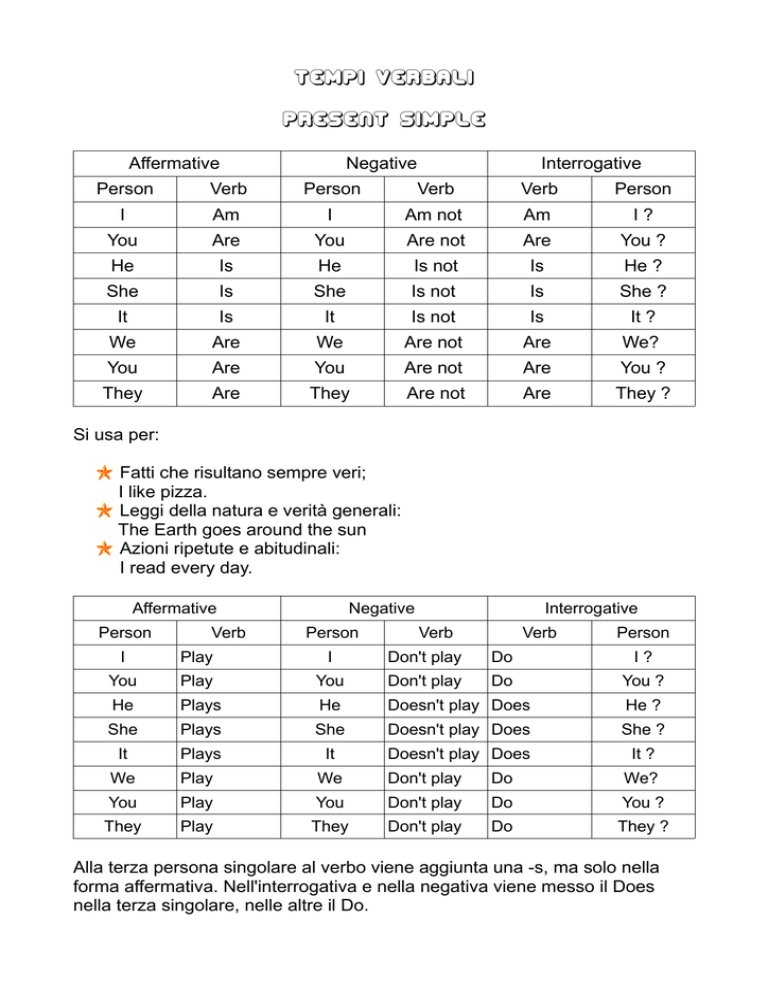
Tempi verbali
present simple
Affermative
Negative
Interrogative
Person
Verb
Person
Verb
Verb
Person
I
Am
I
Am not
Am
I?
You
Are
You
Are not
Are
You ?
He
Is
He
Is not
Is
He ?
She
Is
She
Is not
Is
She ?
It
Is
It
Is not
Is
It ?
We
Are
We
Are not
Are
We?
You
Are
You
Are not
Are
You ?
They
Are
They
Are not
Are
They ?
Si usa per:
Fatti che risultano sempre veri;
I like pizza.
Leggi della natura e verità generali:
The Earth goes around the sun
Azioni ripetute e abitudinali:
I read every day.
Affermative
Person
Verb
Negative
Person
Interrogative
Verb
Verb
Person
I
Play
I
Don't play
Do
I?
You
Play
You
Don't play
Do
You ?
He
Plays
He
Doesn't play Does
He ?
She
Plays
She
Doesn't play Does
She ?
It
Plays
It
Doesn't play Does
It ?
We
Play
We
Don't play
Do
We?
You
Play
You
Don't play
Do
You ?
They
Play
They
Don't play
Do
They ?
Alla terza persona singolare al verbo viene aggiunta una -s, ma solo nella
forma affermativa. Nell'interrogativa e nella negativa viene messo il Does
nella terza singolare, nelle altre il Do.
Es: Do you play football?
Does he study history?
Nei verbi che terminano con la -y preceduta da consonante cade la -y e viene
sostituita da -ies.
Study = Studies
Try = Tries
I verbi che terminano con -s, -sh, -ch, -x o -z aggiungono -es al fondo.
Miss = Misses
Finish = Finishes
I verbi do e go aggiungono -es.
Do = Does
Go = Goes
Frasi:
I am Nicole.
Are you American?
He is not my friend.
Quando vengono usati degli avverbi, devono essere posizionati tra il soggetto
e il verbo.
Es: I always read a book before go to bed.
