Parte primaGrammatica di base della lingua inglese
Capitolo 4 I
pronomi personali
Sommario4.1 I pronomi personali soggetto. - 4.2 I pronomi personali complemento.
- 4.3 La posizione dei pronomi personali complemento.
4.1 I pronomi personali soggetto
Vengono utilizzati come soggetto di un verbo e devono sempre essere espressi, tranne
che nelle frasi coordinate alla principale; sono quelli elencati nello specchietto.
I
persona singolare
I
io
II persona singolare
you
tu
III persona singolare
he - she - it
egli - ella - lui - lei - esso/a
I
we
noi
II persona plurale
persona plurale
you
voi
III persona plurale
they
essi/e
• Il pronome di I persona singolare si scrive sempre con la lettera maiuscola: I. Quando
si accompagna a nomi o pronomi di altra persona, si colloca sempre per ultimo, come
forma di cortesia.
I live in Rome.
Io vivo / abito a Roma.
Paul and I went to the cinema last night. Paul e io siamo andati al cinema ieri sera.
• You è l’unico pronome per la II persona singolare e plurale, cosicché in italiano
corrisponde sia a «tu» che a «voi», ma equivale anche alla forma di cortesia «Lei».
Where do you go at weekend, John?
Where do you go at weekend, John
and Alan?
Dove vai / Dove va (Lei) per il weekend,
John?
John e Alan, dove andate per il weekend?
• La III persona singolare ha tre forme diverse: he per il maschile, she per il femminile, it per il neutro. He e she si possono usare anche per fare riferimento ad animali
(soprattutto domestici) rispettivamente di sesso maschile e femminile, mentre it si usa
per quelli di sesso indefinito, nonché per indicare le cose.
Martin is tired, he is in bed.
Martin è stanco, è a letto.
18
Parte prima Grammatica di base della lingua inglese
I can’t find Ann. Is she at home?
Non riesco a trovare Ann. È a casa?
It is a fantastic boat.
È un’imbarcazione fantastica.
We work for IBM.
Lavoriamo per l’IBM.
• We si utilizza in riferimento a un gruppo di persone, compresa quella che parla. Tale
pronome s’incontra spesso nel linguaggio scritto, quando l’autore intende coinvolgere
il lettore.
Come abbiamo visto a pagina 4…
As we saw on page 4…
• They è l’unico pronome che si adopera alla III persona plurale, sia essa maschile,
femminile o neutra.
Peter and Helen come from Dublin:
they are Irish.
Peter ed Helen vengono da Dublino: sono
irlandesi.
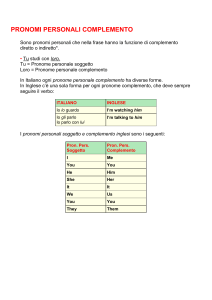
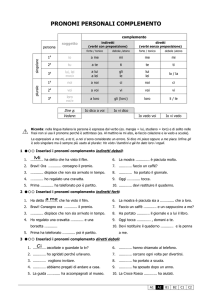
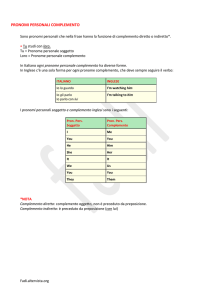
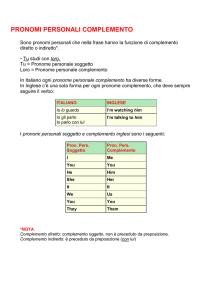
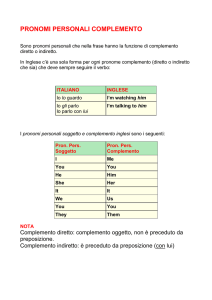
4.2 I pronomi personali complemento
Sono quelli indicati nello specchietto.
I persona singolare
me
me, mi
II persona singolare
you
te, ti
III persona singolare maschile him
lo, gli, lui
III persona singolare femminile
her
la, le, lei
III persona singolare neutra
it
lo, la, gli, le
I persona plurale
us
noi, ci, ce
II persona plurale
you
voi, vi, ve
III persona plurale
them
loro, essi/e, gli, li, le
Di norma si usano:
• come complemento oggetto (Follow me, please, Seguimi, per favore);
• come complemento di termine (George sent you these flowers, mummy, George ti
ha mandato questi fiori, mamma);
• dopo una preposizione (Peter lives here now, and Jane lives with him, Peter vive
qui ora, ­­e Jane vive con lui);
• dopo il verbo to be, nella forma impersonale con it, adoperata comunemente nell’inglese parlato (Who is it? It’s me, Chi è? Sono io).
4.3 La posizione dei pronomi personali complemento
I pronomi personali complemento seguono sempre il verbo, con il quale non si fondono
mai (I drink coffee: I drink it with milk, Io bevo caffè: lo bevo con il latte).
