Corso di Biologia Molecolare per Odontoiatria
2 CFU
Anno Accademico 2012-2013
docente: Vito De Pinto, Dipartimento di Scienze Biologiche Geologiche Ambientali, Sez. di
Biochimica e Biologia Molecolare
(III piano, Edif. 12, Viale Doria, 6 Catania; tel. 095-7384244, fax: 095-337036)
Programma di insegnamento
GLI ACIDI NUCLEICI: STRUTTURA 1^ - STRUTTURA 2^
I GENOMI EUCARIOTICI - GENI INTERROTTI – loro caratteristiche - Famiglie geniche
e Superfamiglie geniche - Pseudogeni
LA TRASMISSIONE DELL'INFORMAZIONE GENETICA E LE MOLECOLE DI RNA:
Il dogma centrale della biologia e sue modificazioni - il tRNA come adattatore - mRNA: funzione
(Batteri ed Eucarioti) - LA REPLICAZIONE: DNApolimerasi
RIPARAZIONE: Danni al DNA - mutazioni - Sistemi di riparazione
RICOMBINAZIONE - Ricombinazione generale od omologa - Str. di Hollyday
SINTESI PROTEICA – Ribosomi - Stadi della sintesi proteica - gli inibitori della sintesi
proteica
IL CODICE GENETICO
LA TRASCRIZIONE – meccanismo e concetti generali - Componenenti dell’unità
trascrizionale: Promotore-sito d’inizio-trascritto-terminatore - Importanza della trascrizione nella
regolazione dell’espressione genica - Fasi generali della trascrizione
REGOLAZIONE DELLA TRASCRIZIONE NEI PROCARIOTI - ORGANIZZAZIONE
AD OPERONI
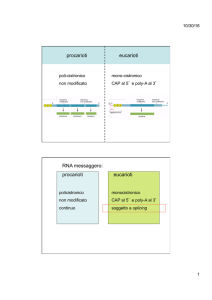
LA TRASCRIZIONE NEGLI EUCARIOTI : RNA polimerasi - Fattori della Trascrizione
PROCESSAMENTO DEGLI RNA - Splicing e Splicing alternativo
REGOLAZIONE DELLA TRASCRIZIONE NEGLI EUCARIOTI – FATTORI DI
TRASCRIZIONE
TECNICHE DI BIOLOGIA MOLECOLARE
MANIPOLAZIONE DEGLI ACIDI NUCLEICI – elettroforesi - enzimi di restrizione –
Southern e Northern blot – sequenziamento del DNA
VETTORI – Plasmidi – principio e pratica del clonaggio
PCR – principi del metodo – analisi dei risultati
Sussidi didattici
Lewin, B., et al, Il Gene, edizione compatta, Zanichelli, 2011
Watson, J.D. et al., Biologia Molecolare del gene VI ed., Zanichelli 2009
Ottimi riassunti degli argomenti da trattare sono anche reperibili nei capitoli finali di buoni
libri di Biochimica, quali ad esempio:
Nelson & Cox, I principi di Biochimica di Lehninger, Zanichelli 2010
Syllabus
NUCLEIC ACIDS: PRIMARY AND SECONDARY STRUCTURE
EUKARYOTIC GENOMES - DISCONTINUOUS GENES - Functional features - Gene
families and superfamilies - Pseudogenes
THE FLOW OF INFORMATION IN BIOLOGY - The central dogma of Biology - RNAS:
tRNA as adaptor, mRNA as messenger; differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes - DNA
duplication: the DNA polymerases
DNA damages and repair. Mutations. Enzymatic recovery of damaged DNA molecules.
RECOMBINATION - General and homologous recombination - Hollyday's structure
TRANSLATION - Ribosomes - Stages in the protein synthesis mechanism - inhibitors of
protein synthesis
The Genetic Code
TRANSCRIPTION - mechanism and general organization - The essential components of
the transcription machinery - the promoter - relevance of transcription for the gene expression tuning enzymatic steps of the transcription
TRANSCRIPTION REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES - THE OPERON
TRANSCRIPTION IN EUKARYOTES: RNApolymerase - Transcription factors
RNA PROCESSING: SPLICING AND ALTERNATIVE SPLICING
TRANSCRIPTION REGULATION IN EUKARYOTES
TECHNIQUES IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
HANDLING NUCLEIC ACIDS - electrophoresis - restriction enzymes - SOuthern and
Northern Blot - DNA sequencing
VECTORS – Plasmids – classical cloning principles
PCR – methods – analysis of results
BOOKS
Lewin, B., et al, The Gene X, Pearson 2010
Watson, J.D. et al., Molecular Biology of the Gene, VI ed., Pearson 2008
Final Chapters of the best Textbooks in Biochemistry, like. i.e.:
Nelson & Cox, Principle of Biochemistry by Lehninger, Pearson 2008