Ipoglicemia
Come arginare
il problema
Giulio Marchesini
Malattie del Metabolismo e
Dietetica Clinica,
Università di Bologna
Disclosures
Giulio Marchesini
• Advisory Board: Sanofi, Roche
• Honoraria: Sanofi, Merck Sharp & Dome,
Novartis
• Clinical Studies: Boehringer Ingelheim,
Sanofi, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, GILEAD,
GENFIT, Jannsen
Hypoglycemia and emergency use
The estimated total cost of the
emergency call, initial
ambulance attendance and
treatment at scene was around
£650 000; if transport to
hospital was necessary, the
additional ambulance transport
costs were £223 000 plus
emergency department costs of
£140 000; and the cost of
primary care follow-up was
estimated as a further £61 000.
The average cost per emergency
call was £263.
By extrapolation, we estimate that, in the whole of England, the annual cost of treatment for
hypoglycemia by the ambulance service (excluding those aged < 1 year), which does not
include the costs of hospital admission, is in the order of £13.6m.
Farmer, Diabet Med 2012
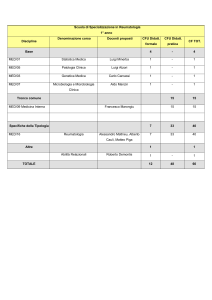
Proportion of
ED Visits Resulting in
Hospitalization
Annual National
Hospitalizations
(N = 99,628)
No
Most commonly implicated medications
%
Warfarin
Insulins
Oral antiplatelet agents
Oral hypoglycemic agents
Opioid analgesics
Antibiotics
Digoxin
Antineoplastic agents
Antiadrenergic agents
Renin–angiotensin inhibitors
Sedative or hypnotic agents
Anticonvulsants
Diuretics
33.3 (28.0–38.5)
13.9 (9.8–18.0)
13.3 (7.5–19.1)
10.7 (8.1–13.3)
4.8 (3.5–6.1)
4.2 (2.9–5.5)
3.5 (1.9–5.0)
3.3 (0.9–5.8)‡
2.9 (2.1–3.7)
2.9 (1.7–4.1)
2.5 (1.6–3.3)
1.7 (0.9–2.4)
1.1 (0.4–1.8)‡
Budnitz, NEJM 2011
33,171
3,854
13,263‡
10,656
4,778
4,205
3,465
3,329‡
2,899
2,870
2,469
1,653
1,071‡
(95%CI)
%
46.2
40.6
41.5
51.8
32.4
18.3
80.5
51.5
35.7
32.6
35.2
40.0
42.4
Length of stay and inpatient mortality of patients with diabetes who had an episode of
hypoglycaemia in a non critical care setting at University Hospital Birmingham, UK
148 admissions (2.3%) with severe hypoglycaemia (</= 2.2 mmol/l), 500 admissions
(7.8%) with mild to moderate hypoglycaemia (2.2-3.9 mmol/l) and 5726 admissions with
no recorded hypoglycaemic episode (> 3.9 mmol/l).
Conclusion: Hypoglycaemia is associated with increased length of stay and inpatient
mortality. Whilst causative evidence is lacking, our data are consistent with the need to
avoid hypoglycaemia in our current and continued approach for optimal glycaemic
control in people with diabetes admitted to hospital.
Nirantharakumar, Diabet Med 2012
ADA/EASD position statement:
DPP-4 inhibitors as 2nd or 3rd line treatment
Inzucchi SE, et al. Diabetes Care 2012;35:1364–79
Number of participants with severe
hypoglycemia (ACCORD Study)
A role for new drugs (incretins, gliptins, glifozins)?
Miller, BMJ 2010
Hypos & cardiovascular outcomes
ADVANCE study
Zoungas, N Engl J Med 2010
Hypos & cardiovascular outcomes
ADVANCE study
Zoungas, N Engl J Med 2010
New therapeutic targets
The patient in the lead
Tailored therapy
Inzucchi. Diabetologia. 2012
Ismail-Beigi . Ann Intern Med 2011
Tailored therapy
Diabetes Care, 2014
Start low e go slow
STENO-2: percentuale di pazienti a target
Gaede, NEJM 2003
CVD prevention in DM
Giorgino, Ann NY Acad Sci 2013
CVD prevention in DM
Giorgino, Ann NY Acad Sci 2013
Hypoglycemia and 5-yr mortality
Data 1020 DM from a diabetes clinic
Type 2 diabetes: n = 797
After 5 years, patients who reported
severe hypoglycemia had 3.4-fold higher
mortality (95% CI 1.5–7.4; P = 0.005)
compared with those who reported
mild/no hypoglycemia.
