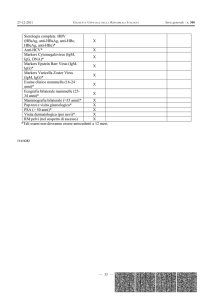
HERPES S.V. tipo 1 IgG
EIA WELL
REF KH1G
96
REF KH1GB
192
Italiano
English
p.
p.
3
11
REAGENTI DEL KIT - KIT REAGENTS
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 1/24
Reag.
MTP
WASH
DIL
NEG
POS
C/O
CONJ
TMB
STOP
Quant.
KH1G
1 x 96
Stato fisico,
Physical state
KH1GB
2 x 96
Pronti per l'uso,
Ready for use
1 x 50 mL 2 x 50 mL Conc.
1 x 20 mL 2 x 20 mL Conc.
1 x 2 mL
1 x 2 mL
1 x 2 mL
1 x 2 mL
1 x 2.5 mL 1 x 2.5 mL
1 x 14 mL 2 x 14 mL
2 x 15 mL 2 x 15 mL
1 x 14 mL 2 x 14 mL
Pronto per l'uso,
Ready for use
Pronto per l'uso,
Ready for use
Pronto per l'uso,
Ready for use
Pronto per l'uso,
Ready for use
Pronto per l'uso,
Ready for use
Pronto per l'uso,
Ready for use
"Le Istruzioni per l'uso tradotte nelle altre lingue di interesse sono consultabili sul sito
Internet all'indirizzo www.radim.com".
“The instructions for use available in the other languages of interest can be viewed on our
website www.radim.com".
“Οι οδηγίες χρήσης μεταφρασμένες στις άλλες ενδιαφερόμενες γλώσσες όπως επίσης στην
ηλεκτρονική διεύθυνση www.radim.com".
“In den anderen Sprachen von Interesse ist die Bedienungsanleitung kann auf der Website
unter der Adresse www.radim.com konsultiertwerden”.
"Le mode d’emploi dans les autres langues intéressées est consultable sur le site Internet à
l'adresse www.radim.com”.
“Las instrucciones de uso traducidas en los otros idiomas de interés se pueden consultar en
nuestro sitio Internet www.radim.com”.
"As instruções de uso traduzidas nos outros idiomas de interesse podem ser consultadas
no nosso site Internet, ao endereço www.radim.com."
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 2/24
DOSAGGIO IMMUNOENZIMATICO PER LA DETERMINAZIONE QUALITATIVA
DEGLI ANTICORPI IgG ANTI-HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS TIPO 1 NEL SIERO O
PLASMA UMANO.
PER USO DIAGNOSTICO IN VITRO
1. APPLICAZIONI CLINICHE
L'Herpes Simplex Virus, il Citomegalovirus, il Virus Varicella Zoster e l'Epstein
Barr Virus, appartengono tutti alla famiglia dei virus erpetici. Si conoscono due tipi
di Herpes Simplex con caratteristiche antigeniche alcune comuni e altre
specifiche:
− Herpes Simplex Virus Tipo 1 (HSV-1): localizzato sulle zone orbitali e
orolabiali;
− Herpes Simplex Virus Tipo 2 (HSV-2): responsabile di patologie dell'apparato
genitale maschile e femminile.
La patogenicità si trasmette per contatto diretto o indiretto e per via sessuale. I
quadri clinici sono tipici e vanno dall'Herpes labialis all'eczema erpetico fino alle
forme più gravi di Herpes genitale e malattie erpetiche congenite, acquisite dal
feto prima della nascita e a carico del virus di tipo 2. Gli anticorpi della classe IgM
anti-HSV appaiono entro 1 settimana dall'inizio della malattia persistendo anche
per diversi mesi. Dopo una decina di giorni compaiono gli anticorpi della classe
IgG che rimangono evidenziabili anche per anni, talvolta con variazioni del titolo
conseguenti a reinfezioni o riattivazioni del virus dallo stato latente.
Le indagini sierologiche di laboratorio più comuni per la determinazione degli
anticorpi anti-HSV sono il test di neutralizzazione, l'immunofluorescenza (indiretta
o diretta), la fissazione del complemento ed i test immunoenzimatici ELISA per
IgG ed IgM.
