Trombo-genomica
Rosa Santacroce
Genetica Medica
Università di Foggia
Malattie multifattoriali
Sono il risultato di più fattori sia ambientali che
genetici.
L’importanza relativa dei fattori genetici è variabile.
Esiste un’aggregazione familiare ma non segue il
caratteristico pattern di segregazione delle malattie da
singolo gene.
Fattori di rischio acquisiti per trombosi
Obesity
Immobility
Trauma or
Surgery
Contraceptives
Who has an increased risk?
Fattori di rischio per trombosi
Obesity
Immobility
Trauma or
Surgery
Contraceptives
Genetic
Predisposition
Fattori di rischio genetici per trombosi
Factor V Leiden
Factor II 20210A
Gain of
Function
Coagulation
Antithrombin
Protein C
Protein S
Loss of
Function
~35% of patients with thrombosis have one of these risk factors
TEST PREDITTIVI
Questi test identificano il rischio relativo :
l'incremento o la riduzione del rischio di ammalarsi di
una determinata malattia nel corso della vita rispetto al
rischio medio di popolazione.
Conferma o esclude, in un soggetto
asintomatico, la propensione ad ammalarsi di una
malattia comune e/o complessa.
A role for additional common genetic variants (SNPs)?
de HAAN et al. BLOOD 2012
A role for additional common genetic variants (SNPs)?
ABO
FII A20210
FV Leiden
de HAAN et al. BLOOD 2012
La contemporanea esistenza all’interno di famiglie con trombosi
di soggetti clinicamente non affetti ma genotipicamente portatori
dei marcatori indagati rispecchia il lato multifattoriale della
trombosi
la coesistenza di difetti multipli ne modula la variabilita’ clinica.
le alterazioni genetiche note giustificano soltanto il 60%delle
condizioni trombofiliche di tipo ereditario
altri polimorfismi o mutazioni rare non ancora individuati sono
probabilmente responsabili dei casi ancora non chiari
Other Inherited Risk Factors
Hyperhomocysteinemia (?)
Factor VIII ↑ (mixed)
Dysfibrinogenemias
Factor V mutations
Factor II mutations
Unique mutations
Very rare
….dove eravamo…
Pannello Trombofilia 4 mutazioni
Valutazione genetica del rischio di patologie cardiovascolari
mediante analisi di mutazione dei geni del Fattore V di Leiden,
Fattore II (protrombina) e metilentetraidrofolatoreduttasi (MTHFR),
varianti C677T e 1298 A/C
Pannello Trombofilia 13 mutazioni
I geni in considerazione sono quelli relativi al fattore V di
Leiden, al fattore II della coagulazione (protrombina) ed il
gene MTHFR (Metilentetraidrofolatoreduttasi).
Altri geni sono stati associati a stati trombotici, tra i quali:
Fattore XIII, Beta Fibrinogeno, PAI-1, HPA, HFE, APO
E, ACE, AGT.
….dove stiamo andando…
NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING
La NGS è anche chiamata high-throughput sequencing (sequenziamento
ad alta resa) perchè, a differenza del sequenziamento tradizionale col
metodo Sanger, consente di sequenziare moltissimi frammenti in parallelo.
Esistono diversi sistemi NGS, sviluppati da diverse compagnie.
Tutti questi sistemi, tuttavia, condividono almeno tre passi fondamentali: la
preparazione e immobilizzazione del DNA (cioè la preparazione della
cosiddetta sequencing library), la reazione di amplificazione e la reazione
di sequenziamento.
NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING
Il principale vantaggio è la possibilità tecnica di produrre un
volume enorme di dati a costi estremamente più bassi ed in
tempi estremamente più rapidi
Il potenziale dell’NGS è simile ai primi tempi della PCR con il
limite principale dovuto all’immaginazione.
“NEXT GENERATION
SEQUENCING”….
AS054
Whole exome sequencing in patients with
inherited thrombocytopenia and excessive
bleeding is an efficient way to identify genetic
variants in known and novel genes
Johnson B
AS132
Validation of a next generation DNA
sequencing panel for haemostatic and platelet
disorders
Goodeve A
AS196
Next-generation DNA sequencing
approach to identify novel genetic
risk factors underlying cerebral vein
Thrombosis.
Gorski MM
Conclusion: We have successfully
applied NGS-based analysis of 740
candidate hemostatic and proinflammatory genes in 469 Italian
CVT
patients
and
controls,
identifying a common indel variant
rs8176719 in the ABOgene that has
been previously associated with deep
vein thrombosis of the lower limbs
and pulmonary embolism.
