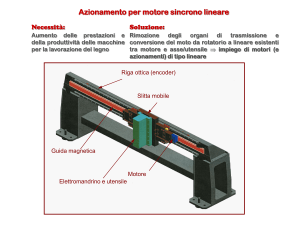
RIEPILOGO
Motori a corrente alternata
SUMMARY
AC motors
Motori sincroni
»
I motori sincroni sono caratterizzati dall’avere una frequenza di rotazione
costante che dipende dalla frequenza della rete di alimentazione e dal numero
di coppie polari.
La frequenza di rotazione di un motore sincrono è indipendente dal carico o
dalla coppia resistente che lo interessa dovuta agli attriti e al carico; il rotore
gira alla stessa frequenza del campo magnetico rotante generato dallo statore.
»
The synchronous motors are characterized by having a constant frequency
of rotation that depends on the frequency of the supply network and the
number of pole pairs.
The frequency of rotation of a synchronous motor is independent of the load
or the resistant torque that interests him caused from the frictions and from
the load; the rotor rotates at the same frequency of the rotating magnetic
field generated by the stator.
Macchina sincrona
» La caratteristica di una macchina sincrona
è quella di lavorare a velocità di rotazione e
frequenza costanti sia nell’uso come motore
che come generatore.
» The characteristic of a synchronous
machine is to work with rotation speed and
frequency constant both in the use as a
motor and as a generator.
Cave statoriche
» Il numero di poli dell’avvolgimento dello statore deve
essere necessariamente uguale al numero dei poli
dell’induttore e tutte e tre le fasi devono risiedere nelle
cave statoriche sottostanti all’influsso di un polo
induttore.
» The number of poles of the stator winding must be
necessarily equal to the number of poles of the inductor
and all three phases must reside in the stator slots
underlying to the influence of a pole inductor.
Motore sincrono
» Il motore sincrono presenta un considerevole difetto: non è
autoavviante. Un modo per ovviare a questo inconveniente è
quello di utilizzare, per l’avviamento, o un motore
autosincrono, oppure un motore ausiliario di lancio, che può
essere un motore asincrono o un motore a corrente continua
oppure un convertitore di frequenza.
» The synchronous motor has a considerable drawback: it is not
bootable. One way to overcome this drawback is to use, for
the starter, or an autosynchronous motor, or an auxiliary
motor of launch, that can be an asynchronous motor or a d.c.
motor or a frequency converter.
Motore sincrono
» I motori sincroni trovano applicazioni soprattutto in
quelle apparecchiature in cui la velocità non deve variare
in base all’entità e alle caratteristiche del carico
applicato, hanno quindi la caratteristica fondamentale di
lavorare a velocità costante.
» The synchronous motors find applications especially in
those devices in which the speed must not vary
according to the size and characteristics of the applied
load, thus have the fundamental characteristic of
working at constant speed.
Disposizione costruttiva
» La disposizione costruttiva di un motore sincrono
trifase è perfettamente uguale a quella del
corrispondente alternatore trifase, in definitiva il motore
sincrono non è altro che un alternatore in funzione di
motore.
» The arrangement construction of a three-phase
synchronous motor is perfectly identical to that of the
corresponding three-phase alternator, ultimately the
synchronous motor is nothing more than an alternator
working as motor.
Collegamento a stella o a triangolo
» Un motore sincrono trifase può essere collegato
alla linea d’alimentazione indifferentemente a
stella o a triangolo a seconda di come
vengono collegate le relative fasi.
» A three-phase synchronous motor can be
connected to the mains, either to star or to
delta depending on how it is connected to the
corresponding phases.
Rendimento
» Il rendimento η di un motore è dato dal
rapporto tra la potenza meccanica resa
all’asse e la potenza elettrica assorbita.
» The efficiency η of a motor is given by the
ratio between the mechanical power
supplied to the axis and the electrical power
absorbed.
Circuito d’eccitazione
» I motori sincroni monofasi a magneti permanenti sono motori
di piccola potenza autoavvianti (massimo 10 W),
costruttivamente più semplici da realizzare ed
economicamente più convenienti rispetto a quelli sincroni
trifasi per la mancanza del circuito d’eccitazione in corrente
continua.
» The synchronous motors with permanent magnets are small
motors (maximum 10 W) autostarted, constructively simpler
to implement and minor cost-effective than three-phase
synchronous motors for the lack of the circuit of excitation
in d.c.
Motori asincroni
» I motori asincroni sono molto utilizzati perché
economici, di semplice costituzione e inoltre non
necessitano di particolari manutenzioni. Le loro
applicazioni riguardano tutti i campi in cui è accettabile
una piccola variazione della loro velocità di rotazione.
» The asynchronous motors are widely used because at
low cost, they are easy to set up and also don’t require
any special maintenance. Their applications are in all
areas where it is acceptable a small variation in their
speed of rotation.
Tipi di rotore
» Nei motori asincroni il rotore può essere realizzato in due
modi: o a “gabbia di scoiattolo” oppure “avvolto”;
quest’ultimo non è molto diffuso perché implica, oltre a
complicazioni costruttive, un costo superiore del motore
e l’introduzione delle spazzole.
