UNITÀ DIDATTICA 4
VERBO ESSERE E VERBO AVERE
HAVE GOT ESPRESSIONI IDIOMATICHE
Verbi ESSERE e AVERE.
TO BE e TO HAVE (TO indica l’infinito).
Sono verbi ausiliari (aiutano gli altri verbi a formare modi e tempi verbali):
− TO BE (forma progressiva, forma passiva).
− TO HAVE (tempi composti).
In inglese è importante il concetto di paradigma verbale (forme base dei verbi da cui si
ottengono tutti i tempi verbali):
− INFINITO PASSATO PARTICIPIO
− BE WAS/WERE BEEN
− HAVE HAD HAD
Ricordiamo che in inglese, al contrario dell’italiano, è sempre necessario specificare il
soggetto, dunque se dico SIAMO omettendo il pronome NOI, in inglese dovrò
obbligatoriamente dire WE ARE.Esattamente come nell'italiano, to be (essere) può
essere sia verbo ordinario che ausiliare.
31
Come ausiliare è usato nella forma passiva e in quella progressiva.
Affermativa
Negativa
Interrogativa negativa
Affermativa Affermativa Negativa Negativa
estesa
contratta
estesa
contratta
I'm
I am not
I'm not
Interrogativa Interrogativa Interrogativa
negativa
negativa
estesa
contratta
Am I?
Am I not?
Aren't I?
Are you?
Are you not?
Aren't you?
Is he?
Is he not?
Isn't he?
Are we not?
Aren't we?
Are you?
Are you not?
Aren't you?
Are they?
Are they not?
Aren't they?
1a
Pers. I am
Sing.
2a
Pers. You are
You're
Sing.
You are You
not
aren't
3a
Pers. He is
He's
He is not He isn't
Sing.
1a
Pers. We are
We're
Plur.
2a
Pers. You are
You're
Plur.
3a
Pers. They are
Sing.
They're
We
not
are
We aren't Are we?
You are You
not
aren't
They are They
not
aren't
Le forme contratte, naturalmente, sono utilizzate solo nel linguaggio informale.La
forma interrogativa-negativa contratta di am I not? è proprio aren't I? anche se la cosa
può sembrare strana.Generalmente alle domande non si risponde solo con "si" o "no",
ma si ripete il pronome soggetto e il verbo della domanda. Nelle risposte negative,
invece, si può usare la forma contratta, anche nel linguaggio formale: Are you
optimistic? Yes, I am = Sei ottimista? Si. Is she French? No, she isn't = È francese?
No.
32
To be come verbo ordinario si usa in modo analogo all'italiano. A differenza
dell'italiano, invece si utilizza nei seguenti casi:
− per indicare uno stato fisico/emotivo personale. Es.: I'm cold = Ho freddo. She's
always in a hurry = Ha sempre fretta. I'm hungry = Ho fame. Sorry, I'm late
= Scusate il ritardo;
− per indicare l'età ed il peso. Es.: He's fifty = Ha cinquanta anni. I'm seventy
kilos = Peso settanta chili;
− per indicare il costo di un oggetto. Es.: How much is it? It's 30 Euros = Quanto
costa? Costa 30 Euro.
Il verbo ESSERE ci permette di dare o chiedere informazioni su chi siamo, cosa
facciamo, come stiamo, che qualità abbiamo, come siamo,… possiamo definire il tempo
atmosferico e cronologico:
− MY NAME IS … / I AM…
− I AM…YEARS OLD.
− I AM ITALIAN / I’M FROM GENOA.
− I’M A STUDENT / I’M A DOCTOR.
− I AM MARRIED / I’M SINGLE.
− IT’S TEN O’CLOCK / IT’S LATE
− I AM COLD / HOT / HUNGRY / RIGHT…
− IT’S SUNNY / WARM / HOT….
− I’M WELL / FINE / BAD.
− MY CAR IS GREY
− HOW MUCH IS IT?
− WHERE’S JIM?
− WHO’S THAT MAN?
− WHAT’S THE TIME?
− WHY ARE YOU ANGRY?
− HOW ARE YOU?
33
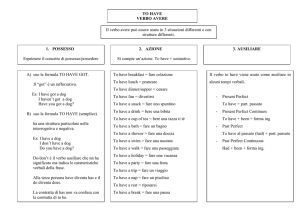
TO HAVE
Per il verbo AVERE non abbiamo riportato tutte le persone, ma solo la 2° (che sta per
tutte le altre) e la 3° singolare.
Forma affermativa: I/WE/YOU/THEY HAVE WE’VE*.
HE/SHE/IT HAS HE‘S*.
I HAVE A BROTHER
I’VE A BROTHER.
Forma interrogativa: inversione verbo + soggetto.
HAVE YOU….?
HAVE YOU A PEN?
Forma negativa: si aggiunge NOT
YOU HAVE NOT
HAVEN’T* ‘VE NOT*
HASN’T* ‘S NOT*
HE HASN’T ANY FRIENDS
Forma interronegativa: inversione verbo + soggetto + NOT
HAVE YOU NOT?
HAVEN’T YOU…?*
HASN’T HE…?*
HAVEN’T THEY A DOG?
*Forme contratte del verbo, più usate nella lingua parlata. La forma negativa permette
due tipi di contrazione: verbo o particella.
