MAGO
Monitoring All Grid Objects
Anna Jannace1, Carmine Spizuoco1, Francesco Adinolfi1, Giovanni Bracco2
1- Consorzio Campano per l’Informatica e l’Automazione Industriale (C.R.I.A.I.)
[f.adinolfi, a.jannace, c.spizuoco]@criai.it
2- ENEA [[email protected]]
Summary
INTEGRATION IN ENEA-GRID
This poster describes the CRESCO subproject 1.2 “MAGO: Monitoring All
Grid Objects of CRESCO”. This High Performance Computing system was
installed to provide the required computing power to the CRESCO project
applications and to integrate CRESCO HPC system into ENEA-GRID
infrastructure.
One of the peculiarities of the environments is the capability to be decentralized, allowing availability and robustness,
also in case of crash involving specific computers.
It was chosen in this work to create a centralized and hierarchical structure, because the system monitors Grid
resources, but it does not manage them, and because such approach allows to minimize maintenance on single host.
This project is the result of the collaboration between ENEA and C.R.I.A.I.
Consorzio Campano di Ricerca per l’informatica e l’automazione
industriale.
The set of mature technologies, which belong to the
infrastructure ENEA, allows to place MAGO as a tool for
monitoring of activities carried out from Grid infrastructure.
The process of Monitoring & Discovery resources is needed in HPC system
to find and solve the malfunctions arising in the infrastructure.
The main ENEA-GRID software components are:
• Multi-site resource manager LSF Multicluster,
• OpenAFS distributed file system,
• Kerberos 5 authentication,
• GUI based on CITRIX technologies.
MAGO
After a technological survey, the Information System model was chosen
in
according
to
the
GLUE
Schema
standard
(http://glueschema.forge.cnaf.infn.it/).
The study was based on the ENEA Grid infrastructure. Its characteristics
imply the choice of Ganglia (http://ganglia.info/) as the core of the
monitoring system.
Monitoring All Grid Objects
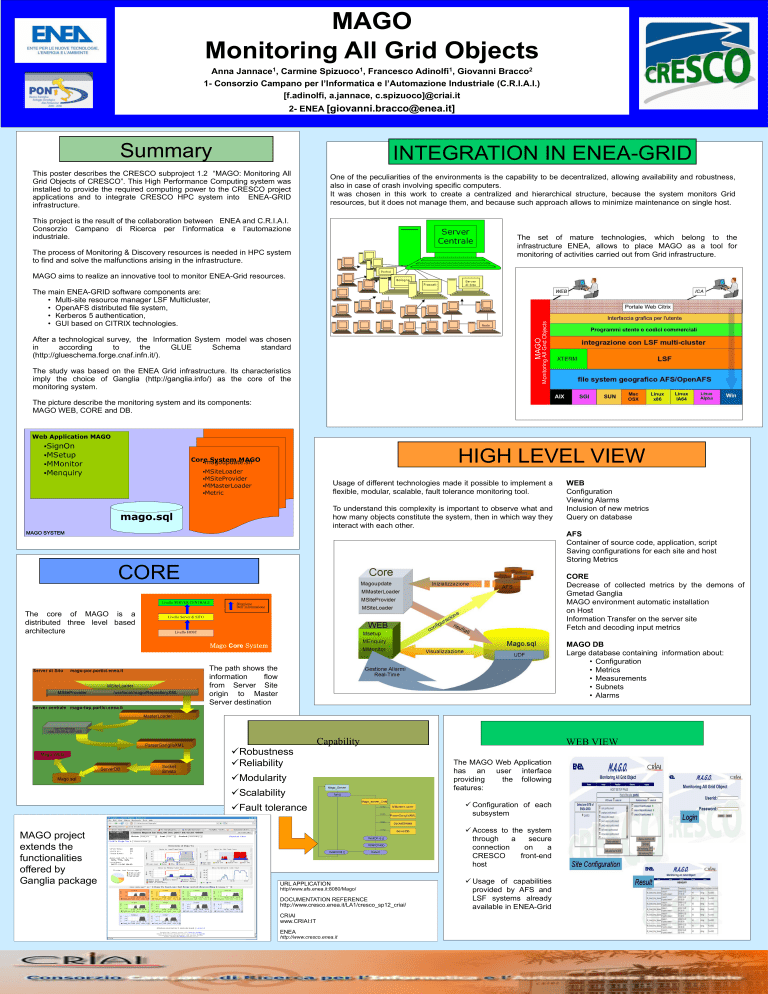
MAGO aims to realize an innovative tool to monitor ENEA-Grid resources.
The picture describe the monitoring system and its components:
MAGO WEB, CORE and DB.
Web Application MAGO
SignOn
MSetup
HIGH LEVEL VIEW
Core
System MAGO
magoupdate.sh
MMonitor
MSiteLoader
MSiteProvider
Menquiry
Usage of different technologies made it possible to implement a
flexible, modular, scalable, fault tolerance monitoring tool.
MMasterLoader
Metric
To understand this complexity is important to observe what and
how many objects constitute the system, then in which way they
interact with each other.
mago.sql
MAGO SYSTEM
AFS
Container of source code, application, script
Saving configurations for each site and host
Storing Metrics
CORE
Livello SERVER CENTRALE
The core of MAGO is a
distributed three level based
architecture
CORE
Decrease of collected metrics by the demons of
Gmetad Ganglia
MAGO environment automatic installation
on Host
Information Transfer on the server site
Fetch and decoding input metrics
Direzione
Dell’informazione
Livello Server di SITO
Livello HOST
MAGO DB
Large database containing information about:
• Configuration
• Metrics
• Measurements
• Subnets
• Alarms
Mago Core System
The path shows the
information
flow
from Server Site
origin to Master
Server destination
Robustness
Reliability
Capability
Modularity
Scalability
Fault tolerance
MAGO project
extends the
functionalities
offered by
Ganglia package
WEB
Configuration
Viewing Alarms
Inclusion of new metrics
Query on database
WEB VIEW
The MAGO Web Application
has an user interface
providing
the following
features:
Configuration of each
subsystem
Access to the system
through
a
secure
connection
on
a
CRESCO
front-end
host
URL APPLICATION
http//www.afs.enea.it:8080/Mago/
DOCUMENTATION REFERENCE
http://www.cresco.enea.it/LA1/cresco_sp12_criai/
CRIAI
www.CRIAI:IT
ENEA
http://www.cresco.enea.it
Usage of capabilities
provided by AFS and
LSF systems already
available in ENEA-Grid


![DAr2Ca [modalità compatibilità]](http://s1.studylibit.com/store/data/007526151_1-adc1d8764078d849ee8ba51d9b24710f-300x300.png)