CONCLUSIONS
Self-report of severe hypoglycemia is
associated with 3.4-fold increased
risk of death. Patient-reported
outcomes, including patient-reported
hypoglycemia, may therefore augment
risk stratification and disease
management of patients with diabetes.
CCI: Charlson Comorbidity Index
McCoy, Diabetes Care 2012
Lipska, JAMA Intern Med 2014
Lipska, JAMA Intern Med 2014
Malnutrition, psychiatric diseases, dementia & functional disability are frequently associated
with hypoglycemia and poor outcome
Lipska, JAMA Intern Med 2014
Emergency Hospitalization for Adverse Drug Events
in Older Americans (65 years of age or older)
National Electronic Injury Surveillance System-Cooperative Adverse Drug Event Surveillance
40
%
33,3
Insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents are implicated in
about 25% of emergency hospitalizations for adverse
drug events
20
13,9
13,3
Insulin
Antiplatelet
agents
10,7
0
Warfarin
Proportion of emergency
department visits
resulting in
hospitalization
Budnitz, N Engl J Med 2011
46.2
40.6
41.5
Oral hypoglycemic
agents
51.8
Lombardo, PloS ONE 2013
Lombardo, PloS ONE 2013
Hospital admission rates for acute diabetic complications in Italy, 2001–2010.
Acute Diabetic Complications
N
Rate /100,000
Residents
Rate / 1000
Diabetics
Hypoglycemic coma
N
Rate /100,000
Residents
Rate / 1000
Diabetics
2001
32,096
56.3
14.4 (13.8–15.1)
1,794
3.1
0.81 (0.84–0.77)
2002
30,304
53.1
13.7 (13.1–14.3)
1,758
3.1
0.80 (0.76–0.83)
2003
30,072
51.7
13.5 (12.9–14.1)
1,615
2.8
0.72 (0.69–0.76)
2004
27,694
46.9
11.9 (11.3–12.4)
1,492
2.5
0.64 (0.61–0.67)
2005
26,861
44.7
11.0 (10.5–11.6)
1,466
2.4
0.60 (0.57–0.63)
2006
26,512
43.5
10.2 (9.7–10.7)
1,445
2.3
0.56 (0.53–0.58)
2007
25,177
40.7
9.3 (8.9–9.7)
1,463
2.3
0.54 (0.52–0.56)
2008
24,732
39.3
8.6 (8.3–9.0)
1,371
2.1
0.48 (0.46–0.50)
2009
22,052
34.5
7.7 (7.3–8.0)
1,275
1.9
0.44 (0.42–0.46)
2010
20,874
32.4
7.1 (6.8–7.4)
1,167
1.7
0.39 (0.38–0.41)
Lombardo, PloS ONE 2013
Geller, JAMA Intern Med 2014
NICE-Sugar study
Intensive treatment & outcome
Finfer. N Engl J Med 2009
Hypos and survival in critically ill pts
NICE-SUGAR study
In critically ill
patients,
intensive
glucose
control leads
to moderate
and severe
hypoglycemia,
both of which
are associated
with an
increased risk
of death
NICE-Sugar Study Investigators, N Engl J Med 2011
Hypoglycaemia in T2DM: A possible link to
increased CV risk/events
Possible mechanisms1,2
Hypoglycaemia as link to tissue ischaemia3
• Haemodynamic changes:
‒
Activation of autonomic nervous system
10–50 fold increased secretion of
adrenaline and noradrenaline
• ECG changes:
‒ Longer QT interval
‒ Hypokalaemia
• Haemorheological changes:
‒ Platelet activation
‒ Increased viscosity
*P <0.01 vs episodes during hyperglycaemia and
normoglycaemia
1Desouza
CV et al. Diabetes Care 2010;33:1389–94
TC et al. Diabetes 2003;52:1469–74
3Desouza C et al. Diabetes Care 03; 26:1485–9
2Robert
Episodes accompanied by
cardiac symptoms (%)
‒
20
15
*
*
10
5
0
Study of 72-h continuous glucose monitoring and simultaneous cardiac
Holter monitoring in patients with T2DM treated with insulin and history
