TO BE - SIMPLE PAST
A differenza di tutti gli altri verbi inglesi che, al Simple Past, utilizzano la stessa forma per tutte le
persone, il verbo to be ha due forme per il Simple Past: WAS e WERE.
Forma affermativa Forma negativa Forma interrogativa
I was
you were
he-she-it was
we were
you were
they were
I was not
you were not
he-she-it was not
we were not
you were not
they were not
was I ?
were you?
was he-she-it?
were we?
were you?
were they?
Nella forma negativa si utilizzano frequentemente le seguenti contrazioni:
WAS NOT WASN'T
WERE NOT WEREN'T
Nota
Si utilizzano le forme contratte nell'inglese parlato corrente e nell'inglese scritto informale.
SIMPLE PAST
Quando si usa
Il Simple Past è il tempo verbale inglese che esprime il concetto
generale di un’azione che si è svolta nel passato e non ha più nessun
rapporto con il presente.
Per poter mettere un verbo al Simple Past devono verificarsi
contemporaneamente tre condizioni.
1. L’azione deve essersi svolta nel passato ed essere
finita nel momento in cui si parla.
2. Il tempo in cui l’azione si è svolta deve essere espresso
nella frase o nel contesto.
Come si costruisce
Il Simple Past, nella forma affermativa, è un tempo semplice, che è dato
dalla seconda voce del paradigma ed è uguale per tutte le persone.
Infinito italiano Paradigma inglese
Lavorare
Andare
work - worked - worked
go - went - gone
Per i verbi regolari il Simple Past si ottiene aggiungendo -ED alla forma
base del verbo, tenendo presente quanto segue.
Regola Forma Base Simple Past
I verbi regolari
aggiungono ed alla
forma base
work (lavorare)
walk (camminare)
worked
walked
I verbi che terminano
per -eaggiungono solo
lad
smile (sorridere) smiled
I verbi che terminano cry (piangere) cried
per -ypreceduta da
consonante, cambiano
la y in i e
aggiungono ed.
I verbi che terminano
per una sola
consonante preceduta
da una vocale
accentata
raddoppiano la
consonante finale.
admit (ammettere)
stop (fermarsi)
admitted
stopped
I verbi che terminano
per -lpreceduta da una
sola vocale
raddoppiano sempre
la l.
travel (viaggiare) travelled
Per i verbi irregolari il paradigma è dato dal dizionario, e bisogna
impararlo a memoria (vedi paradigma dei verbi irregolari).
Esempio:
Infinito italiano Paradigma inglese
essere be - was - been
andare go - went - gone
correre run - ran - run
avere have - had - had
Essendo un tempo semplice, il Simple Past dei verbi non-ausiliari ha
bisogno dell’aiuto di un ausiliare per fare le forme interrogative e
negative. Si usa l’ausiliare DID, in presenza del quale il verbo dalla
frase resta invariato nella sua forma base.
Forma Costruzione Esempio
Forma
affermativa
SOGGETTO + 2° VOCE
DEL PARADIGMA
I worked
you worked
he / she / it worked
we worked
you worked
they worked
Forma
interrogativa
DID + SOGGETTO +
FORMA BASE
Did you work last
night?
(Hai lavorato ieri
sera?)
Forma negativa SOGG. + DID + NOT +
FORMA BASE
DID NOT>>>DIDN’T
I didn’t work last
night
(Non ho lavorato ieri
sera)
Nota:
Ieri mattina Yesterday morning
Ieri pomeriggio Yesterday afternoon
Ieri sera Yesterday evening
Ieri notte / sera tardi Last night
Le espressioni di tempo che collocano l’azione in un momento
definito del passato possono essere di diverso tipo.
Posso esprimere il tempo
mediante
Esempio
Avverbi di tempo. Yesterday (ieri)
Complementi di tempo Last week (la settimana scorsa)
During my summer holidays
(durante le mie vacanze estive)
Three days ago (tre giorni fa)
Proposizioni temporali When I was a child (quando ero
bambino)
When I was three years old
(quando avevo tre anni)
Un evento storico During World War II
(durante la seconda guerra
mondiale)
Nota
Si usa il Simple Past anche in assenza di espressione di tempo passato,
nei seguenti casi:
Circostanza Esempio
Nelle domande al passato
con WHEN, perché si
presuppone nella risposta
la collocazione dell’azione
in un momento preciso del
passato.
