Conoscenza della Lingua
Inglese (1 CFU)
Prof.ssa Silvia Cavalieri
([email protected])
Programma d'Esame
GRAMMAR
Present Simple
Present Continuous
Past Simple
Present Perfect
Future (will, to be
going to, present
continuous)
VOCABULARY
Family and Friends
Education
Free Time
Food and Drinks
Holidays
Weather
Testi di Riferimento
Dispensa con estratti presi da:
Coe N., Harrison M. & Paterson k.
(2006). Oxford Practice Grammar –
Basic. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Twain M., (2007), The Prince and the
Pauper, Black Cat Publising - Cideb
Editrice, Step 1.
Modalità d'Esame
Test scritto con esercizi di grammatica e/o
lessico (completamento, costruzione frasi
ecc.)
Passaggio preso dal testo di lettura con
domande di comprensione
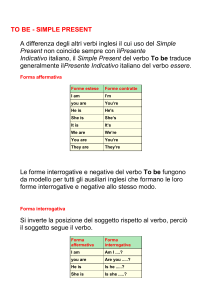
Present Simple: TO BE
FORMA AFFERMATIVA
I am (I'm)
IO SONO
You are (you're)
TU SEI
He is (he's)
LUI E'
She is (she's)
LEI E'
It is
ESSO E'
(it's)
We are (we're)
NOI SIAMO
You are (you're)
VOI SIETE
They are (they're)
ESSI SONO
IT= NEUTRO
1. Oggetto
2. Animale non domestico
3. Luogo
4. Organizzazione
5. Qualcosa di astratto
E.G.
1) I’ve seen Toy Story before. It’s a good film for kids.
2) ‘Have you been to London?’ Yes, it was very crowded.’
3) How much would the company be worth if it were sold?’
4) It is an idea that has much public support.
5) If the shark is still around it will not escape.
6) How Winifred loved the baby! And how Stephanie hated it!
Present Simple: to BE
FORMA NEGATIVA
I am not (I'm not)
You are not (you aren't)
He is not (he isn't)
She is not (she isn't)
It is not (it isn't)
We are not (we aren't)
You are not (you aren't)
They are not (they aren't)
IO NON SONO
TU NON SEI
LUI NON E'
LEI NON E'
ESSO NON E'
NOI NON SIAMO
VOI NON SIETE
ESSI NON SONO
Present Simple: TO BE
FORMA INTERROGATIVA
Verbo + Soggetto
Am I?
Are you?
Is he/she/is?
Are we?
Are you?
Are they?
La forma interrogativa non si contrae mai!
USO DEL VERBO TO BE
Il verbo TO BE si usa per:
Parlare di noi stessi (caratteristiche
fisiche, nazionalità, professione, ecc.)
I'm Steve, this is my friend Bill. We're
from Scotland
I'm Sandra, I'm thin and I'm from Italy. I'm
Italian
Parlare del tempo meteorologico
It's cold but it's sunny
Dare indicazioni temporali (ora,
ecc)
Parlare di luoghi
It's quarter past ten
You're late!
Milan is in the north of Italy
Dire l'età delle persone
My sister is 7 years old (MA IN ITA: mia sorella
ha 7 anni!)
Parlare di come ci si sente
I'm happy
They are bored
We're hungry (MA IN ITA: Abbiamo fame!)
He's thirsty (MA IN ITA: Lui ha sete!)
Chiedere come sta chi incontro
A: How are you?
B: I'm fine thanks. How are you?
Chiedere scusa
I'm sorry, I didn't mean to hurt you
Descrivere le cose
It isn't expensive. It's cheap.
It's an old film, but it's good.
THERE + BE
Si usa per indicare la presenza/posizione
delle cose nello spazio
There's a supermarket in the street
There is a telephone over the shelf
There are some good restaurants in the
down-town
Le domande si fanno con l'inversione del soggetto (THERE) e del verbo essere
Is there a cafeteria near here?
Present Simple: TO HAVE
FORMA AFFERMATIVA
FORMA NEGATIVA
I/we/you/they have
('ve)
I/we/you/they have
not (haven't)
He/she/it
He/she/it has not
(hasn't)
has ('s)
TO HAVE
Al Simple Present è seguito da got*, nelle seguenti circostanze:
1)Significa possedere.
I have got a new car. (Ho una macchina nuova.)
2)Si parla di caratteristiche fisiche.
I have got blue eyes. (Ho gli occhi azzurri.)
3)Si parla di familiari.
I have got one brother and two sisters.(Ho un fratello e due
sorelle.)
4. Si parla dello stato di salute.
I have got a headache.
(Ho il mal di testa.)
Forma Negativa
I have not got a new car.
(Non ho una macchina nuova.)
