ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
September 8th, 2008
Prof. Marco Sampietro
Number N°
NAME
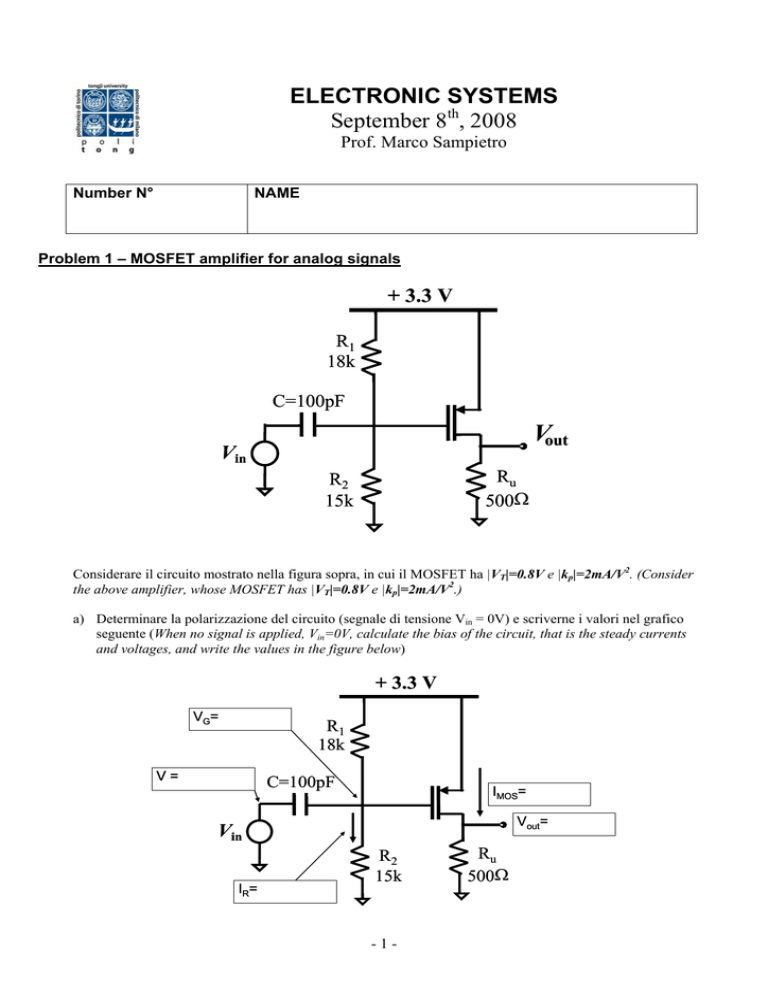
Problem 1 – MOSFET amplifier for analog signals
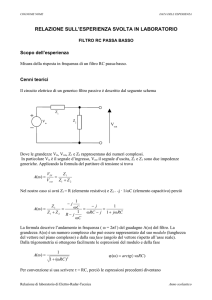
+ 3.3 V
R1
18k
C=100pF
Vout
Vin
i
Ru
500Ω
R2
15k
Considerare il circuito mostrato nella figura sopra, in cui il MOSFET ha |VT|=0.8V e |kp|=2mA/V2. (Consider
the above amplifier, whose MOSFET has |VT|=0.8V e |kp|=2mA/V2.)
a) Determinare la polarizzazione del circuito (segnale di tensione Vin = 0V) e scriverne i valori nel grafico
seguente (When no signal is applied, Vin=0V, calculate the bias of the circuit, that is the steady currents
and voltages, and write the values in the figure below)
+ 3.3 V
VG=
R1
18k
V=
C=100pF
IMOS=
Vout=
Vin
i
IR=
R2
15k
-1-
Ru
500Ω
b) Calcolare la potenza totale assorbita dalle alimentazioni e la potenza dissipata dal solo transistore in
assenza di segnale. Calcolare anche le ore in cui si può tenere acceso il circuito quando è alimentato da
una batteria da 3 Ampere x ora (Calculate the total power taken from the power supply by the circuit and
the power dissipated by the transistor, when no signal is present. Also calculate how many hours you
can keep on the circuit when powered by a battery of 3 Ampere x hour).
Psupply =
PMosfet =
Hours =
c) Calcolare l’espressione ed il valore del guadagno di tensione del circuito, G=Vout/Vin quando si applica
un piccolo segnale di tensione, Vin, a media frequenza (C chiuso) all’ingresso (Apply a small voltage
signal at the input and calculate the espression and the value of the voltage gain at medium frequency (C
short circuited).
Vout
=
G=
Vin
=
espression
value
d) Tracciare sul grafico qui sotto l’andamento della tensione Vout quotando bene gli assi, quando
all’ingresso è applicato il gradino di tensione positivo ampio 20mV della figura seguente. (Draw in the
section below the time behaviour of the output voltage Vout when the input is the positive step voltage of
20mV indicated in the following figure).
Vin
20mV
Vout
t
0
t
0
e) Disegnare il diagramma di Bode (modulo e fase) di G(s)=Vout(s)/Vin(s) del circuito. (Draw the Bode plots
of the gain G(s)=Vout(s)/Vin(s) of the circuit due only to the capacitance C.)
-2-
G
f
Phase
+90°
0°
f
-90°
-180°
-270°
f) Immaginando di volere aumentare il guadagno aumentando il valore della resistenza Ru, trovare
il massimo valore di Ru possibile, giustificando la scelta. (Calculate the maximum value of the
resistor Ru that could be used in the circuit in order to increase the voltage gain of the circuit.)