of frequent hypoglycaemia and coronary artery disease (n=19)
54 episodes of hypoglycaemia reported (BGL <70 mg/dL)
59 episodes of hyperglycaemia reported (BGL >200 mg/dL)
Hsu, Diabetes Care 2013
Risk for severe hypoglycaemia
(incidence rate ratio)
Declining renal function increases risk of
severe hypoglycaemia
+ CKD
+ Diabetes
– CKD
+ Diabetes
+ CKD
– Diabetes
– CKD
– Diabetes
Around 74% of sulphonylurea-induced severe hypoglycaemic events
(loss of consciousness) occur in patients with reduced renal function
1. Moen MF, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Jun;4(6):1121–1127
RIFLESSIONI: trial di prevenzione CV
• Tutti i grandi trial di prevenzione CV degli ultimi 5-6 anni CON
QUALSIASI PROTOCOLLO hanno fallito (ACCORD, ADVANCE,
VADT, ORIGIN, NICE-SUGAR)
• Nella maggior parte dei casi si documenta un effetto negativo
dell’ipoglicemia (pazienti fragili), che aumenta il rischio CV
• Il rischio non era evidente negli studi più vecchi, con target
meno ambiziosi (Effetto LEGACY)
• Mortalità CV nei trial scesa da 3% a <1%: statine, antipertensivi,
rivascolarizzazione …..
• Come giungere ad un controllo ottimale senza ipoglicemia?
• Quali effetti questo potrebbe avere sul rischio CV?
• Quali regole?
Vantaggi/svantaggi degli inibitori del DPP-4
VANTAGGI
SVANTAGGI
• Ben tollerati
• Alto costo
• Basso rischio di ipolicemie
• Scarsi dati su uso
prolungato
• Efficacia simile ai vecchi
antidiabetici orali (dati AIFA:
HbA1c - 0.9%)
• Effetto neutro sul peso
• Associabili ad altre terapie
(anche insulina)
• Utilizzabili anche in IRC
• Maggiore efficacia su
glicemia post-prandiale
Vantaggi/svantaggi delle incretine
VANTAGGI
• Riduzione peso (dati AIFA: –
3.5 kg)
• Buona efficacia (dati AIFA:
HbA1c – 1.1%)
• Basso rischio di ipoglicemia
• Associabili ad altri farmaci
(anche insulina)
• Maggiore efficacia su
iperglicemia post-prandiale
• Potenziali effetti protettivi
sulla beta-cellula
SVANTAGGI
• Somministrazione iniettiva
• Alto costo
• Scarsi dati su uso
prolungato
• Effetti avversi (nausea,
vomito, diarrea)
Composite endpoints
DPP-4i & GLP-1a
Composite endpoints
DPP-4i & GLP-1a
Vantaggi/svantaggi degli SGLT2-inibitori
VANTAGGI
• Riduzione peso (3-5 kg)
• Buona efficacia (HbA1c –
1.1%)
• Basso rischio di ipoglicemia
• Associabili ad altri farmaci
(anche insulina)
• Maggiore efficacia su
iperglicemia post-prandiale
SVANTAGGI
• Scarsi dati su uso
prolungato
• Effetti avversi (infezioni vie
urinarie)
• Costo (?)
Phase III pooled efficacy data - Empaglifozin
Placebo corrected values
Canaglifozin – Effects on body weight
Cefalù, ADA Chicago 2013
Canaglifozin – Episodes of hypoglycemia
Cefalù, ADA Chicago 2013
Prevalenza e costi del DM farmaco-trattato:
periodo 1997-2012
Prevalenza 1997-2012 (15 anni): +70%
Documento regionale incretine
Aggiunta di 2° farmaco a metformina
Al 31 Dicembre 2013
Documento regionale incretine
Aggiunta di 2° farmaco a metformina
Al 31 Dicembre 2013
Documento regionale incretine
Cross da SULF a INCR
Aprile-Settembre 2013
Il paziente al centro
Personalised Medicine
“E’ molto più
importante sapere
che tipo di persona
ha una malattia
piuttosto che quale
malattia abbia una
certa persona
Ippocrate, 400 a.C.