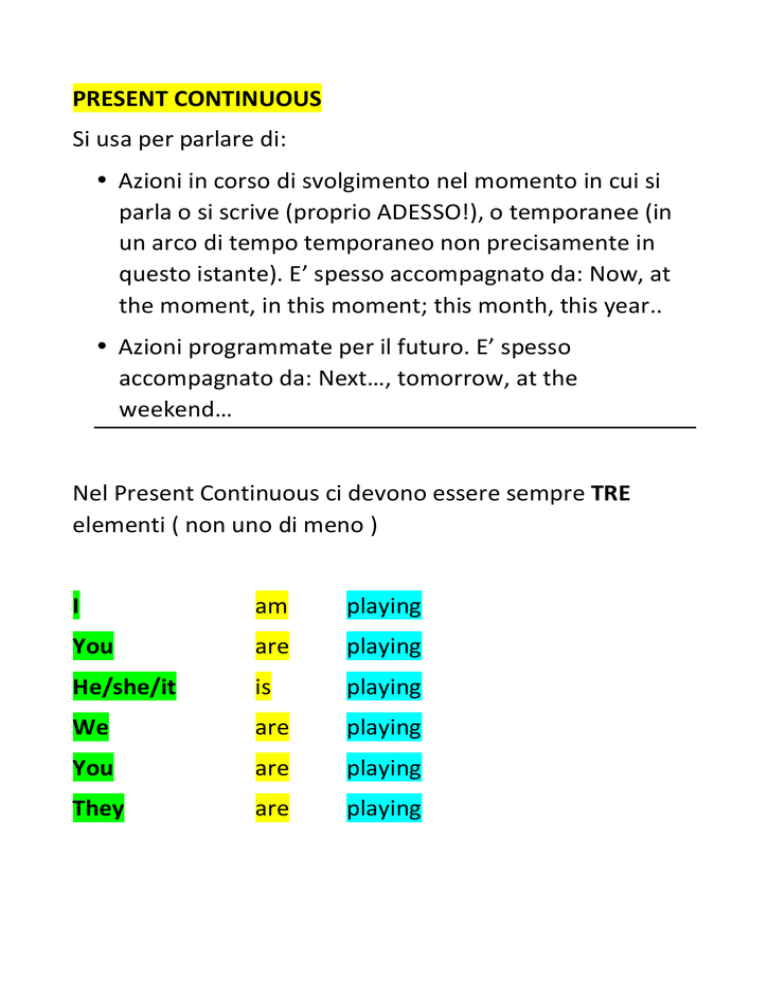
PRESENT CONTINUOUS Si usa per parlare di: • Azioni in corso di svolgimento nel momento in cui si parla o si scrive (proprio ADESSO!), o temporanee (in un arco di tempo temporaneo non precisamente in questo istante). E’ spesso accompagnato da: Now, at the moment, in this moment; this month, this year.. • Azioni programmate per il futuro. E’ spesso accompagnato da: Next…, tomorrow, at the weekend… Nel Present Continuous ci devono essere sempre TRE elementi ( non uno di meno ) I am playing You are playing He/she/it is playing We are playing You are playing They are playing FORMULE: +) soggetto-­‐verbo be-­‐verbo in ing. ?) verbo be-­‐ soggetto-­‐ verbo in ing. -­‐) soggetto-­‐ verbo be–not-­‐verbo in ing. QUESTION FORM NEGATIVE FORM AM/IS/ARE+SOGG+ING FORM SOGG+AM/IS/ARE+NOT+ING FORM AM I PLAYING? I AM NOT PLAYING ARE YOU PLAYING? YOU AREN’T PLAYING IS HE PLAYING? HE ISN’T PLAYING IS SHE PLAYING? SHE ISN’T PLAYING IS IT PLAYING? IT ISN’T PLAYING ARE WE PLAYING? WE AREN’T PLAYING ARE YOU PLAYING? YOU AREN’T PLAYING ARE THEY PLAYING? THEY AREN’T PLAYING Variazioni ortografiche prima di aggiungere ING al verbo base • Verbi terminanti in –IE, cambiano ‘IE’ in ‘Y’ To die à dying. • Verbi monosillabici terminanti con una SOLA consonante preceduta da una SOLA vocale, raddoppiano la consonante finale To stop à stopping (Fanno eccezione, perché non sono monosillabici, i verbi To Travel à travelling e To Prefer à preferring). MA: To clean à cleaning • Verbi terminanti in ‘E’ muta, perdono la ‘E’ To smoke à smoking.