2. PRINCIPIO DEL METODO
Il presente kit è basato sul metodo immunoenzimatico (ELISA) ed utilizza come
marcatore enzimatico la perossidasi.
Durante la prima incubazione, gli anticorpi anti-HSV 1 della classe IgG
eventualmente presenti nel siero in esame, si legano all'antigene HSV 1 adeso
alla superficie dei pozzetti.
Tramite lavaggio viene eliminato il materiale non legato; in una successiva
incubazione gli anticorpi anti-IgG umane, coniugati alla perossidasi, reagiscono
con il complesso precedentemente formatosi tra antigene ed anticorpo anti-HSV1.
Dopo ulteriore lavaggio viene aggiunta tetrametilbenzidina (TMB) incolore che
reagendo con la perossidasi presente, produce un composto colorato. La
reazione di sviluppo del colore è bloccata con l'aggiunta di H2SO4 e l'intensità del
colore, misurata mediante spettrofotometro a 450 e a 405 nm, è direttamente
proporzionale alla concentrazione di anticorpi IgG anti-HSV 1 presenti nei controlli
e nei campioni in esame.
3. REAGENTI CONTENUTI NEL KIT: PREPARAZIONE E STABILITA'
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 3/24
− I reagenti sono sufficienti per 96 pozzetti (REF KH1G) o per 192 pozzetti
(REF KH1GB).
− Il kit deve essere conservato a 2-8°C.
− La data di scadenza di ciascun reagente è indicata sulla rispettiva etichetta.
− Una volta aperto il kit è stabile 2 mesi a 2-8°C.
3.1 Reagenti Specifici
•
MTP Micropiastra Sensibilizzata: 1 o 2 micropiastre da 96 pozzetti
ciascuna divisibili singolarmente, sensibilizzati con estratto di antigene
Herpes Simplex Virus tipo 1 purificato ed inattivato. I pozzetti non utilizzati
devono essere conservati a 2-8°C nella bustina di plastica trasparente
fornita, sigillata accuratamente.
•
POS Controllo Positivo: matrice sierica reattiva per IgG anti-HSV tipo 1.
Conservante: NaN3 (<0.1%). Pronto per l'uso.
•
C/O Controllo Cut-off: matrice sierica reattiva per IgG anti-HSV tipo 1.
Conservante: NaN3 (<0.1%). Pronto per l'uso e colorato in azzurro.
•
CONJ Coniugato Enzimatico: anticorpi monoclonali (topo) anti-IgG
umane, coniugati con perossidasi di rafano (HRPO) in matrice sierica e
stabilizzanti. Conservante: Neomicina. Pronto per l'uso e colorato in rosa.
3.2
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Reagenti Comuni per i kit delle Linee To.R.C.H.–M.S.T., Malattie
dell’infanzia, Patologia Gastroenterica e Morbo Celiaco
WASH Soluzione di Lavaggio (concentrata): PBS-Tween-20.
Conservante: Mertiolato (<0.05%). Al momento dell'uso diluire la quantità
necessaria 1:20 con H2O distillata. Nel caso siano presenti cristalli insoluti,
risospenderli ponendo il flacone a 37°C per qualche minuto. Dopo diluizione
il tampone di lavaggio è stabile 30 giorni a 2-8°C.
DIL Diluente dei Campioni (concentrato): matrice sierica e stabilizzanti,
colorato in rosso. Conservante: NaN3 (<0.1%). Al momento dell'uso diluire
1:20 con la soluzione di lavaggio già diluita. Il diluente così preparato è
stabile 30 giorni a 2-8°C.
NEG Controllo Negativo: matrice sierica non reattiva per IgG anti-HSV tipo
1. Conservante: NaN3 (<0.1%). Pronto per l'uso e colorato in rosso.
TMB Cromogeno: Tetrametilbenzidina (TMB) in tampone citrato-fosfato,
DMSO e H2O2. Pronto per l’uso.
STOP Reagente Bloccante: H2SO4 1N. Pronto per l'uso.
CPA Copripiastra adesivo
Bustina di plastica trasparente con minigrip
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 4/24
4. MATERIALE NECESSARIO MA NON FORNITO
4.1 Dosaggio Manuale
− Micropipette automatiche a puntali intercambiabili a volume variabile.
− Stufa termostatata a 37±2°C.
− Cilindri graduati per la diluizione dei reattivi.