Quando hai visto quel film?
When did you see that movie?
Nelle proposizioni
temporali introdotte da
WHEN
Quando lo conobbi…..
When I first met him …..
Quando si parla di una
persona che non vive più.
Shakespeare scrisse molte opere
teatrali.
Shakespeare wrote many plays.
Write the complete paradigm of the following regular and irregular verbs
1) meet
♥ to meet - met - met
2) love
♥ to love - loved - loved
3) spring
♥ to spring - sprang - sprung
4) tell
♥ to tell - told - told
5) wake up
♥ to wake up - woke up - woken up
6) study
♥ to study - studied - studied
7) play
♥ to play - played - played
8) wear
♥ to wear - wore - worn
9) to win
♥ to win - won - won
10) set
♥ to set - set – set
USED + INFINITO
Quando, in un contesto di Simple Past (azione passata - tempo espresso e finito), si
parla
di un’azione che si svolgeva abitualmente nel passato, in luogo del Simple Past si può
utilizzare la formula:
SOGGETTO + USED + INFINITO
Esempio:
L’anno scorso mi alzavo alle sette del mattino.
Il contesto è di Simple Past (l’anno scorso), ed il verbo esprime un’abitudine nel
passato.
Last year I used to get up at seven o’clock in the morning.
Nel tradurre dall’inglese "used" non viene solitamente tradotto, il verbo della frase
viene in
genere espresso in Italiano all’imperfetto (mi alzavo). Può anche essere utilizzata
l’espressione "essere solito":
L’anno scorso ero solito alzarmi alle sette.
Fill in the gaps in the following sentences with USED TO
1) I (live) in a small town. Now I live in Paris.
I USED TO live in a small town. Now I live in Paris.
2) She (+not smoke) before she met Dan.
She DIDN'T USE TO smoke before she met Dan.
3) Mary-Ann (work) for a big company in 1998.
Mary-Ann USED TO work for a big company in 1998.
4) I (get up) early in the morning.
I USED TO to get up early in the morning.
5) She (+not eat) to eat very much. Now she eats normally.
She DIDN'T USE TO eat very much. Now she eats normally.
6) I (think) he wasn’t nice. Now I’ve changed my mind.
I USED to think he wasn’t nice. Now I’ve changed my mind.
7) He (work) in a cinema before he went to University.
He USED to work in a cinema before he went to University.
8) They (sell) a lot of computers. Now business is bad.
9) I (eat) fish when I was young. Now I hate it.
I USED to eat fish when I was young. Now I hate it.
10) I (smoke) a lot. Now I can’t bear the smell of a cigarette.USED to
smoke a lot. Now I can’t bear the smell of a cigarette.
cin
I was watching TV last night, when
the telephone rang
Quando si usa
Il Past Continuous è il tempo verbale che si utilizza per esprimere un'azione che era in corso di
svolgimento in un momento definito del passato.
Esempio:
At 11.30 last night I was watching a film on TV.
Ieri sera alle 11.30 stavo guardando un film alla televisione.
(Avevo iniziato a guardare il film prima di quel momento ed ho continuato a guardarlo dopo. L'azione
non si è
esaurita nel momento di cui parlo - le 11.30 di sera - ma era in corso di svolgimento.)
This time yesterday I was flying to London. (To fly = volare, andare in aereo)
Ieri a quest'ora stavo andando in aereo a Londra.
(Il viaggio era iniziato prima di quest'ora, ed è proseguito dopo.)
Frequentemente il Past Continuous è associato al Simple Past quando si descrive un'azione che si è
prolungata per un certo periodo di tempo nel passato e che è stata interrotta da un'azione breve.
L'azione
lunga è espressa al Past Continuous,
quella breve che la interrompe al Simple Past.
Esempio:
I was watching TV last night, when the telephone rang.
Guardavo la televisione ieri sera, quando è squillato il telefono.
Sto parlando di un evento collocato nel passato: last night.