Solo nel caso in cui sia presente il verbo essere l'avverbio va dopo il verbo.
Es: I am often late for school.
Past simple
Affermative
Negative
Interrogative
Person
Verb
Person
Verb
Verb
Person
I
Was
I
Was
Was
I?
You
Were
You
Were
Were
You ?
He
Was
He
Was
Was
He ?
She
Was
She
Was
Was
She ?
It
Was
It
Was
Was
It ?
We
Were
We
Were
Were
We?
You
Were
You
Were
Were
You ?
They
Were
They
Were
Were
They ?
Si usa per indicare un'azione passata e conclusasi nel passato.
Quando si pone una domanda si usa il Did e il verbo torna alla forma base.
Es: Did you go to the bar, yesterday?
Per accentuare il fatto che è un'azione passata, si usano gli avverbi di tempo:
yesterday, the day before yesterday, last night, last week, three years ago...
Frasi:
I was there, yesterday.
Where were you, last week?
We weren't here, last night.
Il passato dei verbi regolari si fa aggiungendo alla forma base del verbo -ed.
Es: Call = Called
Visit = Visited
I verbi che terminano per -e aggiungono solo la -d finale.
Es: Like = Liked
Love = Loved
I verbi che terminano per -y preceduta da consonante tolgono la –y e mettono
-ied. Al contrario quelli che terminano con la -y preceduta da vocale
aggiungono solo -ed.
Es: Study = Studied
Cry = Cried
Play = Played
I verbi che terminano con una consonante preceduti da una vocale
raddoppiano l'ultima consonante e aggiungono -ed. Vale per tutti i verbi
tranne per quelli terminanti con la -l.
Es: Stop = Stopped
Travel = Traveled
Invece il passato dei verbi irregolari, si fa usando la tabella dei verbi irregolari,
usando la seconda colonna.
Verbi Irregolari Tabella
Present continuoUs
Affermative
Negative
Interrogative
Person
Verb
Person
Verb
Verb
Person
I
Am wearing
I
Am not
wearing
Am
I wearing ?
You
Are wearing
You
Aren't
wearing
Are
You
wearing ?
He
Is wearing
He
Isn't wearing Is
He
wearing ?
She
Is wearing
She
Isn't wearing Is
She wearing
?
It
Is wearing
It
Isn't wearing Is
It wearing ?
We
Are wearing
We
Aren' t
wearing
Are
We
wearing ?
You
Are wearing
You
Aren't
wearing
Are
You
wearing ?
They
Are wearing
They
Aren't
wearing
Are
They
wearing ?
Il present continuous si forma con il verbo essere + il verbo alla forma base +
ing alla fine del verbo.
Wear = I am wear + ing= I am wearing
Casi particolari:
Study = Studying
Play = Playing
Lie = Lying
Die = Dying
Stop = Stopping
Travel = Travelling
Si usa quando si indica un'azione che si sta svolgendo in questo preciso
istante:
They are playing football.
Loro stanno giocando a calcio.
Per accentuare il ancora di più il fatto che l'azione si sta svolgendo ora, si
usano gli avverbi di tempo. Esempio:
Now, At the moment, In this moment...
In this moment, I'm reading a book.
Past continuous
Affermative
Negative
Interrogative
Person
Verb
Person
Verb
Verb
Person
I
Was wearing
I
Was not
wearing
Was
I wearing ?
You
Were
wearing
You
Weren't
wearing
Were
You
wearing ?
He
Was wearing
He
Wasn't
wearing
Was
He
wearing ?
She
Was wearing
She
Wasn't
wearing
Was
She wearing
?
It
Was wearing
It
Wasn't
wearing
Was
It wearing ?
We
Were
wearing
We
Weren' t
wearing
Were
We
wearing ?
You
Were
wearing
You
Weren't
wearing
Were
You
wearing ?
They
Were
wearing
They
Weren't
wearing
Were
They
wearing ?
Si usa per:
Esprimere un'azione che era in corso in un preciso istante;
At 8,00 this morning i was sleeping.
Per descrivere due azioni che si svolgevano
contemporaneamente
I was studying, while my brother was playing videogames.
Il past continuous e il past simple possono essere usati insieme,
divisi da un when o da un while.
While I was studying, I heard a noise;
When I heard the noise, I was studying.
Present perfect
Affermative
Negative
Interrogative
Person
Verb
Person
Verb
Verb
Person
I
Have
studied
I
Haven't
studied
Have
I studied ?