− Pompa aspirante oppure apparecchiatura automatica per il lavaggio delle
micropiastre.
− Spettrofotometro di precisione per micropiastre, con possibilità di misura in
assorbanza nell'intervallo 0-3.0 A ad una lunghezza d'onda di 450 e 405 nm.
− H2O distillata.
4.2 Dosaggio Automatico
− Il dispositivo può essere utilizzato con strumentazione automatica di kit ELISA
su micropiastra.
− Si garantisce l’applicabilità su strumentazione RADIM e/o SEAC
− Qualora si utilizzi strumentazione automatica di altri fornitori, è responsabilità
dell’utilizzatore assicurarsi che il kit sia stato opportunamente validato.
5. AVVERTENZE E PRECAUZIONI
Per ottenere risultati corretti e riproducibili, è necessario osservare le
seguenti norme:
− Non mescolare i reagenti specifici (vedi 3.1) di lotti differenti.
− E’ possibile utilizzare reagenti comuni (vedi 3.2) di lotti differenti.
− Non usare i reagenti dopo la data di scadenza.
− Non esporre i reattivi e i campioni a calore intenso o a forti sorgenti di
inquinamento.
− Usare vetreria perfettamente pulita ed esente da contaminazioni di ioni
metallici o sostanze ossidanti.
− Usare acqua distillata o deionizzata, conservata in recipienti perfettamente
puliti.
− Evitare accuratamente contaminazioni tra campioni; a tal fine è consigliabile
usare pipette con puntali monouso per ogni campione e per ogni reattivo.
− Non modificare in alcun modo il Procedimento Operativo di esecuzione del
test. Eventuale non rispetto di:
•
sequenza e quantità nell’aggiunta dei reattivi
•
tempi e temperatura di incubazione
può dare luogo a risultati clinici errati.
− Ricostituire gli eventuali reagenti liofili secondo le modalità descritte sulle
etichette. Eventuale utilizzo di reattivi o volumi non idonei, può provocare
l’ottenimento di dati clinici non attendibili.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 5/24
− In caso di procedura manuale è importante l’utilizzo di pipette calibrate e
possedere un’adeguata manualità tecnica. In particolare è essenziale una
buona precisione nella preparazione e dispensazione dei reattivi. E’
necessario un adeguato piano di manutenzione (pulizia e calibrazione) di tale
strumentazione.
− Assicurarsi che la pompa di aspirazione oppure l’apparecchiatura automatica
per il lavaggio delle micropiastre sia perfettamente funzionante. Un lavaggio
non accurato delle micropiastre può dare luogo a misclassificazione dei
campioni. E’ necessario un adeguato piano di manutenzione di tale
strumentazione.
− Assicurarsi che lo spettrofotometro per micropiastre sia perfettamente
funzionante. L’utilizzo di uno spettrofotometro non calibrato o con filtri non
puliti, può comportare un errore nella lettura dei campioni, con conseguente
possibile misclassificazione degli stessi. E’ necessario un adeguato piano di
manutenzione (pulizia e calibrazione) di tale strumentazione.
− Assicurarsi che la stufa termostatata (se necessaria) sia perfettamente
funzionante. L’incubazione a temperature diverse da 37±2°C può dare luogo a
perdita di sensibilità e/o a denaturazione biologica dei materiali (reattivi e/o
campioni). E’ necessario un adeguato piano di manutenzione di tale
strumentazione e un controllo periodico della temperatura registrata.
− Assicurarsi che l’agitatore per micropiastre (se necessario) sia perfettamente
funzionante. L’agitazione in condizione diverse dall’atteso può dare luogo a
misclassificazione dei campioni . E’ necessario un adeguato piano di
manutenzione di tale strumentazione.
− Assicurarsi che la strumentazione utilizzata per la conservazione dei campioni
e/o del dispositivo sia perfettamente funzionante. La conservazione a
temperature diverse dall’atteso, può dare luogo a denaturazione biologica dei
materiali (reattivi e/o campioni). E’ necessario un adeguato piano di
manutenzione di tale strumentazione e un controllo periodico della
temperatura registrata.
− Utilizzare un adeguato metodo per la corretta identificazione dei campioni.
Possibili conseguenze possono essere sia la perdita di specificità del
dispositivo che risultati analitici errati.