I was watching TV: azione prolungata nel tempo, espressa al Past Continuous.
The telephone rang: azione breve (il telefono è squillato) che la interrompe, espressa al Simple Past.
I saw her in the library yesterday, she was reading a book.
L'ho vista ieri in biblioteca, stava leggendo un libro.
L'azione è collocata nel passato: yesterday.
She was reading a book: azione che si è prolungata per un certo tempo, espressa al Past Continuous.
I saw her: azione breve al Simple Past.
Nota
Naturalmente non si può usare il Past Continuous con i verbi che
non vengono utilizzati nei tempi progressivi (vedi: uso della -ing form >>>tempi progressivi).
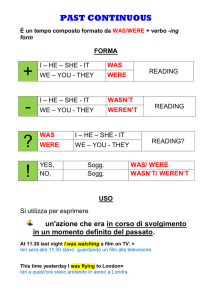
Come si costruisce
Il Past Continuous è un tempo composto che utilizza l'ausiliare to be al Simple Past ed il verbo nella ing
PAST CONTINUOUS
form (vedi: uso della -ing form >>>tempi progressivi).
Forma Costruzione Esempio
Forma
affermativa
SOGGETTO +
WAS/WERE +
-ING FORM
To read (leggere)
I was reading
you were reading
he/she/it was reading
etc…
Forma negativa SOGG. + WAS/WERE +
NOT + -ING FORM
WAS NOT >>> WASN'T
WERE NOT
>>>WEREN'T
I was not reading
you were not reading
he/she/it was not
reading
etc…
Forma
interrogativa
WAS/WERE + SOGG. +
-ING FORM
Were you reading…?
Was he reading…?
etc…
1. Rewrite the following sentences using the PAST CONTINUOUS
1) Are you eating in the dining-room?
WERE you eating in the dining-room?
2) Isn’t your husband working?
WASN'T your husband working?
3) Are you having breakfast?
WERE you having breakfast?
4) We aren’t listening to music. We WEREN'T listening to
music.
5) Barbara’s watching television.
Barbara WAS watching television.
6) They’re studying hard.
They WERE studying hard.
7) I’m going to school.
I WAS going to school.
8) Is she driving her new car?
WAS she driving her new car?
9) Isn’t Joe reading that book?
WASN'T Joe reading that book?
10) Susan’s washing her bike.
Susan WAS washing her bike.
2. Fill in the gaps with the Past Continuous or the Simple Past form
1) I (walk) into the house when I (hear) a noise.
was walking into the house when I heard a noise.
2) When she (come) home, my father had already gone out.
When she came home, my father had already gone out.
3) He (become) a doctor in 1986.
He became a doctor in 1986.
4) When the telephone (ring) I (be) in the bathroom.
When the telephone rang, I was in the bathroom.
5) Beth (eat) when I (arrive).
Beth was eating when I arrived.
6) When Agatha arrived, we (do) the gardening.
When Agatha arrived, we were doing the gardening.
7) Last month I (read) an English book. Now (read) a Spanish
one. Last month I read an English book. Now I am reading a Spanish one.
8) We (not go) out because it (rain).
We didn’t go out because it was raining.
9) She (not say) anything when Peter (announce) his marriage.
She didn’t say anything when Peter announced his marriage.
10) I (drink) something at the pub when I suddenly (realise) I had
lost my keys.
I was drinking something at the pub when I suddenly realised I had lost my
3. Fill in the gaps with the Past Continuous form of the verb using WAIT - COOK - SLEEP -
DRIVE - LISTEN - PLAY - HAVE - TEXT - WORK - TALK
1) Eve interrupted us while we .
Eve interrupted us while we WERE TALKING.
2) Matt (+not) to the radio when Mum arrived.
Matt WASN’T LISTENING to the radio when Mum arrived.
3) (you) lunch with Tom when it began to rain?
WERE YOU HAVING lunch with Tom when it began to rain?
4) I without my seat belt on, so I got fined.
I WAS DRIVING without my seat belt on, so I got fined.
5) It began to snow just as I tennis with Jim.
It began to snow just as I WAS PLAYING tennis with Jim.
6) When the boss came into her office she John. When the boss came
into her office she WAS TEXTING John.