You
Have
studied
You
Haven't
studied
Have
You
studied ?
He
Has studied
He
Hasn't
studied
Has
He studied ?
She
Has studied
She
Hasn't
studied
Has
She
studied ?
It
Has studied
It
Hasn't
studied
Has
It studied ?
We
Have
studied
We
Haven't
studied
Have
We
studied ?
You
Have
studied
You
Haven't
studied
Have
You
studied ?
They
Have
studied
They
Haven't
studied
Have
They studied
?
Quando i verbi sono irregolari si usa la forma al participio, cioè la terza
colonna nella tabella dei paradigmi. Per i verbi regolari valgono le regole del
Past Simple.
Si usa per indicare:
Un'azione non avvenuta nel passato senza specificare quando.
There has been a strike.
Un'azione che è avvenuta nel passato ma che ha ancora
riflessi nel presente.
I've lost my keys. I can't get into the house.
Un'azione avvenuta in un tempo non concluso e per parlare di
esperienze fatte in passato ma che si potrebbero ripetere.
I've travelled to France two times.
Ever & Never:
Si usa never per indicare che qualcuno non mai fatto qualcosa in
passato.
Si usa ever nelle domande, per sapere se qualcuno ha mai fatto
qualcosa prima d'ora.
Es: She has never written a book.
Have you ever worked in a society?
Been & Gone
Si usa been per indicare che qualcuno è andato in un posto ed è già
tornato.
Si usa gone per indicare che qualcuno è andato in un posto ma non
è ancora tornato.
Es: David has been to the shop.
Paul has gone to America.
Just, Already, Yet & Still
Si usa just (appena) per indicare che un'azione si è appena
conclusa.
Si usa already (già) per indicare che un'azione si è un conclusa già
da un po'.
Si usa yet (ancora/già) per indicare che un'azione o si è appena
conclusa o deve ancor finire.
Si usa still (ancora) per indicare che un'azione è ancora in corso.
Es: I've just finished the book I was reading.
Ho appena finito il libro che stavo leggendo
I've already eaten.
Ho già mangiato.
I haven't finished yet.
Non ho ancora finito.
Have you finished your homework yet?
Hai già fatto i compiti?
It is still raining.
Sta ancora piovendo.
Since & For
Si usa since per indicare un punto preciso nel tempo.
Si usa for per indicare la durata di un'azione o di uno stato.
Es: I've lived here since I was born.
He hasn't seen her for ages.
Si usa molto nelle frasi con How much/many/often? E quando si
indicano quantità specifiche.
Es: How many e-mails have you written?
I've written five e-mails.
Si usa anche con i verbi di percezione: know, understand, forget e
con i verbi be, have, stop e break.
Es: They have had a great day!
PRESENT PERFECT CONTInuous
Affermative
Negative
Interrogative
Person
Verb
Person
Verb
Verb
Person
I
Have been
playing
I
Haven't
been playing
Have
I been
playing ?
You
Have been
playing
You
Haven't
been playing
Have
You been
playing ?
He
Has been
playing
He
Hasn't been
playing
Has
He been
playing ?
She
Has been
playing
She
Hasn't been
playing
Has
She been
playing ?
It
Has been
playing
It
Hasn't been
playing
Has
It been
playing ?
We
Have been
playing
We
Haven't
been playing
Have
We been
playing ?
You
Have been
playing
You
Haven't
been playing
Have
You been
playing ?
They
Have been
playing
They
Haven't
been playing
Have
They
been playing
?
Si usa per:
Descrivere un'azione che è iniziata nel passato ma che ha dei risultati
nel presente.
Es: Why are you so dirty? I've been playing football.
Descrivere situazioni temporanee che sono iniziate nel passato e
continuano nel presente.
Es: The war correspondents have been staying in a hotel for the past
month.
Azioni ripetute dal passato al presente.
Es: I've been phoning her for days, but she's never at home.
Si usa anche con espressioni di tempo del tipo: all day, for ages, lately,
recently, per indicare la continuità dell'azione.
Es: It's been raining all day.
For & Since
Si usa con for e since per indicare la durata o l'inizio dell'azione:
I've been writing for hours.
I've been writing since this morning.
Il present perfect continuous non si deve usare con i verbi di percezione:
know, forget, understand e con i verbi be, have, stop e break.
Solo nel caso in cui have si a un verbo d'azione, può essere usato ancheil
Present perfect continuous.
I've been having breakfast at the bar lately.
Si usa molto nelle domande che iniziano con How long? E nelle frasi con
since e for.
