Lesson 10
(A2/B1)
Past continuous
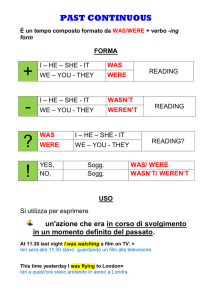
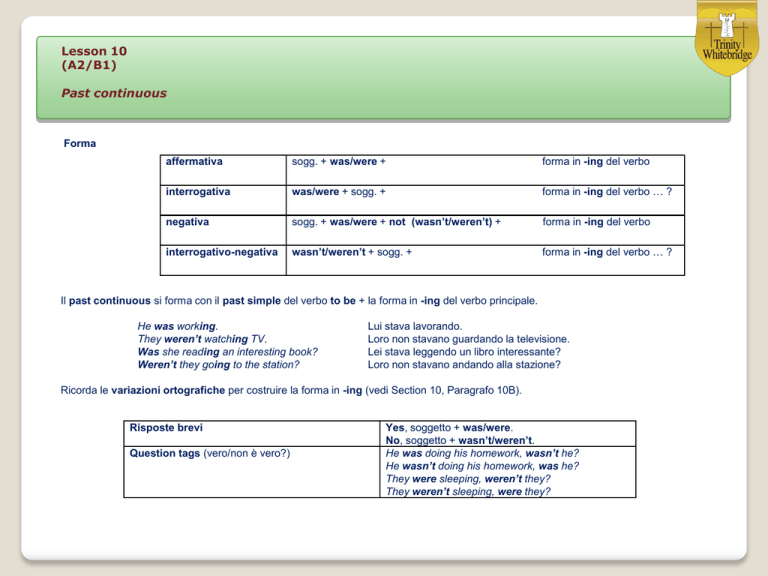
Forma
affermativa
sogg. + was/were +
forma in -ing del verbo
interrogativa
was/were + sogg. +
forma in -ing del verbo … ?
negativa
sogg. + was/were + not (wasn’t/weren’t) +
forma in -ing del verbo
interrogativo-negativa
wasn’t/weren’t + sogg. +
forma in -ing del verbo … ?
Il past continuous si forma con il past simple del verbo to be + la forma in -ing del verbo principale.
He was working.
They weren’t watching TV.
Was she reading an interesting book?
Weren’t they going to the station?
Lui stava lavorando.
Loro non stavano guardando la televisione.
Lei stava leggendo un libro interessante?
Loro non stavano andando alla stazione?
Ricorda le variazioni ortografiche per costruire la forma in -ing (vedi Section 10, Paragrafo 10B).
Risposte brevi
Question tags (vero/non è vero?)
Yes, soggetto + was/were.
No, soggetto + wasn’t/weren’t.
He was doing his homework, wasn’t he?
He wasn’t doing his homework, was he?
They were sleeping, weren’t they?
They weren’t sleeping, were they?
Lesson 10
(A2/B1)
Past continuous
Quando si usa
Il past continuous corrisponde all’imperfetto indicativo o alla forma “stare + gerundio” dell’italiano.
Si usa per:
• parlare di un’azione che era in corso di svolgimento in un momento determinato del passato.
Yesterday at 5.00 p.m. we were waiting for the bus.
Ieri alle cinque del pomeriggio aspettavamo / stavamo aspettando l’autobus.
• indicare che un’azione era già in corso di svolgimento quando se ne è verificata un’altra che ha interrotto la prima.
He was having a shower when the telephone rang.
Lui stava facendo la doccia quando il telefono squillò.
• descrivere due o più azioni che si svolgevano contemporaneamente.
While I was watching TV, mum was making dinner.
Mentre io guardavo la televisione, la mamma preparava la cena.
Inoltre si usa per:
• esprimere irritazione o disapprovazione nei confronti di un’abitudine del passato (come avviene con il present continuous nei
confronti di un’abitudine del presente).
She was complaining all the time, which was really disappointing.
Lei si lamentava in continuazione, il che era veramente irritante.
• parlare di un’azione programmata per un tempo futuro in relazione ad un tempo del passato
They were meeting the following day.
Si sarebbero incontrati il giorno successivo.
Lesson 10
(A2/B1)
Past continuous
Past simple / Past continuous
Il past simple descrive un’azione iniziata e conclusa nel passato.
Il past continuous descrive un’azione in corso di svolgimento nel passato.
Spesso il past simple e il past continuous si trovano insieme introdotti da: while e when.
• while (mentre)
introduce un’azione lunga in corso di svolgimento (un’azione che stava accadendo) che è stata interrotta ed è seguito da un past
continuous.
He arrived while I was having dinner.
While I was driving to work I had an accident.
Lui arrivò mentre io stavo cenando.
Mentre stavo andando al lavoro ebbi un incidente.
• when (quando)
generalmente introduce un’azione breve che interrompe un’azione in corso di svolgimento ed è seguito da un past simple.
I was having dinner when he arrived.
I was driving to work when I had an accident.
Stavo cenando quando lui arrivò.
Stavo andando al lavoro quando ebbi un incidente.
When può introdurre anche l’azione in corso di svolgimento, ma in questo caso ha il significato di “mentre” come while.
I had an accident when/while I was driving to work.
Attenzione!
