unit
5
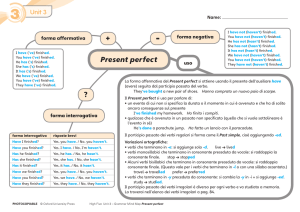
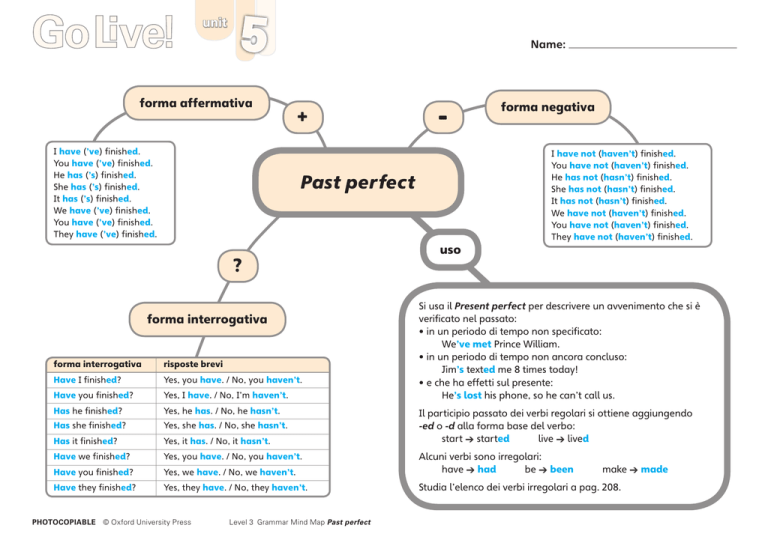
forma affermativa
I have (’ve) finished.
You have (’ve) finished.
He has (’s) finished.
She has (’s) finished.
It has (’s) finished.
We have (’ve) finished.
You have (’ve) finished.
They have (’ve) finished.
Name:
+
-
Past perfect
?
forma interrogativa
uso
forma negativa
I have not (haven’t) finished.
You have not (haven’t) finished.
He has not (hasn’t) finished.
She has not (hasn’t) finished.
It has not (hasn’t) finished.
We have not (haven’t) finished.
You have not (haven’t) finished.
They have not (haven’t) finished.
Si usa il Present perfect per descrivere un avvenimento che si è
verificato nel passato:
• in un periodo di tempo non specificato:
We’ve met Prince William.
• in un periodo di tempo non ancora concluso:
Jim’s texted me 8 times today!
• e che ha effetti sul presente:
He’s lost his phone, so he can’t call us.
forma interrogativa
risposte brevi
Have I finished?
Yes, you have. / No, you haven’t.
Have you finished?
Yes, I have. / No, I’m haven’t.
Has he finished?
Yes, he has. / No, he hasn’t.
Has she finished?
Yes, she has. / No, she hasn’t.
Has it finished?
Yes, it has. / No, it hasn’t.
Have we finished?
Yes, you have. / No, you haven’t.
Have you finished?
Yes, we have. / No, we haven’t.
Alcuni verbi sono irregolari:
have ➔ had be ➔ been make ➔ made
Have they finished?
Yes, they have. / No, they haven’t.
Studia l’elenco dei verbi irregolari a pag. 208.
PHOTOCOPIABLE © Oxford University Press Level 3 Grammar Mind Map Past perfect
Il participio passato dei verbi regolari si ottiene aggiungendo
-ed o -d alla forma base del verbo:
start ➔ started live ➔ lived