Lesson 8
(A2)
Past simple: forma affermativa
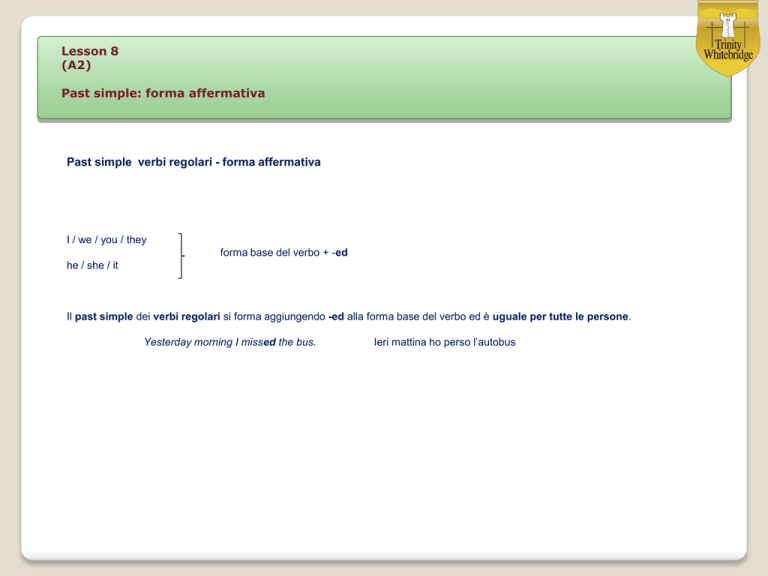
Past simple verbi regolari - forma affermativa
I / we / you / they
forma base del verbo + -ed
he / she / it
Il past simple dei verbi regolari si forma aggiungendo -ed alla forma base del verbo ed è uguale per tutte le persone.
Yesterday morning I missed the bus.
Ieri mattina ho perso l’autobus
Lesson 8
(A2)
Past simple: forma affermativa
Variazioni ortografiche
Forma base
phone
play
study
Termina in
-e
-y preceduta da vocale
-y preceduta da consonante
Past simple
aggiunge solo -d
aggiunge -ed
cambia y in i + -ed
Esempi
phoned
played
studied
stop
monosillabici terminanti in
consonante preceduta da
vocale accentata
raddoppiano la consonante
stopped
travel - prefer
bisillabi terminanti in -l o -r
raddoppiano la consonante l o r
travelled
preferred
Lesson 8
(A2)
Past simple: forma affermativa
Quando si usa
Il past simple si usa per indicare azioni ed eventi completamente passati e conclusi, ciò evidente dal contesto o dalla presenza di
espressioni di tempo determinato come:
yesterday
in 1987
last night/week/month/year
when I was a child
two days/weeks/months /… ago
When I was a child I lived in a house by the sea. Quando ero bambino vivevo in una casa vicino al mare.
Il past simple può tradurre un imperfetto, un passato remoto o un passato prossimo.
A few years ago I lived in London.
We decided to move to Manchester.
I stayed at home last night.
Alcuni anni fa vivevo a Londra.
Decidemmo di trasferirci a Manchester.
Sono rimasto a casa ieri sera.
Lesson 8
(A2)
Past simple: forma affermativa
Past simple – verbi irregolari: forma affermativa
I verbi irregolari non prendono la desinenza -ed, ma ciascuno ha una forma propria del past simple che corrisponde alla seconda
forma del paradigma.
Presentano una sola forma per tutte le persone. Fa eccezione il verbo to be che ha due forme: was (per la 1a e la 3a persona
singolare) e were (per tutte le altre).
Ecco il paradigma di alcuni verbi irregolari tra i più comuni:
Infinitive
to be
to have
to go
to come
to see
to read (pron: riid)
to write
to drink
to eat
to buy
essere
avere
andare
venire
vedere
leggere
scrivere
bere
mangiare
comperare
I drank a lot of beer at the pub last night.
Ho bevuto molta birra al pub ieri sera.
Past simple
was / were
had
went
came
saw
read (pron: red)
wrote
drank
ate
bought
Past participle
been
had
gone
come
seen
read (pron: red)
written
drunk
eaten
bought
EXERCISE 1
Scriviamo il past simple dei seguenti verbi regolari.
1.
walk
7.
stop
2.
travel
8.
stay
3.
prefer
9.
carry
4.
decide
10. plan
5.
wash
11. play
6.
work
12. rebel
EXERCISE 2
Quali tra i seguenti verbi sono regolari e quali sono irregolari?
Trasciniamo ciascun verbo nel riquadro appropriato e scriviamo di fianco a ciascun verbo il past simple.
take
write
start
spend
think
drink
read
speak
brake
ring
live
try
cost
die
enjoy
leave
like
begin
go
listen
remember
sing
become
IRREGULAR VERBS
eat
arrive
come
fall
break
REGULAR VERBS
forget
feel
fly
bring
tell
swim
buy
say
teach
hear
EXERCISE 3
Osserviamo in ciascuna frase il verbo tra parentesi: è regolare o irregolare?
Sottolineiamo i verbi regolari in verde e i verbi irregolari in rosso.
Completiamo ciascuna frase con la forma affermativa del past simple del verbo tra parentesi.
1.
Our weekend in London was fantastic. We really (enjoy) …………………… it.
2.
Last summer Mark and Josh (spend) ………………… a few days in Paris.
3.
They (walk) …………………… for two hours to get to the top of the hill.
4.
He was a composer. He (write) …………………… more than 70 pieces of music.
5.
Mrs Ashley was a teacher. She (teach) ………………… German for about thirty years.
6.
Three people (die) …………………….. in the car crash.
7.
Bob’s sister (go) ……………………. to China on holiday two months ago.
8.
The children (break) …………………….. the window a few minutes ago.
9.
Kevin (phone) ………………………… last night.
10.
They (send) ……………………… us a postcard from the USA.
EXERCISE 4
Completiamo queste frasi con il past simple dei verbi irregolari tra parentesi.
1.
David (fall) ………………… down the stairs and (hurt) ………………… himself badly.
2.
I (light) …………………… some candles but the wind immediately (blow)
……………….. them out.
3.
My brother (build) …………………… a model aeroplane and (sell) ……………….. it on the Internet.
4.
Mr Todd (fight) …………………… in the Second World War and (keep)
……………….. a diary.
5.
George (hold) …………………… the shaker in both hands and (shake)
……………….. it hard.