N.B. Queste forme negative, interrogative e interronegative di Have sono abbastanza
arretrate, oggigiorno si usano pochissimo, mentre gli inglesi e gli anglofoni
abitualmente usano l’ausiliare DO, come per tutti gli altri verbi regolari e irregolari, ad
eccezione dei verbi modali, come poi vedremo più avanti, nell’unità 24.
Il verbo HAVE può essere seguito da GOT che è un rafforzativo ed indica possesso.
Si usa solo al presente e non quando HAVE ha il significato di “fare”.
I’VE GOT A SISTER
È facoltativo ma molto usato.
34
Il verbo AVERE ci permette di dare o chiedere informazioni su ciò che abbiamo e
possediamo, su come siamo, su azioni che facciamo:
− I’VE GOT BLUE EYES.
− I’VE GOT TWO SISTERS.
− I’VE GOT A HEADACHE.
− I HAVE BREAKFAST.
− I HAVE A HOLIDAY / A PARTY / A SHOWER.
− I HAVEN’T A PEN.
− I HAVEN’T GOT A PEN.
− I DON’T HAVE A PEN.
− DO YOU HAVE A RUBBER?
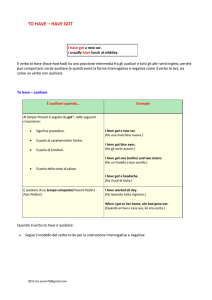
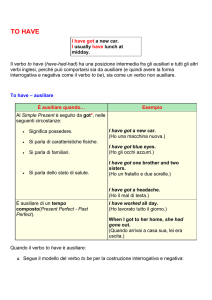
VERBO TO HAVE (GOT)
Il verbo avere in inglese si traduce con TO HAVE e quando è usato con il significato di
possedere può essere seguito dal rafforzativo GOT. Nelle forme interrogativa, negativa
e interronegativa del Simple Present GOT è sempre richiesto.
AFFERMATIVA NEGATIVA
INTERROGATIVA
Forma per I have (got)
I have not got
Have I got …?
esteso
You have (got)
You have not got
Have you got …?
He has (got)
He has not got
Has he got …?
She has (got)
She has not got
Has she got …?
It has (got)
It has not got
Has it got …?
We have (got)
We have not got
Have we got …?
You have (got)
You have not got
Have you got …?
They have (got)
They have not got Have they got …?
35
Forma
I’ve (got)
I haven’t got
contratta
You’ve (got)
You haven’t got
He’s (got)
He hasn’t got
She’s (got)
She hasn’t got
It’s (got)
It hasn’t got
We’ve (got)
We haven’t got
You’ve (got)
You haven’t got
They’ve (got)
They haven’t got
Attenzione: quando TO HAVE (GOT) è seguito dalla preposizione TO significa
DOVERE.
Forma AFFERMATIVA: Soggetto + TO HAVE (GOT) + complemento (Es: Mark has
(got) a car.)
Forma NEGATIVA: Soggetto + TO HAVE GOT + NOT + complemento (Es: Mark
hasn't got a car.)
Forma INTERROGATIVA: TO HAVE + soggetto + GOT + complemento (Es: Has
Mark got a car?)
Forma INTERRONEGATIVA: forma contratta di TO HAVE e NOT+ soggetto + GOT
+ complemento (Es: Hasn’t Mark got a car?).
36
Simple Present
Molte espressioni italiane in cui abbiamo AVERE si traducono in inglese con
BE.
Si riportano qui alcuni usi particolari di to be:
To be right
Aver ragione
To be sleepy
Aver sonno
To be wrong
Aver torto
To be cold
Aver freddo
To be hungry
Aver fame
To be ashamed Aver vergogna
To be thirsty
Aver sete
To be afraid
Aver paura
I'm afraid è molto utilizzato nel senso di temere per attenuare il senso negativo della
frase successiva.
Esempi:
− i'm afraid I'm hungry = A dire il vero ho fame .
− I'm afraid I can't help you = Temo di non poterti aiutare .
37
Test
1. Traduci in inglese le seguenti frasi.
a) Mi chiamo Giovanni, ho 30 anni e sono impiegato.
b) Gli studenti sono già a scuola. Hanno paura del compito in classe.
c) Hai sete? Sì, ma ho anche fame.
d) Ogni giorno faccio colazione alle 8.00.
e) Cara Maria, hai torto! Ho solo 20 anni ma sono intelligente.
f) Non ho una macchina. Ho soltanto una bicicletta.
g) Ho un terribile mal di testa!
h) Hai ragione. Fa molto caldo.
i) Paolo non è architetto. È un ingegnere.
j) Mi chiamo Tom e vengo da Milano. Sono un avvocato.
k) Abbiamo un cane nuovo e tre gatti.
l) Non avete fratelli o cugini?
m) Marian ha un terribile raffreddore e James ha mal di schiena.
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
38
2. Compila questa scheda personale e rileggi ad alta voce.
a) What’s your name?
……………………………………………………………..
b) How old are you?
……………………………………………………………..
c) Where are you from? ……………………………………………………………..
d) What do you do?
……………………………………………………………..
e) How are you?
……………………………………………………………..
f) What colour are your eyes? ……………………………………………………..
g) Are you married or single?
……………………………………………………..
h) Have you got a car? ……………………………………………………………..
i) Where are you now? ……………………………………………………………..
j) What time is it?
……………………………………………………………..
39