Per evitare contaminazioni personali ed ambientali, è necessario osservare
le seguenti norme di sicurezza:
− Utilizzare guanti monouso durante la manipolazione di materiale
potenzialmente infetto e durante il dosaggio.
− Non pipettare i reagenti con la bocca.
− Non fumare, mangiare, bere o applicare cosmetici durante l'esecuzione del
dosaggio.
− Le soluzioni di Cromogeno e Reagente Bloccante vanno manipolate con
cautela. Evitare il contatto con la pelle, gli occhi e le mucose. In caso di
incidente lavare abbondantemente con acqua.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 6/24
− I materiali di origine umana utilizzati nella preparazione del presente kit sono
stati saggiati per la presenza di HBsAg, anti-HIV e anti-HCV e sono risultati
ripetutamente negativi. Comunque nessun test attualmente disponibile
garantisce l'assenza degli agenti virali responsabili della sindrome da
immunodeficienza acquisita, dell'epatite B ed epatite C. Tutti i reagenti
contenenti materiale biologico e tutti i campioni di siero umano devono essere
considerati potenzialmente infettivi.
− Evitare la produzione di schizzi e la formazione di aerosol; qualora ciò si
verificasse ripulire accuratamente con ipoclorito di sodio ad una
concentrazione del 3%. Il mezzo adoperato per la pulizia deve essere trattato
come residuo potenzialmente infetto ed eliminato secondo le modalità
opportune.
− La sodio azide contenuta come conservante in alcuni reagenti, può reagire con
il piombo ed il rame delle tubature formando azidi di metallo altamente
esplosive. Per evitare l formazione e l'accumulo di tali composti far scorrere
abbondante acqua sui reagenti eliminati.
− Ai sensi del D.L. italiano n. 22 del 05.02.97, che fa riferimento alle direttive
CEE (91/156/CEE, 91/689/CEE, 94/62/CEE) tutti i rifiuti provenienti da
lavorazioni manuali e/o in automatico sono classificati rifiuti speciali pericolosi
con codice di classificazione CER 180103; devono quindi essere eliminati
affidandoli a ditte autorizzate al ritiro ed allo smaltimento.
6. RACCOLTA E PREPARAZIONE DEI CAMPIONI
Il dosaggio può essere effettuato su siero o plasma umano. Campioni
moderatamente lipemici non influenzano i risultati del dosaggio; campioni
fortemente lipemici o emolizzati possono alterare i risultati. La presenza di
filamenti di fibrina può interferire nel dosaggio; assicurarsi pertanto che i campioni
siano perfettamente limpidi prima di dosarli. I campioni possono essere conservati
per un periodo non superiore ad una settimana se correttamente mantenuti a 28°C, a-20°C per tempi più lunghi. Si consiglia di non congelare e scongelare
ripetutamente i campioni.
Prima dell'uso, diluire i campioni 1:300 con il Diluente dei Campioni
precedentemente preparato (es. 10 µL di campione + 2990 µL di diluente).
7. PROCEDIMENTO OPERATIVO *
− Attendere che i reagenti ed i campioni raggiungano la temperatura ambiente.
− Agitare i campioni per inversione prima dell'uso.
7.1
Preparare i pozzetti necessari al dosaggio, prevedendo la determinazione in
duplicato per i Sieri di Controllo ed in singolo per il Bianco ed i Campioni.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 7/24
7.2
Dispensare 100 µL dei Sieri di Controllo e Campioni precedentemente
diluiti, nei rispettivi pozzetti.
N.B.: i Sieri di Controllo non devono essere diluiti.
7.3 Dispensare 100 µL di Diluente Campioni diluito nel pozzetto del Bianco.
7.4 Incubare per 60±5 minuti a 37±2°C, coprendo la micropiastra con il
copripiastra adesivo fornito nel kit.
7.5 Effettuare 4 lavaggi con un volume di 350 µL per pozzetto, impiegando la
Soluzione di Lavaggio diluita. Aspirare accuratamente il liquido da tutti i
pozzetti.
7.6 Dispensare 100 µL di Coniugato Enzimatico in tutti i pozzetti.
7.7 Incubare per 30±2 minuti a 37±2°C, coprendo la micropiastra con il
copripiastra adesivo fornito nel kit.