Confronta i seguenti esempi:
1. When Peter arrived we were having dinner. Quando Peter arrivò stavamo cenando.
(Peter arrivò nel mezzo di un’azione in corso; in questo caso un’azione in corso di svolgimento è stata interrotta da un’altra azione.)
2. When Peter arrived we had dinner.
Quando Peter arrivò cenammo.
(Peter arrivò e poi cenammo; in questo caso gli eventi sono in sequenza, un evento dopo l’altro.)
EXERCISE 1
Immaginiamo questa situazione. Ieri sera alle 20.00 è stato commesso un furto in un palazzo. Nessuno degli inquilini ha
visto o sentito qualcosa perché erano tutti impegnati a fare qualcosa.
Completiamo le frasi con il past continuous dei verbi tra parentesi per descrivere ciò che gli inquilini stavano facendo in
quel momento.
1.
The Browns, who live on the ground floor, (listen to) ……………………………… music.
2.
Mr Jordan, who lives on the first floor, (watch) …………………………. TV.
3.
Mrs Jones, who lives next to Mr Jordan, (cook) …………………………………. .
4.
Helen, who lives on the second floor, (check) …………………………………….. her e-mail.
5.
George, who lives next to Helen, was with a friend. They (study) ………………………… for an exam.
6.
The Ashleys, who live on the third floor, (talk) ……………………………….
7.
Sheila Barnes, who also lives on the third floor, (talk) …………………………… on the phone.
EXERCISE 2
Immaginiamo questa situazione. Successivamente al furto avvenuto ieri sera (Exercise 1) la polizia ha rivolto delle
domande specifiche agli inquilini.
Formuliamo le domande della polizia usando i suggerimenti forniti tra parentesi e il past continuous dei verbi, e
completiamo adeguatamente le risposte degli inquilini.
1.
A: (What / you / watch ) ………………………………………on TV, Mr Jordan?
B: I …………………………… a football match.
2.
A: (What / you / cook) ………………………………………………, Mrs Jones?
B: I (roast) …………………………………………………… a chicken.
3.
A: (What / you and your friend / study) …………………………….., George?
B: We …………………………………………… History.
4.
A: What exactly (you / do) …………………………………….… on your computer ?
B: I (check) …………………………….………………… my e-mail.
5.
A: (What / you / talk about) ……………………………………., Mr and Mrs Ashley?
B: We ………………………………………… our son’s school problems.
6.
A: (Who / you / talk to) ………………………………………….., Miss Barnes?
B: I …………………………………………….. a friend.
7.
A: (What / you / listen to) ………………………………………., Mr and Mrs Brown?
B: We ………………………………………….. to jazz music on the radio.
EXERCISE 3
Immaginiamo questa situazione. Carol è una donna in carriera. Lavora presso una grande azienda a Londra ed è sempre
occupatissima. Spesso svolge due azioni contemporaneamente. Ieri in particolare è stata una giornata molto impegnativa.
Completiamo le frasi con il past continuous dei verbi tra parentesi.
1.
(8.00) While Carol (have) …………………………….. breakfast, she
(talk) ……………………….… to her assistant on the phone.
2.
(9.00 -10.30) While she (travel) ………………………… to Manchester by train, she (write)
………………………….. a report on her tablet.
3.
(11am) At eleven she (discuss) …………………………….. a marketing campaign with the marketing manager
while they (have) ………………………… coffee.
4.
(12.00-14.00) While she and John Miles, the media buyer, (have) …………………… lunch, they (look)
…………………………….. at some statistics in order to choose the best advertising media.
5.
(15.00-16.30) While she (sit) …………………………….. on the train back to London, she (analyse)
………………………….. the sales figures of the previous quarter.
EXERCISE 4
Past simple o past continuous? Osserviamo queste frasi e completiamole
con il tempo verbale corretto dei verbi tra parentesi. Motiviamo la scelta.
1.
While the Campbells (have) ……………………….. dinner, their daughter
(call) …………………………… from Los Angeles.
2.
David (rush) ………………………… downstairs when he (slip) ……………………… and (sprain)
……………………………… his ankle.
3.
My computer (crash) ………………………… while I (check) ………………….… my e-mail.
4.
The train (stand) …………………………….. in the station. George (run) …………………… to catch it but, when he
(reach) ……………………… the platform, the train (move) ………………………… off.
5.
We (enjoy) …………………………….. a wonderful view of the city from the top of the tower when the sky
suddenly (become) …………………….. dark.
6.
We (see) ……………………… Mr Collins. He (sit) ………………………… at a café and (drink)
……………………… coffee, but he (not / see) …………………… us.
EXERCISE 5
Questi tre paragrafi raccontano un evento imbarazzante accaduto ad un ragazzo, ma sono disposti nell’ordine sbagliato.
Leggiamoli velocemente per farci un’idea generale della storia, poi mettiamoli nell’ordine corretto e completiamo gli spazi
con il past simple o il past continuous dei verbi tra parentesi.
A.
… . She (look at) ………………………… me strangely and then (walk) ………………… across the street towards
me. I (think) …………………….. that she (come) …………………………… over for a chat.
B.
… . But then she (walk) ……………………….. straight past, and I (realise) ………………… that she had been
waving at his boyfriend behind me.
C.
… . Yesterday afternoon, I (queue) ………………………….. at the bus stop in the high street when suddenly a girl
from my school that I liked (wave) ………………………….. at me from the other side of the street, so I (wave)
………………… back.