Forma Interrogativa
Have you got a new car?
(Hai una macchine nuova?)
Yes, I have/No, I haven't
• Il verbo to have sostituisce frequentemente i verbi to eat e to
drink (in italiano corrisponde ai verbi mangiare, bere e
prendere riferito al cibo).
I usually have tea at five o'clock.
(Di solito prendo il tè alle cinque.)
Let’s have pizza tonight!
(Mangiamo pizza questa sera!)
• Si usa il verbo to have nelle seguenti espressioni riferite ai
pasti:
To have breakfast: fare colazione
To have lunch: pranzare
To have dinner / supper: cenare
To have a snack: fare uno spuntino
To have a holiday: fare una vacanza
To have a party: dare una festa
To have a rest: fare un riposino
To have a nap: fare un pisolino
To have a chat: fare una chiacchierata
To have a look: dare un'occhiata
To have a bath/shower: fare il bagno/doccia
To have a swim: fare una nuotata
To have a good time / To have fun: divertirsi
ATTENZIONE:
I have a shower every day.
(Faccio la doccia ogni giorno.)
I don’t have a shower every day.
(Non faccio la doccia ogni giorno.)
Does Mark have a shower every day?
(Mark si fa la doccia ogni giorno?)
QUANDO HAVE NON INDICA POSSESSO PER LE
NEGATIVE/DOMANDE SI USA AUSILIARE
DO/DOES (vedi espressioni precedenti)
The present tense
PRESENT SIMPLE
IL PRESENTE INDICATIVO è ALL’INFINITO
SENZA IL TO (es. to sing = sing)
TRANNE TERZA PERSONA SINGOLARE
(he/she/it) CHE AGGIUNGE -S
Forma affermativa
I
YOU (tu, voi)
WE
WORK
THEY
to work =lavorare
HE/SHE/IT
WORKS
NOTA: se il verbo da concordare
con he, she, it termina con ss, sh,
ch, x, o si aggiunge – es:
e.g He catches
She passes
It goes
To catch = lui prende
To pass = lei passa
To
go = esso va
Se un verbo termina con una consonante (b,
e, d etc.) + y (e.g. study), si cambia -y in ies per le forme di he/she/it:
I study > he studies
I fly > it flies
Forma Interrogativa
DO
I
YOU
WE
THEY
DOES
WORK ?
HE/SHE/IT
YES, I DO / NO I DON’T
YES, HE DOES/ NO, HE DOESN’T
Forma Negativa
I
YOU (tu, voi)
DO NOT
WE
(DON’T)
THEY
HE/SHE/IT
DOES NOT
(DOESN’T)
Uso del Present Simple
FATTI CHE SI MANTENGONO
INALTERATI
e.g I come from Italy (Vengo dall'Italia)
He doesn’t speak German
We live in Dublin
PER AZIONI RIPETUTE O ABITUDINARIE
(spesso con avverbi di frequenza indefiniti)
e.g I get up at six o’clock everyday
(mi sveglio alle sei tutte le mattine)
I don’t see them very often
(non li vedo molto spesso)
What time do you leave work?
(a che ora parti dal lavoro?)
ALWAYS = sempre
USUALLY = di solito
OFTEN = spesso
SOMETIMES = qualche volta
RARELY = raramente
NEVER = mai
STATI D’ANIMO
e.g
Do you feel nervous before an exam?
(ti senti nervoso?)
I hate moments like that
(odio momenti come quello)
VERITA' ASSOLUTE
e.g
The sun rises in the east
(il sole si alza a ovest)
Water boils et 100 C°
(L'acqua bolle a 100 C°)
• OPINIONI
E.G
I think you’re nice
(penso che tu sia simpatica)
I don’t share her ideas
(non condivido le sue idee)
ALTRI USI
• IL PRESENTE INDICATIVO HA SIGNIFICATO DI
FUTURO:
QUANDO SI RIFERISC A COSE GIA'
PROGRAMMATE, PRESTABILITE E DI SOLITO
LEGATE A UNA TIMETABLE (treni, bus, aerei,
ecc.) O CALENDARIO
e.g
School starts on September 20 th
Our plane leaves Heathrow airport at
8.30
Presente Progressivo
SI FORMA CON IL PRESENTE DEL VERBO
TO BE + IL GERUNDIO DEL VERBO
PRINCIPALE.
IL GERUNDIO SI FORMA AGGIUNGENDO ALLA
FORMA BASE DEL VERBO IL SUFFISSO -ING
TO PLAY
PLAYING
I’M STUDYING HARD
(sto studiando molto)
SHE’S NOT FOLLOWING THE COURSE
(non sta seguendo il corso)
ARE THEY STILL WORKING HERE?
(lavorano ancora qui?)