7.8 Lavare i pozzetti come al punto 7.5.
7.9 Dispensare 100 µL di Cromogeno in tutti i pozzetti.
7.10 Incubare per 10 minuti a 37±°C o 15 minuti a temperatura ambiente
(18-25°C), al riparo dalla luce.
7.11 Dispensare 100 µL di Reagente Bloccante in tutti i pozzetti.
7.12 Leggere la densità ottica delle soluzioni a 450 nm in uno spettrofotometro
preferibilmente bicromatico con lunghezza d'onda di riferimento a 620 nm
(azzerando lo strumento con il Bianco). Nel caso di estinzione in overflow,
utilizzare la lettura spettrofotometrica a 405 nm. La lettura deve essere
effettuata entro 15 minuti dal termine del dosaggio.
* Qualora si utilizzasse nel procedimento operativo uno strumento automatico per
micropiastre RADIM E/O SEAC, far riferimento al relativo manuale.
8. SCHEMA DEL DOSAGGIO: vedi p. 23
9. CALCOLO DEI RISULTATI *
Considerare la densità ottica di ciascun controllo negativo, cut-off e positivo.
Confrontando la densità ottica dei campioni con la densità ottica del controllo cutoff (valore soglia) si determina la reattività o non reattività verso gli anticorpi IgG
anti-HSV tipo 1.
I campioni con valori di densità ottica inferiori a quello relativo al controllo cut-off
sono da considerare non reattivi per gli anticorpi IgG anti-HSV tipo 1. Campioni
con valori di densità ottica superiori al controllo cut-off sono da considerare reattivi
per gli anticorpi IgG anti-HSV tipo 1. I campioni con valori di densità ottica
compresi tra il controllo cut-off ± 10% sono da considerare di incerta
interpretazione e devono pertanto essere ridosati.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 8/24
* Nel caso si utilizzi uno strumento automatico per micropiastre RADIM E/O
SEAC, la lettura spettrofotometrica è eseguita automaticamente a 3 lunghezze
d'onda: 450, 405 e 620 nm, permettendo l'ampliamento del range di lettura.
9.1 Esempio di Calcolo
I valori sotto riportati debbono essere considerati unicamente un esempio e non
devono essere utilizzati in luogo dei dati sperimentali.
Descrizione
D.O. 450 nm
Controllo Negativo
0.082
Controllo Cut-off
0.504
Controllo Positivo
1.992
Campione
0.889
Il campione dosato risulta essere positivo agli anticorpi IgG anti-HSV tipo 1.
9.2 Criteri di Accettazione
Prima di procedere al calcolo dei risultati verificare che le assorbanze dei controlli
rispettino i seguenti valori:
Descrizione
Valore atteso
Controllo Negativo
< 0.200
Controllo Positivo
> 0.700
Se i valori ottenuti non rispecchiano quelli attesi, è necessario ripetere il dosaggio.
9.3 Interpretazione dei Risultati
− I campioni non reattivi sono da considerare negativi per gli anticorpi IgG antiHSV tipo 1.
− I campioni reattivi sono da considerare positivi per gli anticorpi IgG anti-HSV
tipo 1.
− I campioni di incerta interpretazione devono essere dosati nuovamente per
conferma.
Successivi prelievi dello stesso paziente possono essere comparati tra loro solo
se inseriti nello stesso dosaggio; in questo caso un aumento del 60% della
densità ottica del secondo campione può essere considerato come significativo di
una infezione recente od in atto. Si consiglia in tal caso, la ricerca delle IgM
specifiche.
10. CARATTERISTICHE METODOLOGICHE
10.1 Specificità Diagnostica
La specificità diagnostica del metodo è stata valutata su un campione
rappresentativo di soggetti non immuni da infezione di HSV tipo 1, risultando pari
a 100%.
10.2 Sensibilità Diagnostica
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 9/24
La sensibilità diagnostica del metodo è stata valutata su un campione
rappresentativo di soggetti con infezione pregressa da HSV tipo 1, risultando pari
a 97.6%.
10.3 Precisione
La precisione é stata valutata misurando la ripetibilità e la riproducibilità
(variabilità intra-saggio ed inter-saggio) su 3 sieri a differenti concentrazioni di IgG
anti-HSV tipo 1.
Ripetibilità (Intra-saggio)
Siero
Media
a
b
c
570
1027
2718
±
(D.O. 450 nm)
±
±
±
D.S.
