivors; etc.)
Therapeutic
alternative Vs
control arm
Incomplete efficacy estimator;
correlation with HR?
ESMO-MCBS
… as I
thought
M.I.D. or
P<0.05?
M.I.D. or
P<0.05?
Clinical
relevance or
P<0.05?
What if
grade 2
diarrhea?
ESMO-MCBS
• To assign the highest grade to trials having adequate
power for a relevant magnitude of benefit, and to
make appropriate grade adjustment to reflect the
observed magnitude of benefit.
• Clinical benefit in either the advanced or potentially
curative settings is judged by both the hazard ratios
achieved and absolute improvement in the prespecified clinical endpoint defined for the trial in
question
• To provide a clear, well-structured and validated
mechanism to indicate the magnitude of benefit in
addition to the level of evidence in ESMO guidelines
ESMO-MCBS
• To assign the highest grade to trials having adequate
power for a relevant magnitude of benefit, and to
make appropriate grade adjustment to reflect the
observed magnitude of benefit.
• Clinical benefit in either the advanced or potentially
curative settings is judged by both the hazard ratios
achieved and absolute improvement in the prespecified clinical endpoint defined for the trial in
question
• To provide a clear, well-structured and validated
mechanism to indicate the magnitude of benefit in
addition to the level of evidence in ESMO guidelines
ESMO-MCBS
Il percorso verso la proposta terapeutica…
• Una volta definito con chiarezza il quesito
clinico…
• sarà necessario verificare:
– l’affidabilità delle evidenze (confidence)
– la diretta (o meno) trasferibilità delle
evidenze disponibili alla tipologia di
paziente oggetto del quesito clinico
(directness)
– la rilevanza clinica degli effetti osservati
(relevance)
Strutturazione del Quesito Clinico sec. modello P.I.C.O.
Nei Pazienti con…
Specifiche caratteristiche di
malattia (stadio, classe di
rischio, ecc.)
I
l’Intervento…
Intervento terapeutico oggetto
del quesito clinico
C
(è suscettibile di
impiego)
in Confronto con…
Trattamento altrimenti considerabile in alternativa all’intervento in esame
O
riguardo agli
Outcome di
beneficio/danno…
Parametri clinico-laboratoristici
ritenuti essenziali per la
decisione terapeutica
P
Il percorso verso la proposta terapeutica…
• Una volta definito con chiarezza il quesito
clinico…
ESMO-MCBS
Guidelines:
• sarà necessario
verificare:
non strutturazione
sec.
– l’affidabilità
delle evidenze
(confidence)
P.I.C.O.
– la diretta (o meno) trasferibilità delle
evidenze disponibili alla tipologia di
paziente oggetto del quesito clinico
(directness)
– la rilevanza clinica degli effetti osservati
(relevance)
Il percorso verso la proposta terapeutica…
• Una volta definito con chiarezza il quesito
clinico…
• sarà necessario verificare:
– l’affidabilità delle evidenze (confidence)
– la diretta (o meno) trasferibilità delle
ESMO-MCBS
Guidelines:
evidenze
disponibili
alla tipologia di
Study
Design,del
Allocation
paziente
oggetto
quesito clinico
Concealment (Attrition?
(directness)
Detection? Performance?
Imprecision?
– la rilevanza
clinica Inconsistency?)
degli effetti osservati
(relevance)
Il percorso verso la proposta terapeutica…
• Una volta definito con chiarezza il quesito
clinico…
• sarà necessario verificare:
– l’affidabilità delle evidenze (confidence)
– la diretta (o meno) trasferibilità delle
evidenze disponibili alla tipologia di
paziente oggetto del quesito clinico
(directness)
ESMO-MCBS Guidelines:
– la rilevanza clinica
degli
effetti
osservati
non strutturazione sec.
(relevance)
P.I.C.O.
Il percorso verso la proposta terapeutica…
• Una volta definito con chiarezza il quesito
clinico…
• sarà necessario verificare:
– l’affidabilità delle evidenze (confidence)
– la diretta
(o meno) Guidelines:
trasferibilità delle
ESMO-MCBS
evidenze
disponibili
allaclinica
tipologia di
Soglie
di rilevanza
paziente
del quesito
clinico
peroggetto
QoL e reazioni
averse?
(directness)
– la rilevanza clinica degli effetti osservati
(relevance)
For
Against
Benefit to Harm ratio
ESMO-MCBS
• Relevance of outcomes
(benefit and harm)
• Quality of Evidence
(confidence , directness)
• Base Risk (related to
disease state)
• Relevance of Effects
(benefits and harms)
Scenari per la
determinazione
del valore di un
farmaco oncologico
(ASCO – ESMO).
Ni, perché…
Giovanni L. Pappagallo