Ru|MAX =
-3-
Problem 2 – Digital CMOS circuit
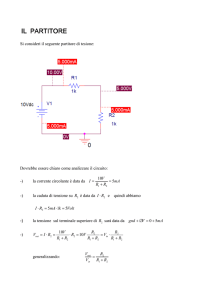
Si consideri il seguente invertitore digitale realizzato con una tecnologia avente le seguenti
caratteristiche: ½µpCox=0.05mA/V2, ½µnCox=0.1mA/V2, |VT|=0.7V, (W/L)n=(W/L)p=2. C1=100pF
è una capacità esterna collegata ai gate dell’invertitore. CL=100fF rappresenta la capacità totale dei
circuiti collegati dopo l’invertitore. (Consider the following digital inverter that uses a technology
with the following characteristics: ½µpCox=0.05⋅mA/V2, ½µnCox=0.1mA/V2, |VT|=0.7V,
(W/L)n=(W/L)p=2. C1=100pF is an external capacitance connected to the gates of the inverter.
CL=100fF is the total capacitance of the circuits following the inverter).
Vdd =+3V
R1
10k
VOUT1
VOUT2
R2
20k
Vin
C1
100pF
CL=100fF
a) Disegnare in un diagramma temporale l'andamento della tensione VOUT1, quotandone tutti i
punti significativi, quando in ingresso sia applicata l'onda quadra mostrata qui sotto (Draw and
quote the time behaviour of the voltage in VOUT1 when the following Vin signal is applied to the
input)
Vin
3V
t
Vout1
0
4µs
8µs
12µs
t
0
4µs
-4-
8µs
12µs
b) Determinare la tensione di soglia Vinv dell’invertitore. (Calculate the value of the inverter
threshold, Vinv)
=
Vinv =
espression
value
c) Determinare il valore minimo della resistenza R2 che consente all'inverter di commutare se in
ingresso e' applicata l'onda quadra Vin del punto a). Motivare la risposta. (Calculate the
minimum value for the resistor R2 below which the inverter does NOT switch anymore when the
input signal Vin of point a) is applied.)
R2|MIN =
d) Calcolare l’espressione ed il valore della frequenza massima di commutazioni affinché la
potenza totale assorbita dalle alimentazioni dall’inverter non superi 5nW. (Calculate the
expression and the value of the maximum frequency of inversions for not absorbing more than
5nW from the power supply by the inverter)
fclockMAX =
Problem 3 – Operational Amplifier circuit
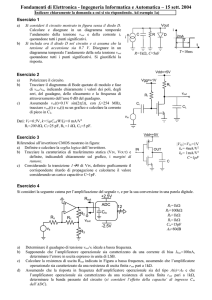
1. Si consideri il circuito della figura seguente. (Consider the following circuit)
R4
5kΩ
R2
5kΩ
R1
1kΩ
Vin
Iin
R3
1kΩ
Vout
R5
500Ω
a- Calcolare la tensione dell’uscita Vout quando in ingresso non c’e’ segnale,Vin=0V e Iin=0A.
(Calculate the value of Vout when Vin=0V and Iin=0A)
Vout =
b- Calcolare l’espressione ed il valore del guadagno G=Vout/Vin a bassa frequenza quando
Iin=0A e l’OpAmp è ideale con guadagno infinito, A(s)=∞. (Calculate the expression and
-5-
the value of the gain G=Vout/Vin at low frequency when Iin=0A and the OpAmp is ideal,
A(s)=∞ ).
G=
Vout
Vin
=
=
Iin = 0 A
expression
value
c- Calcolare l’espressione ed il valore del guadagno di transresistenza Vout/Iin a bassa frequenza
quando Vin=0V e l’OpAmp è ideale con guadagno infinito, A(s)=∞. (Calculate the
expression and the value of the transresistance “gain” Vout/Iin at low frequency when
Vin=0V and the OpAmp is ideal, A(s)=∞ ).
Vout
I in
=
=
Vin =0
expression
value
d- Calcolare l’espressione e tracciare il grafico quotato del guadagno d’anello (modulo e fase)
del circuito quando si usa un OpAmp con il seguente guadagno (Calculate the expression of
the loop-gain of the circuit when using an OpAmp with the following gain A(s) and draw the
Bode plot of the modulus and of the phase of the loop gain):
10 5
A( s ) =
con f = 1/2πτ = 70Hz.
1 + sτ
Gloop(s) =
|Gloop|
f
-6-
Phase
+90°
0°
f
-90°
-180°
-270°
-360°
e- Calcolare la banda passante del circuito che ha guadagno G=Vout/Vin e disegnare il modulo
del guadagno G=Vout/Vin in funzione della frequenza nel grafico sottostante. (Calculate the
bandwidth of the circuit that has gain G=Vout/Vin and draw the Bode plot of the modulus of
the gain G=Vout/Vin ).
Bandwidth : from fmin=
………….
untill fmax=
………….
Vout
Vin
f
f- Calcolare la banda passante del circuito che ha guadagno di transresistenza Vout/Iin e
disegnare il modulo della transresistenza Vout/Iin in funzione della frequenza nel grafico
sottostante. (Calculate the bandwidth of the circuit that has a transresistance gain Vout/Iin
and draw the Bode plot of the modulus of the transresistance gain Vout/Iin ).
Bandwidth : from fmin=
………….
-7-
untill fmax=
………….
Vout
I in
f
g- Calcolare il margine di fase del circuito qualora si usasse un OpAmp con due poli come il
seguente (Draw the Bode plots of the circuit if the OpAmp would have the following 2-poles
gain and calculate the phase margin):
10 5
1
A( s ) =
⋅
con f1 = 1/2πτ1 = 70Hz and f2 = 1/2πτ2 = 7 kHz
1 + sτ 1 1 + sτ 2
ϕmargin =
|X|
f
Phase
+90°
0°
f
-90°
-180°
-270°
-360°
-8-