7) I the chicken when the bell rang.
I WAS COOKING the chicken when the bell rang.
8) (+not, you) in a factory when you met her?
WEREN’T YOU WORKING in a factory when you met her?
9) I for the bus when Susan came along.
I WAS WAITING for the bus when Susan came along.
10) When Terry came home the baby .
When Terry came home the baby WAS SLEE
IL COMPARATIVO DEGLI AGGETTIVI
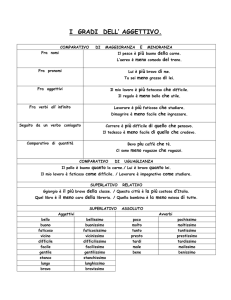
Comparativo di maggioranza
Come si forma
Per formare il comparativo di maggioranza degli aggettivi si applica il seguente schema.
Come si forma Esempio
Aggettivi monosillabici:
aggettivo –er.
Casi particolari:
- Gli aggettivi che terminano per –eaggiungono solo
la –r.
- Gli aggettivi che terminano per una consonante
preceduta da vocale raddoppiano la consonante e
aggiungono la -er.
- Gli aggettivi monosillabici o bisillabici che
terminano per –y cambiano la y in i e aggiungono –
er.
tall >>>taller
(alto, più alto)
nice >>> nicer
(carino/simpatico, più carino/più simpatico)
hot >>>hotter
(caldo, più caldo)
happy >>> happier
(felice, più felice)
Aggettivi con più di due sillabe*:
more + aggettivo
interesting >>> more interesting
(interessante, più interessante)
Aggettivi irregolari good (buono) >>> better
bad (cattivo) >>> worse
far (lontano) >>> farther (più lontano) -
further (ulteriore)
Il secondo termine di paragone è sempre preceduto da than.
Mark è più alto di John.
Mark is taller than John.
Questo libro è più costoso di quello.
This book is more expensive than that one.
Quando il secondo termine di paragone è un pronome personale, si utilizza il pronome
personale complemento
(non il pronome soggetto).
He is taller than me / you / him / her / us / them.
Egli è più alto di me / te etc…
Usi particolari del comparativo di maggioranza
Molto / poco più…
Il comparativo di maggioranza può essere preceduto da uno dei seguenti avverbi allo scopo di
modularne
l’intensità.
much / a lot / far + comparativo = molto più…
We’re going to Paris by car. It’s much cheaper.
Andremo a Parigi in auto. È molto più economico.
Travelling by plane is far more expensive.
Viaggiare in aereo è molto più costoso.
a little / a bit / slightly + comparativo = poco più…
My suitcase is slightly heavier than yours.
La mia valigia è leggermente più pesante della tua.
Mark is a little taller than John.
Mark è poco più alto di John.
Sempre più…
comparativo + and + comparativo = sempre più…
It’s getting colder and colder.
Si sta facendo sempre più freddo.
Its becoming more and more difficult to find a permanent job.
Trovare un lavoro stabile sta diventando sempre più difficile.
Quanto più…tanto più…
the + comparativo + the + comparativo
The sooner you leave, the sooner you will arrive.
Quanto prima parti, tanto prima arriverai.
In queste espressioni il verbo to be viene frequentemente sottinteso.
The sooner, the better.
Quanto prima sarà, tanto meglio sarà.
Old >>> older / elder
L’aggettivo old (vecchio) ha due forme comparive:
a) Older si può usare sempre.
My house is older than yours.
La mia casa è più vecchia della tua.
He is older than me.
È più vecchio di me.
I have an older brother.
Ho un fratello più vecchio.
b) Elder, utilizzato per paragonare l’età di membri di una stessa famiglia. Può essere usato
solo se seguito
direttamente da un sostantivo.
My elder brother is a teacher.
Il mio fratello maggiore è un insegnante.
Comparativo di minoranza
Come si forma
Come si forma Esempio
Less + aggettivo tall >>> less tall
alto, meno alto
expensive >>> less expensive
costoso, meno costoso
Il secondo termine di paragone è sempre preceduto da than.
John is less tall than Mark.
John è meno alto di Mark.
Come il comparativo di maggioranza, anche il comparativo di minoranza può essere
preceduto da un avverbio
che ne modula l’intensità.