» In induction motors, the rotor can be achieved in two
ways: or “squirrel cage” or “wrapped”; the latter is
not very widespread because it implies, in addition to
constructive complications, a higher cost of the motor
and the introduction of the brushes.
Scorrimento
» Lo scorrimento s è dato dal rapporto tra la
velocità di scorrimento nS e la frequenza di
rotazione nC del campo rotante. Lo scorrimento
è di norma espresso in percentuale.
» The slide s is given by the ratio between the
sliding speed nS and the frequency of rotation
nC of the rotating field. The slide is normally
expressed as a percentage.
Caratteristica meccanica
» La caratteristica meccanica di un motore
correla l’andamento della coppia motrice in
funzione della velocità di rotazione del rotore
o dello scorrimento.
» The mechanical characteristic of a motor
correlates the trend of driving torque in
function of the speed of rotation of the rotor
or of the slide.
Zona di stabilità
» A differenza di quanto avviene per i motori sincroni,
il motore asincrono è in grado di riprendere
spontaneamente a funzionare nella zona di
stabilità se viene alleggerito il carico a cui è
collegato.
» Unlike what happens for synchronous motors, the
asynchronous motor is able to resume
spontaneously to work in the zone of stability if it
is lightened the load to which it is connected.
Collegamento a stella o a triangolo
» Un motore asincrono trifase può essere collegato a
stella (gli avvolgimenti sono predisposti per una
tensione di 230 V) o a triangolo (gli avvolgimenti
sono predisposti per una tensione di 400 V).
» A three-phase asynchronous motor can be
connected to star (the windings are predisposed for
a voltage of 230 V) or to delta (the windings are
predisposed for a voltage of 400 V).
Avvio di un motore asincrono
» Uno dei maggiori limiti del motore asincrono è relativo alla fase di
avviamento. In questa fase la coppia (coppia d’avvio o di spunto) non
è molto grande ma le correnti che circolano negli avvolgimenti hanno
valori molto elevati. L’avvio di un motore asincrono trifase può
avvenire con un “avvio diretto” oppure “avvio indiretto” con
modalità diverse.
» One of the major limitations of the asynchronous motor is related to
the start-up phase. At this phase the torque (starting torque or peak
torque) is not very big but the currents flowing in the windings have
very high values. The start up of a three-phase asynchronous motor
can be done with a “start up direct” or “start up indirect” in
different ways.
Convertitore di frequenza
»
In numerose applicazioni industriali è necessario far ruotare i motori con
frequenze di rotazioni diverse, per esempio, nei ventilatori, negli ascensori
ecc. È possibile variare la frequenza di rotazione in due diversi modi:
a) agendo sul numero delle coppie di polari dello statore (solamente nel caso
di motori trifase);
b) modificando la frequenza d’alimentazione del campo rotante statorico
tramite un convertitore di frequenza.
»
In many industrial applications it is necessary to rotate the motor with
different frequencies of rotations, for example, in the fans, in the elevators
ecc. It’s possible to vary the frequency of rotation in two ways:
a) by acting on the number of pairs polar of the stator (only in the case of
three-phase motors);
b) changing the supply frequency of the statoric rotating field via a frequency
converter.
Motore asincrono trifase usato in monofase
» Il motore asincrono trifase può funzionare in
monofase collegando un condensatore in
derivazione su due morsetti, qualunque sia il tipo di
collegamento utilizzato per collegare le fasi del
motore.
» The three-phase asynchronous motor can be
operated in single phase connecting a capacitor in
shunt on the two terminals, whatever the type of
connection used to connect the phases of the motor.
Diagramma circolare
»
Uno strumento grafico, attualmente poco usato perché laborioso, per lo
studio dei motori e delle macchine asincrone in genere, è quello del
diagramma circolare. Si tratta di un grafico nel quale sono riportate le
correnti in funzione dello scorrimento supponendo costanti la tensione
d’alimentazione e la sua frequenza. La sua costruzione può essere
effettuata automaticamente e velocemente mediante un computer usando
software specifici.
»
A graphical tool, currently little used because laborious, for the study of
motors and induction machines, in general, is that of the circular
diagram.
It is a graph that shows the current as a function of the slide assuming
constant the supply voltage and its frequency. Its construction can be
done automatically and quickly by a computer using specific software.
Targhetta segnaletica
» Un motore elettrico deve essere sempre di provvisto di una
targhetta segnaletica (o anche più targhette), di solito posizionata
sulla carcassa, in modo che sia facilmente accessibile alla lettura nella
sua normale posizione di utilizzo.
La norma CEI EN 60034-1 relativa alle “macchine elettriche rotanti”
indica i principali dati da riportare sulla targa.
» An electric motor must always be provided with a data plate (or
even more data plates), usually positioned on the casing, so that it is
easily accessible to the reading in its normal position of use.
The CEI EN 60034-1 relative to the “rotating electrical machines”
indicates the main informations to report on the data plate.