Lesson 5
(A1/A2)
Present continuous
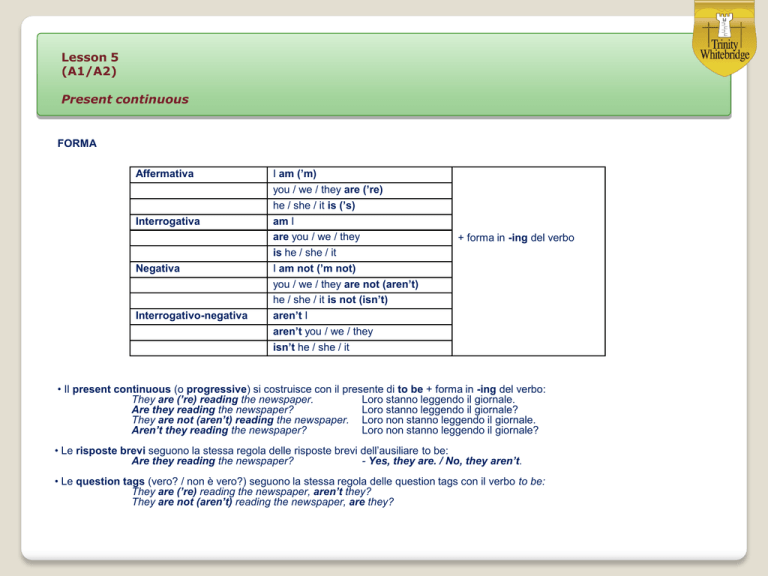
FORMA
Affermativa
Interrogativa
Negativa
Interrogativo-negativa
I am (’m)
you / we / they are (’re)
he / she / it is (’s)
am I
are you / we / they
is he / she / it
I am not (’m not)
you / we / they are not (aren’t)
he / she / it is not (isn’t)
aren’t I
aren’t you / we / they
isn’t he / she / it
+ forma in -ing del verbo
• Il present continuous (o progressive) si costruisce con il presente di to be + forma in -ing del verbo:
They are (’re) reading the newspaper.
Loro stanno leggendo il giornale.
Are they reading the newspaper?
Loro stanno leggendo il giornale?
They are not (aren’t) reading the newspaper. Loro non stanno leggendo il giornale.
Aren’t they reading the newspaper?
Loro non stanno leggendo il giornale?
• Le risposte brevi seguono la stessa regola delle risposte brevi dell’ausiliare to be:
Are they reading the newspaper?
- Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
• Le question tags (vero? / non è vero?) seguono la stessa regola delle question tags con il verbo to be:
They are (’re) reading the newspaper, aren’t they?
They are not (aren’t) reading the newspaper, are they?
Lesson 5
(A1/A2)
Present continuous
Quando si usa
Il present continuous si usa per parlare di:
• azioni in corso di svolgimento
What are you doing? - I’m having lunch.
Che cosa stai facendo? - Sto pranzando.
In questo caso è spesso accompagnato da espressioni di tempo come:
now
ora
at the moment
al momento
at present
attualmente
today
oggi
these days
in questi giorni
Mary is studying at the moment.
Mary sta studiando al momento.
Lesson 5
(A1/A2)
Present continuous
FORMA IN -ING
La forma in -ing (-ing form) si ottiene aggiungendo -ing alla forma base del verbo, ma ricorda che:
❖ nei verbi che terminano con -e muta, la e cade
arrive ➝ arriving
❖ i verbi monosillabi che terminano con una sola consonante preceduta da una sola vocale raddoppiano la consonante finale
stop ➝ stopping;
run ➝ running; cut ➝ cutting
❖ i verbi bisillabi che terminano con una consonante preceduta da una sola vocale accentata raddoppiano la consonante finale
begin ➝ beginning
❖ i verbi che terminano in -l preceduta da una sola vocale raddoppiano la l
travel ➝ travelling
❖ i verbi che terminano in -y mantengono la y ed aggiungono -ing
study ➝ studying;
play ➝ playing
❖ i verbi che terminano in -ie costruiscono la forma in -ing come segue:
die ➝ dying;
lie ➝ lying
Lesson 5
(A1/A2)
Present continuous
Confronta il diverso uso del present simple e del present continuous.
Present simple
Present continuous
azioni abituali, ripetute
(spesso con: always, usually, never, …)
John usually gets up early.
John di solito si alza presto.
azioni in corso di svolgimento
(spesso con: now, at the moment, at present, …)
John is getting up at the moment.
John si sta alzando in questo momento.
Attenzione!
Il present continuous
• si usa solo con i verbi di azione come:
get up, eat, drink, work, listen to, write, read, go, look at,
have breakfast/lunch/dinner, have a shower, have a swim, …
• non si usa con verbi di stato come:
like, love, hate, prefer, want, have (possesso), own, belong,
remember, forget, know, understand, …
EXERCISE 1
Costruiamo la forma in -ing dei seguenti verbi.
1. enjoy
6. stay
2. make
7. run
3. cry
8. sit
4. begin
9. study
5. travel
10. die
EXERCISE 2
A. Completiamo le seguenti frasi con la forma affermativa del present continuous.
1.
He (play) ……………………….. football.
2.
They (make) ………………………. a sandcastle.
3.
It (rain) ………………………. today.
4.
They (swim) ……………………… at the moment.
B. Ora trasformiamo le frasi in forma interrogativa, negativa, interrogativo-negativa.
1.
............................................................
............................................................
............................................................
2.
............................................................
............................................................
............................................................
3.
............................................................
............................................................
............................................................
4.
............................................................
............................................................
............................................................
EXERCISE 3
Immaginiamo questa situazione. La signora Campbell è al lavoro e i suoi figli sono a casa con la baby-sitter. La signora
Campbell telefona a casa e fa domande alla baby-sitter.
Costruiamo le domande usando i suggerimenti tra parentesi e completiamo le risposte anche con risposte brevi.
1.
A: (Ken / do / his homework / ?)
...................................................
B: No, ……………………… .
2.
A: (What / he / do / ?)
...................................................
B: He (watch) …………………….. TV.
3.
A: (the baby / sleep / ?)
...................................................
B: Yes, he …………………… .
4.
A: (What / Thelma and Julie / do / ?) ...................................................
B: They (do) ………………………………… their homework.
5.
A: (you / help / them / ?)
B: Yes, ……………………….. .
...................................................
EXERCISE 4
Completiamo questi mini-dialoghi con le question tags e le risposte brevi appropriate.
1.
A: John is sleeping, ………………….?
B: Yes, ………… .
2.
A: Mrs White is teaching at the moment, …………………?
B: No, ………… . It’s Saturday. She never teaches on Saturdays.
3.
A: You aren’t playing computer games, …………………?
B: No, ………… . I’m listening to music at the moment.
4.
A: They aren’t picking strawberries, ……………………?
B: No, ………… .
5.
A: They are having a good time in the mountains, …………………?
B: No, ………….. . Unfortunately, the weather is awful there these days.
EXERCISE 5
Present simple o present continuous?
Osserviamo queste frasi e riflettiamo: quali elementi ci fanno comprendere quale tempo verbale è corretto?
Sottolineiamo con il colore verde l’alternativa corretta e motiviamo la scelta.
1.
It is raining / rains heavily today.
2.
The sun shines / is shining at the moment.
3.
Tom is playing / plays the piano in his free time.
4.
Frank usually wears / is wearing jeans and a pullover.
5.
Kevin is in the sitting room. He is watching / watches TV.
6.
The sun is rising / rises in the east.