OR176
Diagnosis of inherited bleeding, thrombotic and platelet diseases
by next generation sequencing.
Simeoni I
Most monogenic inherited bleeding, thrombotic and platelet
disorders (BTPD) except Haemophilia and von Willebrand’s
diseases are extremely rare.
Reaching a conclusive laboratory diagnosis remains challenging
in the routine health care settings. Next generation sequencing
(NGS) will change their laboratory diagnosis bringing benefits
to patient care.
PO543-MON
Genetic variability of KNG1and F11genes using next generation sequencing
Martin-Fernandez L1
Background: Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a complex disease with a
high heritability. However, only a portion of the genetic component is
accounted for by genetic risk factors. From the GWAS of factor XI (FXI)
performed in the GAIT-1 (Genetic Analysis of Idiopathic Thrombophilia)
project significant associations were identified at KNG1andF11loci.
Aims: We performed Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) of the KNG1and
F11 genes to identify genetic variants that might be involved in the risk of
thrombosis.
Bleeding symptoms or bleeding disorder? That is the question
Fasulo MR
Conclusion: Our results show that the majority of patients with
history of bleeding symptoms has not necessary a hemostatic
defect. In patients with a severe bleeding diathesis further
evaluation using next generation sequencing might help to
understand the role of novel genes encoding for unknown
proteins involved in haemostasis.
OR394
Identification of new genetic risk factors for venous thrombosis by targeted
sequencing: results of the MILES study
de Haan HG
Conclusion:Using a targeted sequencing strategy we were able to identify new
genetic risk factors for venous thrombosis. Replication and functional studies
are needed to confirm our findings and to unravel the biological mechanisms
involved
OR266
Meta-analysis of 65,734 individuals identifies TSPAN15andSLC44A2as two
new susceptibility loci for venous thromboembolism
Morange P-E
Conclusion: We identified 2 loci (TSPAN15andSLC44A2) that had novel
associations with VTE yet do not belong to canonical pathways leading to
thrombosis and have not been associated with other cardiovascular endpoints.
These findings may provide etiologic and mechanistic insights into VTE
pathophysiology.
PO653-MON
The use of next-generation sequencing to screen for disorders of
coagulation using a 24 gene panel
Bignell P
Aims: We sought to investigate the clinical utility of NGS for
understanding haemostatic disease by sequencing 24 coagulation genes
using a designed TruSeq Custom Amplicon (TSCA) panel.
Methods:Samples were run on the Illumina MiSeq platform
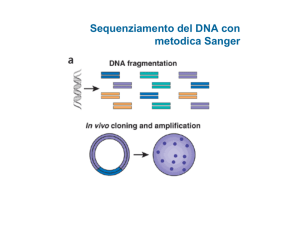
Sanger Sequencing
Determining the nucleotide sequence (A, T, C and G) of a DNA of a gene
Next generation sequencing (NGS)
Next generation sequencing (NGS) is often referred to as massively
parallel sequencing of clonally amplified or single DNA molecules
that are spatially separated in a flow cell.
NGS generates hundreds of megabases to gigabases of nucleotidesequence output in a single instrument run, depending on the
platform.
Next generation sequencing (NGS)
ADVANTAGES OF NGS
Revolutionary improvements in cost and speed of
data generation
Provides exquisite resolution for many types of
experiments
Next generation sequencing (NGS)
DIS-ADVANTAGES OF NGS
Shorter read lenght sequenced are produced
Bioinformatics-based analysis
File size traumatize IT infrastructures
Next generation sequencing (NGS)
Sanger vs Next Generation Sequencing
Sequencing workflow
NGS Data Analysis flowchart
Immagini
.TIFF
Visualizzazione
Intensità
Filtraggio
delle varianti
Reads
FASTQ
Quality control:
FastQC,
FastXtoolkit
Allineamento
SAM
BAM
BED
Bowtie
BWA
Maq
Identificazione
delle varianti
.vcf
GATK
SAMtool
Varscan
Reads and coverage
Quella dei test genetici è forse l’area in
più rapida espansione e ricca di
problematiche con un impatto pratico
immediato sulla vita reale delle
persone.
L’informazione derivante dal test genetico è
permanente in quanto non si modifica
nell’arco di vita dell’individuo.
Il test genetico fornisce informazioni non
solo sull’individuo testato ma anche sui suoi
familiari.
Venous thrombosis is a multifactorial disease
VTE
Threshold
Number
of risk
factors
for VT
GRAZIE PER L’ATTENZIONE!