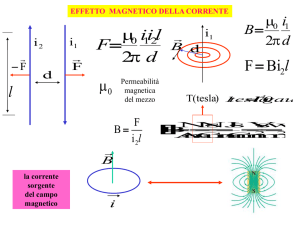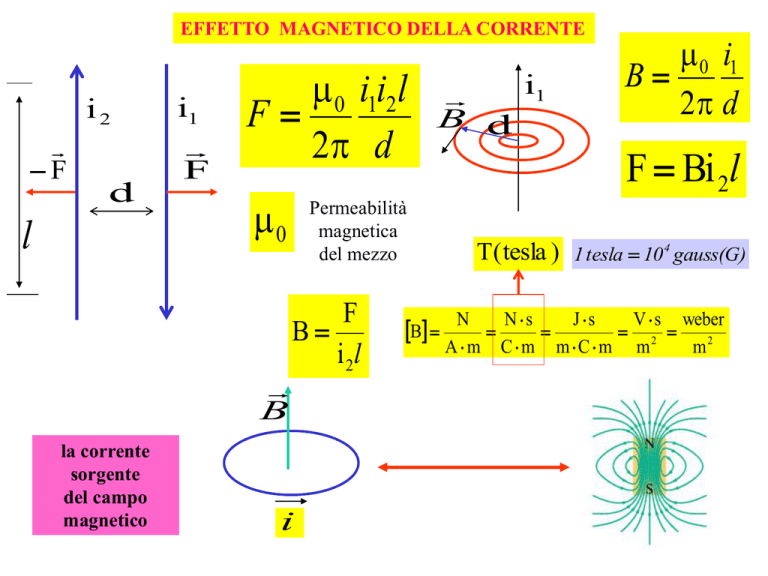
EFFETTO MAGNETICO DELLA CORRENTE
i2
F
d
l
i1
F
0 i1i2l
F
2 d
0
B
la corrente
sorgente
del campo
magnetico
i1
B d
Permeabilità
magnetica
del mezzo
F
B
i 2l
i
B
T ( tesla )
0 i1
B
2 d
F Bi 2l
1 tesla 10 4 gauss(G)
N
Ns
J s
V s weber
2
Am Cm mCm m
m2
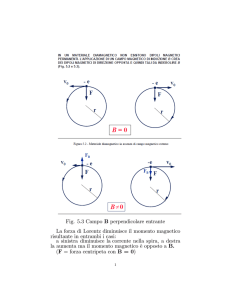
FORZA DI LORENTZ
B
v
F
F qv B
q
v
Lavoro della forza di Lorentz
ds
dL F ds ds F qds v B qds B 0
dt
poiché
ds
B ds
dt
FORZA DI LORENTZ
F qv B
Elettroni e positoni
q
v
e
e
B
uscente
e
26/05/06
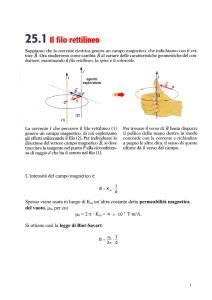
CAMPO MAGNETICO DI UN SOLENOIDE
B
d
i
0 i
B
2 d
B 0i n
solenoide
Al centro del solenoide
Al centro della spira
n
Numero di spire
Per unità di lunghezza
INDUZIONE MAGNETICA
C:/STUDENTI/weblab/corr-ind/indcur_ita.htm
S
B
B
B S
n
B dS
S
f .e.m.
t
R
i
f .e.m.
i
R
AUTOINDUZIONE
corrente
i
Flusso di campo
magnetico concatenato
Coefficiente di Dipende dalla
forma geometrica
L
autoinduzione
del circuito
i
Li L i
i
f .e.m.
L
t
t
AUTOINDUZIONE
L
V
i
V t
i e
R
V
i (1 e t )
R
t
chiusura
interruttore
apertura
interruttore
ON
OFF
CORRENTE ALTERNATA
Produzione con
l’alternatore
C:/STUDENTI/weblab/gen-fem/generator_ita.htm
Trasformazione col
trasformatore
i I sen (t )
L
Un circuito in generale contiene
R, C, L
C
Relazione fra V ed i
V
V V0 sen( t )
I I0 sen (t I )
V I 0 V I
V I 90
V
I
R
V I 90
I VC
V
I
L
V V0 sen( t )
V
I
R
I I 0 sen( t )
I VC
V
I
L
L
C
V
I
R
I VC
Resistenza
Reattanza capacitiva
V
I
Z
V
impedenza
V
I
L
Reattanza induttiva
1
Z R L
C
2
in media
1
1
L
0
C
LC
Condizione
di risonanza
ZR
2
W VI V ( t )I ( t ) Veff I eff cos
Potenza trasferita alla resistenza se
Veff
V0
2
I eff
I0
2
90
W0
TRASFORMATORI
In una spira
d B
Espira
dt
VP NP Espira
VS NS Espira NS
VP NP Espira NP
Per la corrente, valendo
la conservazione
dell’energia
31/05/06
I P VP ISVS
VS NS Espira
NS
VS VP
NP
VP
NP
IS I P
IP
VS
NS