27.6
63.5
103.6
C.V.
%
4.8
6.2
3.8
Replicati
n.
12
12
12
C.V.
%
13.8
15.3
11.1
Dosaggi
n.
10
10
10
Riproducibilità (Inter-saggio)
Siero
Media
a
b
c
0.431
1.870
3.547
±
(D.O. 450 nm)
±
±
±
D.S.
59.8
286
397
11. LIMITI DEL DOSAGGIO
E' da tenere presente che, per definire lo stato immunitario di un paziente verso
l'HSV, la presenza di anticorpi di tipo IgG a qualsiasi livello non esclude la
possibilità di un'infezione in atto, mentre il dosaggio degli anticorpi specifici di tipo
IgM si rivela di fondamentale importanza per la diagnosi precoce dell'infezione
acuta.
Un tempestivo intervento in caso di malattia in atto, permette di ridurre
notevolmente i rischi che ne conseguono.
Comunque i risultati del dosaggio devono essere interpretati con cautela e
convalidati da valutazioni cliniche ed ulteriori prove diagnostiche.
12. LEGENDA SIMBOLI: vedi p. 20
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 10/24
ENZYME IMMUNOASSAY FOR QUALITATIVE DETECTION OF ANTI-HERPES
SIMPLEX VIRUS IgG ANTIBODIES TYPE 1 IN HUMAN SERUM OR PLASMA.
FOR IN VITRO DIAGNOSTIC USE ONLY
1. CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
Herpes Simplex, Cytomegalovirus, Varicella Zoster and Epstein Barr Virus, all
belong to the Herpes Viruses family.
Two kinds of Herpes Simplex are known, with some common and some specific
antigenic characteristics.
− Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1): localized on the orbital and labial
regions.
− Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2): responsible for pathologies of male and
female reproductive organs.
This Virus has a considerable pathogenic capacity; transmission occurs by direct
or indirect contact and by venereal transmission. Clinical manifestations are
Herpes labialis, herpetic eczema up to the most serious forms of Herpes genitalis
and congenital diseases, contracted by the fetus during pregnancy (mainly
caused by type 2 Virus).
Anti-HSV IgM antibodies appear within 1 week from the disease onset, persisting
for several months. IgG class antibodies appear about ten days from the infection
and may be evidenced for years thereafter, sometimes with titer fluctuations due
to re-infections or re-activation of the latent virus.
The most common serological tests for the detection of HSV antibodies are: the
neutralization test, immunofluorescence (direct or indirect) and ELISA enzyme
immunoassays for IgG and IgM.
2. PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This kit is based upon an enzyme immunoassay method (ELISA), where
horseradish peroxidase is used as enzyme conjugate. During the first incubation,
the sample anti-HSV 1 IgG antibodies, if any, are bound to the HSV 1 antigen
coated wells. A wash cycle eliminates all unbound material. In the incubation that
follows, a second antibody (anti-human IgG conjugated with horseradish
peroxidase) will bind to the HSV 1-antigen-antibody complex. After a further wash
cycle a colorless Chromogen solution (tetramethylbenzidine, TMB) in a substratebuffer is added to the wells, where it yields a colored compound, by reacting with
the peroxidase enzyme. Color development will be stopped by adding H2SO4. The
color intensity, measured in a spectrophotometer at 450 and 405 nm, will thus be
directly proportional to the anti-HSV 1 IgG antibody concentration in controls and
samples.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 11/24
3. REAGENTS PROVIDED WITH THE KIT: PREPARATION AND STABILITY
− The reagents are sufficient for 96 wells (REF KH1G) or for 192 wells
(REF KH1GB).
− Store the kit at 2-8°C.
− The expiry date of each reagent is shown on the vial label.
− Once opened, the kit is stable at 2-8°C for 2 months.
3.1 Specific Reagents
•
MTP Coated Microplate: 1 or 2 microplates for 96 breakable wells each,
coated with purified and inactivated Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 antigen
extract. Keep unused wells at 2-8°C in the provided plastic bag and
accurately sealed.
•
POS Positive Control: serum matrix reactive for anti-HSV type 1 IgG.
Preservative: NaN3 (<0.1%). Ready for use.
•
C/O Cut-Off Control: serum matrix reactive for anti-HSV type 1 IgG.