John is slightly less tall than Mark.
John è leggermente meno alto di Mark.
Travelling by train is far less expensive than travelling by plane.
Viaggiare in treno è molto meno caro che viaggiare in aereo.
Comparativo di uguaglianza
Come si forma
Come si forma Esempio
as + aggettivo + as + secondo termine di paragone Mary is as tall as Susan.
Mary è alta quanto Susan.
In frasi negative l’aggettivo può essere preceduto da as oppure da so.
This cake is not as / so good as the cake my grandmother makes.
Questa torta non è buona quanto la torta che fa mia nonna.
Quando il secondo termine di paragone è un pronome personale, si utilizza il pronome
personale complemento
(non il pronome soggetto).
He is as tall as me / you / him / her / us / them.
Egli è alto quanto me / te etc…
Si usa frequentemente il comparativo di uguaglianza in frasi negative, in luogo del
comparativo di minoranza.
John is less tall than Mark. = John isn’t as tall as Mark.
John è meno alto di Mark. = John non è alto quanto Mark.
1. Write the 3 forms of the comparative for each of the adjectives provided.
Example: taller than / as tall as / less tall then
1) Serious ore Happier than/as happy as/less
happy than
2) Interesting ore interesting than/as interesting
as/less interesting than
3) Far
Farther-further than/as far as/less far than
4) Good
Better than/as good as/less good than
5) Patient More patient than/as patient as/less
patient than
6) Famous
More famous than/as famous as/less famous than
7) Small
Smaller than/as small as/less small than
8) Old
Older than/as old as/less old than
9) Dark
Darker than/as dark as/less dark than
10) Easy
Easier than/as easy as/less easy than
2. Fill in the gaps with the appropriate comparative form
1) I wasn’t well yesterday, but I feel (good) today.
I wasn’t well yesterday, but I feel better today.
2) An elephant is (big) than a dog.
An elephant is bigger than a dog.
3) My parents’ house is (old) than mine.
My parents’ house is older than mine.
4) This book is (interesting) than that one.
This book is more interesting than that one.
5) We are (tall) than our friends.
We are taller than our friends.
6) This red wine is terrible but the white wine is even (bad).
This red wine is terrible but the white wine is even worse.
7) That coat is (expensive) than yours.
That coat is more expensive than yours.
8) My coffee is (hot) than yours.
My coffee is hotter than yours.
9) This exercise is (difficult) than the previous one.
This exercise is more difficult than the previous one.
10) Mary is (happy) than her sister.
Mary is happier than her sister.
IL SUPERLATIVO DEGLI AGGETTIVI
Mark is very tall.
Mark is the tallest boy in the classroom.
Esistono due forme di superlativo:
a. superlativo assoluto: Mark è altissimo.
b. superlativo relativo: Mark è il ragazzo più alto della classe.
C’è un termine di riferimento (la classe).
Il superlativo assoluto
In inglese il superlativo assoluto di un aggettivo si esprime mediante gli avverbi:
very / really / extremely + aggettivo
This book is very interesting.
Quel libro è interessantissimo / molto interessante.
Mark is really tall.
Mark è altissimo / veramente alto.
Alcuni aggettivi hanno un significato di per sé superlativo:
freezing (freddissimo)
wonderful (meraviglioso)
fantastic (fantastico)
marvelous (meraviglioso)
perfect (perfetto)
essential (essenziale)
enormous (enorme)
delicious (delizioso)
awful (orribile)
etc…
Con questi aggettivi non si usano gli avverbi very ed extremely. Si può invece utilizzare
absolutely o
really (meno formale):
This cake is absolutely delicious!
Questa torta è assolutamente deliziosa!
It’s really freezing today.
Fa veramente freddissimo oggi.
Il superlativo relativo
Come si forma
Per formare il superlativo relativo degli aggettivi si applica il seguente schema.
Come si forma Esempio
Aggettivi monosillabici:
the + aggettivo + –est.
Casi particolari:
- Gli aggettivi che terminano per –eaggiungono
solo –st.
- Gli aggettivi che terminano per una consonante
preceduta da vocale raddoppiano la consonante e
aggiungono -est .