Es: How long have you been practising the piano?
I've been practising for five years.
Past perfect
Affermative
Negative
Interrogative
Person
Verb
Person
Verb
Verb
Person
I
Had phoned
I
Hadn't
phoned
Had
I phoned?
You
Had phoned
You
Hadn't
phoned
Had
You
phoned?
He
Had phoned
He
Hadn't
phoned
Had
He phoned?
She
Had phoned
She
Hadn't
phoned
Had
She
phoned?
It
Had phoned
It
Hadn't
phoned
Had
It phoned?
We
Had phoned
We
Hadn't
phoned
Had
We phoned?
You
Had phoned
You
Hadn't
phoned
Had
You
phoned?
They
Had phoned
They
Hadn't
phoned
Had
They
phoned?
Si usa per :
Parlare di un'azione avvenuta prima di un'altra azione
ugualmente passata.
Es: Sue left at 7.00. When we arrived at Sue's house she had
already left.
Si usa anche con espressioni temporali come : when, since, for,
already, yet, by the time.
Es: When we arrived at the airport, the plane had just taken off.
Si trova anche con verbi come think, know, be sure, realize,
remember, suspect, understand ecc....
I thought I had seen this film, but I hadn't.
Si usa anche per il discorso indiretto.
He said he had locked the door.
Futuro con will
Affermative
Negative
Interrogative
Person
Verb
Person
Verb
Verb
Person
I
Will
I
Won't
Will
I?
You
Will
You
Won't
Will
You?
He
Will
He
Won't
Will
He ?
She
Will
She
Won't
Will
She ?
It
Will
It
Won't
Will
It ?
We
Will
We
Won't
Will
We?
You
Will
You
Won't
Will
You ?
They
Will
They
Won't
Will
They ?
Si usa per:
Fare previsioni basate su un'opinione con perhaps, probably,
be sure, don't think...
Es: I'm sure Jim will pass all his exams.
Indicare eventi futuri che sono certi.
Es: It'll be dark soon.
Offrire di fare qualcosa.
Es: I'll post that letter for you.
Promettere.
Es: I'll give you the money tomorrow.
Decisioni prese sul momento.
Es: What would you like? I'll have the chicken.
Fare richieste.
Es: Will you turn the volume down, please.
Fissare appuntamenti.
Es: I'll see you tomorrow.
Esprimere rifiuto.
Es: I won't give it back.
To be going to
Affermative
Negative
Person
Verb
Person
I
Am going to
I
You
Are going to
He
Interrogative
Verb
Verb
Person
Am not
going to
Am
I going to?
You
Aren't going
to
Are
You going
to?
Is going to
He
Isn't going to
Is
He going to?
She
Is going to
She
Isn't going to
Is
She going
to?
It
Is going to
It
Isn't going to
Is
It going to?
We
Are going to
We
Aren't going
to
Are
We going
to?
You
Are going to
You
Aren't going
to
Are
You going
to?
They
Are going to
They
Aren't going
to
Are
They going
to?
Si usa per:
Esprimere intenzioni future, ma senza una pianificazione precisa.
Es: Linda is going to learn Chinese.
Esprimere decisioni future già prese.
Es: Your television set is broken. I know. I'm going to buy a new one
soon.
Previsioni fatte su osservazioni di fatti.
Es: Look. Thoose book are going to fall.
Per indicare il futuro si possono usare anche il Present Simple e il Present
continuos.
Schema riassuntivo futuro
Forma
Uso
Esempi
I expect it will rain
tomorrow.
Will/won't
Previsioni, intuizioni,
speso con think,believe,
hope, expect...
Offerte
I'll drive you home if you
want
Promesse e rifiuti
I promise I'll pay you
tomorrow
Decisioni prese al
momento
It's cold. I'll close the
window
Intenzioni
He said he's going to learn
Chinese
Previsioni basate
sull'osservazione dei fatti
Look at thoose clouds! It's
going to rain
Decisioni per il futuro
prese in precedenza
I'm going to see the new
Hunger Games film soon.
To be going to
Present continuous
Azioni programmate
(spesso con espressioni di
tempo come tonight,
tomorrow, next week...)
I'm having my hair cut
tomorrow
Present Simple
Appuntamenti e orari
The flight to Madrid leaves
at 9.00
Nelle frasi subordinate
dopo when, after, before,
unless, in case, as soon
as, until, by the time, the
next time
Give me a ring when you
arrive.