Uso del Present Continuous
per esprimere un'azione nel suo svolgimento:
e.g
e.g
What's the man in this photograph
doing?
He 's sitting on a park bench reading.
per indicare un'azione che dura per un
periodo di tempo limitato:
e.g
We're doing an English course for
one month.
per parlare di qualcosa che sta cambiando o
progredendo:
e.g
John 's growing very fast.
Il presente progressivo si trova anche con un
avverbio di frequenza:
e.g
per disapprovare un'azione che si ripete troppo spesso
You're always quarrelling with her.
Forma Interrogativa del
Present Continuous
SINGOLARE
PLURALE
AM
I
ARE
YOU
IS
HE/SHE/IT
ARE
WE
ARE
YOU
ARE
THEY
WINNING?
Short Answers
NO,
YES,
I
YOU (tu, voi)
ARE
I
YOU (tu, voi)
WE
AREN'T
WE
THEY
THEY
HE/SHE/IT
IS
HE/SHE/IT
ISN'T
'How are you?' (= Come stai?) = How's it going? How
are you getting on? How are you doing?
FORME INFORMALI
Forma Negativa del Present
Continuous
SINGOLARE
I
AM NOT
YOU
ARE NOT
HE/SHE/IT IS NOT
PLURALE
WE
ARE NOT
YOU
ARE NOT
THEY
ARE NOT
WINNING
Present Simple vs. Present
Continuous
Si usa il Present Simple per parlare di fatti (cose che sono Si usa il Present Continuous per parlare di azioni che
vere in qualsiasi momento):
stanno avvenendo nel momento stesso in cui si parla:
I come from Italy.
Avverbi di frequenza come usually, often, every
vengono usate con il Present Simple:
We usually go to the disco at weekends.
Si usa il Present Simple per parlare di situazioni che
esistono da tanto tempo e per azioni che si ripetono (es.
abitudini, o eventi programmati ad orario):
Joe works for Aston University.
She can't come. She's speaking on the phone at the moment
Ma si può usare il Present Continuous con always per
dire che qualcosa succede troppo spesso:
Sheila is always speaking too loudly..
Si usa il Present Continuous per parlare di azioni o
situazioni che durano per un periodo limitato di tempo
riferito più o meno al momento in cui si parla (es.
vacanze, visite, lavori temporanei, corsi, ecc.)
John is working in England for 3 weeks.
Si usa il Present Simple con i verbi che
esprimono attività della mente e sentimenti
e i verbi di possesso (es. know, like, want,
love, hate, remember, understand,
have):
I remember this film, it was really interesting..
Di solito non si usa il Present Continuous con i verbi
che esprimono attività della mente e sentimenti e i
verbi di possesso:
non I'm remembering the film....
non I'm having two brothers.
PLURALE DEI NOMI
SI AGGIUNGE “S” - One cat> two cats
“ES” = sostantivi terminano con sh, ss, x o
s–
Bush- bushes
Glass- glasses
Box – boxes
Bus – buses
“ES” = parole che terminano con ch,
Church-churches
Match- matches
Speech-speeches
- parole che terminano con una consonante seguita da
y= “IES”
country – countries
lady – ladies
- parole che terminano con una vocale seguita da y=
“S”
Boy-boys
Day-days
- sostantivi che terminano con le lettere f o fe=“VES”
half halves
knife knives
leaf leaves
life lives
scarf scarves
shelf shelves
thief thieves
wife wives
- Per molte parole che finiscono per o= “S”
photo-photos
radio-radios
- PERÓ = “OES”
domino,tomato, hero, potato
PLURALI IRREGOLARI:
man men
woman women
tooth teeth
mouse mice
foot feet
child children
l
- L'irregolarità
dei pronomi rimane anche nei nomi composti
policeman policemen
postman postmen
policewoman policewomen
grandchild grandchildren
- Nomi tecnici o scientifici di origine Latina o greca
thesis theses
crisis crises
basis bases
datum data
Nomi Collettivi Singolari
•
information (informazione/informazioni)
•
knowledge (conoscenza/conoscenze)
•
news (notizia/notizie)
•
forniture (mobilio/mobilia/mobili)
•
advice (consiglio/consigli)
ATTENZIONE! questi nomi vogliono sempre il
verbo al singolare – this information is really
good (queste informazioni sono davvero
buone.)
Nomi Sempre Plurali
•
people (persone/gente)
•
police (polizia)
•
trousers (pantaloni/calzoni)
•
spectacles (occhiali)
•
pyjamas (pigiama)
•
scissors (forbici)
•
E.G People are happy here (la gente è felice qui)
Plurale = Singolare
•
series (serie)
•
species (specie)
•
sheep (pecora)
•
deer (cervo)
•
News (notizia)