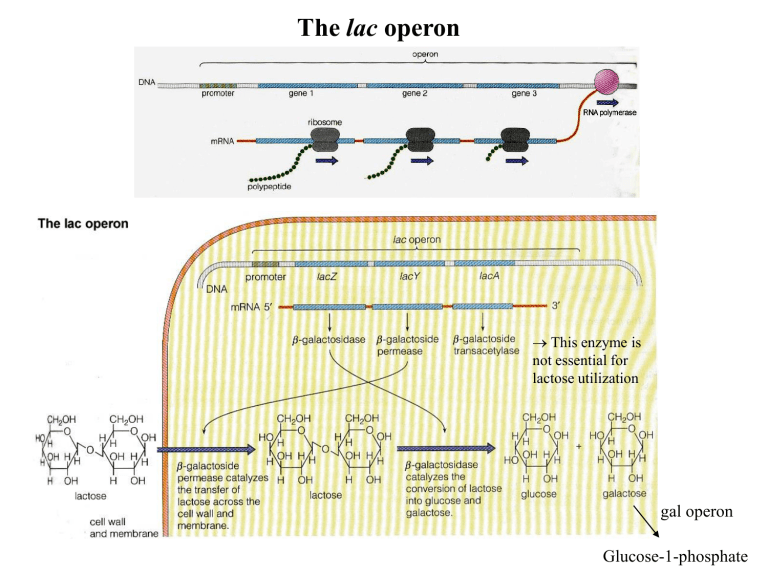
The lac operon
This enzyme is
not essential for
lactose utilization
gal operon
Glucose-1-phosphate
La presenza di lattosio e/o glucosio
controlla l’espressione dei geni lac
lac operon is induced only when lactose is present
- lacI gene is located outside the operon
- It is constitutively expressed (10 molecules per cell)
- LacI repressor is a tetrameric protein
-The repressor protein has the greatest affinity for
binding to O1 and lesser affinity to O2 and O3
- The lac operon is occasionally transcribed also in the
presence of LacI repressor
The mRNA
transcribed
from lac operon
is very unstable
L’operatore è caratterizzato da una
sequenza palindromica.
Ogni meta del sito è legato dal DNA
binding domain del repressore LacI.
La struttura secondaria, denominata elicagiro-elica (helix-turn-helix) media il
riconoscimento del repressore LacI con la
sequenza target.
Questo dominio costa di 2 α-eliche di cui
una si inserisce nel solco maggiore del
DNA.
Il repressore LacI si lega come tetramero.
O3
O1
O2
Allolactose is the
inducer, a molecule that
binds to the repressor
causing it to leave the
DNA.
Mutations in the lac operon
1) Repressor
gene mutations
2) Operator mutation In
most cases, mutations in
operators either (O1) prevent
repressor binding or reduce the
binding strength, resulting in
constitutive expression of lac
operon.
3) Mutations in enzymes genes
lacZ and lacY alleles cause a
lac- phenotype, whereas lacAdoes not. Mutations in lacZ are
polar mutations.
Negative and positive regulation of lac operon
The CAP (catabolite activator protein), called also CRP, is able to activate the expression of the lac
operon. Activation occurs only in the absence of glucose.
Cyclic AMP interacts directly with CAP.
When the concentration of glucose is low or absent, the concentration
of cAMP is high.
With no cAMP bound to it, CAP separates from DNA and looses its
capacity yo stimulate lac expression.
(5’-3’)
No glucose, no lactose
Glucose and lactose
very low
conc. cAMP
CAP is inactive in absence of cAMP
Only lactose
high conc.
cAMP
CAP is active in presence of cAMP