- Gli aggettivi mono o bisillabici che terminano per
–y cambiano la y in i e aggiungono –est.
tall >>>the tallest
(alto, il più alto)
nice >>> the nicest
(carino/simpatico, il più carino / simpatico)
hot >>> the hottest
(caldo, il più caldo)
happy >>> the happiest
(felice, il più felice)
Aggettivi con più di due sillabe*:
the + most + aggettivo
interesting >>> the most interesting
(interessante, il più interessante)
Aggettivi irregolari good (buono) >>> the best
bad (cattivo) >>> the worst
far (lontano) >>> the farthest / furthest (il più
lontano)
* Usi particolari dei superlativi
old >>> oldest / eldest
L’aggettivo old (vecchio) ha due forme superlative:
a) the oldest che si può usare sempre
That is the oldest building in the town.
Quello è l’edificio più vecchio della città.
b) eldest che si può utilizzare al posto di oldest quando si parla dell’età delle persone di una
famiglia.
She is my eldest daughter.
È la mia figlia maggiore.
1. Correct the wrong superlative
1) The most beautiful/the most easy/the most expensive
The easiest
2) The fastest/the oldest/the most far
The furthest/the farthest
3) The baddest/the most popular/the prettiest
The worst
4) The most horrible/the saddest/the interestingest
The most interesting
5) The shortest/the most romantic/the most high
The highest
6) The best/the most boring/the convenientest
The most convenient
7) The most comfortable/the longest/the most cheap
The cheapest
8) The most efficient/the most big/the most famous
The biggest
9) The most long/the most exciting/the most elegant.
The longest
10) The happiest/the tallest/the most early The earliest
2. Make correct sentences replacing the words in brackets with the superlative form
1) Helen is (clever girl) in her class.
Helen is the cleverest girl in her class.
2) This is (good game) of the year.
This is the best game of the year.
3) This is (big animal) I've ever seen.
This is the biggest animal I’ve ever seen.
4) That is (expensive bag) in the shop.
That is the most expensive bag in the shop.
5) This is (old church) in town.
This is the oldest church in town.
6) King’s Road is (dangerous street) in the whole country.
ing’s Road is the most dangerous street in the whole country.
7) That was (bad meal) I’ve ever had in a restaurant.
That was the worst meal I’ve ever had in a restaurant.
8) Who is (intelligent student) in your class?
Who is the most intelligent student in your class?
9) Who is (popular actor) in the world?
Who is the most popular actor in the world?
10) What’s the name of (high mountain) in your country?
What’s the name of the highest mountain in your country
Would like
Il condizionale di like è utilizzato nel significato di vorrei ed è sempre seguito
dall’infinito
con to. È seguito dall’infinito passato quando si vuole esprimere rimpianto.
Vorrei aiutarlo.
I would like to help him.
Vorrei averlo aiutato (ma non l’ho fatto).
I would like to have helped him.
Quanto ti piace?
Per esprimere quanto ci piace fare qualcosa, si possono utilizzare i seguenti verbi,
elencati in ordine di intensità, dal più negativo al più positivo.
In inglese In italiano
To hate Odiare
Il verbo to hate è usato più
frequentemente di quanto non venga
utilizzato l’italiano odiare.
I hate pizza.
Non mi piace affatto la pizza.
Can’t bear / can’t stand Non sopportare
To dislike Non piacere
To mind Importare
Utilizzato in forma negativa, I don’t
mind,significa non mi dispiace.
I don’t mind working at night.
Non mi dispiace lavorare di notte.
To quite like
To like
To really like
Piacere abbastanza
Piacere
Piacere molto
To enjoy Piacere, riferito ad una situazione in cui si
sta bene.
I really enjoyed the party.
Mi è veramente piaciuta la festa.
To love Amare
Il verbo to love è usato più
frequentemente di quanto non venga
usato amare in italiano.
I love chocolate!
Mi piace moltissimo il cioccolato!
Nota
I verbi To love, to hate, can’t bear possono essere seguiti sia dalla –ing form che
dall’infinito.
I verbi to enjoy, to dislike, to mind e can’t stand sono sempre seguiti dalla –ing
form.