Capitolo 4 I pronomi personali
19
Quando è complemento di termine il pronome personale comunemente precede il complemento oggetto, e in tale posizione perde la preposizione to. Tuttavia, è possibile anche
collocarlo dopo il complemento oggetto, ma in questo caso deve essere preceduto da to.
I give him an apple. / I give an apple
Gli do una mela.
to him.
Se il complemento oggetto è un pronome, è meglio attenersi alla costruzione normale
(soggetto + verbo + complemento oggetto + complemento di termine), la quale va seguita anche quando il complemento di termine è più lungo del complemento oggetto,
oppure se si vuole dare maggiore enfasi al complemento di termine.
Give it to my Italian friend.
Dallo al mio amico italiano.
They explain the lesson to her.
Le spiegano la lezione.
Alcuni verbi, per lo più di origine latina, richiedono sempre il dativo con la preposizione
to, come avviene, ad esempio, per to explain (spiegare), to reply (rispondere), to say
(dire, affermare), to speak (parlare), to talk (chiacchierare, parlare). Con questi verbi,
qualora in una frase figurino sia il complemento oggetto che il complemento di termine,
si seguirà puntualmente la costruzione normale, per cui il primo precederà il secondo.
Parte secondaLe prove dei concorsi
1Ortografia, lessico,
morfologia e sintassi
Choose the best verb form to complete the following sentences
1) If I … a cake, will you bring some wine?
❏❏ A) will make
❏❏ B) make
❏ C) had made
❏ D) would be making
2) Would you like a coffee before … back to work?
❏❏ A) you go
❏❏ B) to go
❏ C) you had gone
❏ D) you will go
3) The bank usually … at 8.20.
❏❏ A) opens
❏❏ B) open
❏ C) opening
o D) is opening
4) By this time next week we … the new computer system.
❏❏ A) will have installed
❏❏ B) have installed
o C) will have been installing
o D) will installing
5) The notebook … in the office yesterday evening, but now it’s gone!
❏❏ A) aren’t
❏❏ B) was
o C) were
o D) be
6) Where did they all … after the party?
❏❏ A) go
❏❏ B) went
o C) gone
o D) going
184
Parte seconda Le prove dei concorsi
7) Whatever job you have, for your first days at work try to wear something
clean, smart and simple. You need to look as if you … an effort, even if the
actual job entails getting your hands and face dirty, or wearing overalls.
❏❏ A) are done
❏❏ B) are made
o C) have done
o D) have made
8) In the era of the European Union and of the single currency, … it still make
sense to maintain national boundaries?
❏❏ A) has
❏❏ B) does
o C) do
o D) is
9) Last month, 3.8 billion people … the Live8 concert.
❏❏ A) watched
❏❏ B) were viewed
o C) looked
o D) seen
10) The employees were told that they would receive a pay rise when the new budget …
❏❏ A) was being approved
❏❏ B) will be approved
o C) had been approved
o D) would be approved
11) Leading historian Robert Bryan called for an investigation into the contamination of the National Archives, after the “Daily Mirror” reported that forged
documents … in.
❏❏ A) had been smuggled
❏❏ B) were smuggling
o C) to be smuggled
o D) will have been smuggled
12) … last week that the Prime Minister had ordered the Home Secretary to limit
the cost of the new identity cards.
❏❏ A) it has been revealed
❏❏ B) it had revealed
o C) it was revealed
o D) they revealed it
13) Are these men really … for a single group?
❏❏ A) work
o C) works
❏❏ B) worked o D) working
14) If the accounts department … the error, we would have found ourselves in a
difficult situation.
❏❏ A) wouldn’t have noticed
❏❏ B) wouldn’t notice
o C) hadn’t noticed
o D) didn’t notice
1 Ortografia, lessico, morfologia e sintassi
185
15) He … in his office when the fire alarm went off.
❏❏ A) had worked
o C) was working
❏❏ B) has been workingo D) worked
16) I really like … to foreign countries.
❏❏ A) visit
❏❏ B) going
o C) seeing
o D) travel
17) It may be necessary to … taxes some time next year.
❏❏ A) raise
❏❏ B) hire
o C) rise
o D) heighten
18) They … us with stationery for the last ten years.
❏❏ A) supply
❏❏ B) could supply
o C) are supplying
o D) have been supplying
Choose the best word to complete the following sentences
19) … do you like your job?
❏❏ A) what
❏❏ B) where
o C) why
o D) who
20) I am no longer satisfied with my job, and I would really like to find something
more …
❏❏ A) attracting
❏❏ B) exhausting
o C) suited
o D) challenging
21) The insurance pays … the medical bills.
❏❏ A) every
❏❏ B) so
o C) a
o D) all
22) Are there … CDs in stock?
❏❏ A) a
❏❏ B) this
o C) of
o D) any
23) If the goods are faulty on arrival, you are entitled to receive a …
❏❏ A) reimburse
❏❏ B) repay
o C) refund
o D) return