Preservative: NaN3 (< 0.1%). Ready for use and blue-colored.
•
CONJ Enzyme Conjugate: mouse monoclonal anti-human IgG with
horseradish peroxidase (HRPO) in serum matrix with stabilizers.
Preservative: Neomycin. Ready for use and pink-colored.
3.2
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Common Reagents for kits of the following Lines: To.R.C.H.–S.T.D.,
Child Disease, Gastroenteric Disease and Celiac Disease
WASH Washing Solution (concentrated): PBS-Tween 20. Preservative:
Thimerosal (<0.05%). Just before use, dilute the needed amount 1:20 with
distilled H2O. In case of undissolved crystals, re-suspend the solution by
placing the vial at 37°C for a few minutes. Store the diluted Washing
Solution for 30 days at 2-8°C.
DIL Sample Diluent (concentrated): serum matrix and stabilizers, redcolored. Preservative: NaN3 (<0.1%). Just before use, dilute 1:20 with the
previously diluted Washing Solution. Store the diluted Sample Diluent for
30days at 2-8°C.
NEG Negative Control: serum matrix non-reactive for anti-HSV type 1 IgG.
Preservative: NaN3 (< 0.1%). Ready for use and red-colored.
TMB Chromogen: Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) with citrate-phosphate
buffer, DMSO and H2O2. Ready for use.
STOP Blocking Reagent: 1N H2SO4. Ready for use.
CPA Adhesive plate sealers
Plastic bag
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 12/24
4. MATERIAL REQUIRED BUT NOT SUPPLIED
4.1 Manual Test
− Adjustable, automatic micropipettes with disposable tips.
− Dry Heater, adjustable at 37±2°C.
− Graduated cylinders for reagent dilution.
− Aspiration pump or automated well washing device.
− Microplate spectrophotometer capable of measuring absorbances within a 03.0 A interval at 450 nm and 405 nm.
− Distilled H2O.
4.2 Automatic Test
− This test can be used with automatic instrument for ELISA kits on microplate.
− We guarantee its applications on RADIM and/or SEAC automatic instruments.
− While using a non RADIM or SEAC automatic instrument for microplate, it is
under end user responsibility, to make sure that it was appropriately tested for
ELISA kits.
5. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
In order to obtain correct and reproducible results, the following rules must
be observed:
− Do not mix specific reagents (see 3.1) from different lots.
− It is possible to mix common reagents (see 3.2) from different lots.
− Do not use reagents beyond their expiry date.
− Do not store or leave reagents and samples at high temperatures or areas of
possible contamination.
− Use thoroughly clean glassware, free from metal ion contamination or oxidizing
substances.
− Use distilled or deionized water, stored in perfectly clean containers.
− Carefully avoid any contamination among samples; for this purpose,
disposable tips should be used for each sample and reagent.
− Do not modify in any way the "Assay Procedure". If you not respect:
•
exact incubation times and quantities adding the reagents
•
incubation times and temperature
may cause incorrect clinical results.
− Reconstitute lyophilized reagents, if present, as described on the relative
labels. Any deviation in reagent use or wrong volumes, may affect the reliability
of results obtained.
− In case of manual procedure, it is important to use calibrated pipettes and
have appropriate technical manuals. Primary importance is a good precision
preparing and dispensing the reagents. Ensure that all the equipment used is
in perfect working order, has been correctly calibrated and is regularly
maintained.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 13/24
− Ensure that the aspiration pump or automated well washing device is in perfect
working order. Inadequate rinsing of wells may cause an incorrect samples
classifications. Ensure that all the equipment used is in perfect working order.
− Ensure that the microplate spectrophotometer is in perfect working order. The
use of a not calibrated spectrophotometer or not clean filters may cause a
wrong reading samples with consequent incorrect samples classifications.
Ensure that all the equipment used is in perfect working order.
− Ensure that the dry heater (if necessary) is in perfect working order. The
incubation temperature different from 37±2°C may cause a sensitivity losses
and/or biological denaturation (samples and/or reagents). Ensure that the
equipment used is in perfect working order and periodically check the recorded
temperature.
− Ensure that the microplate shaker (if necessary) is in perfect working order.
Incorrect agitation may cause wrong samples classifications. Ensure that the
equipment used is in perfect working order.
− Ensure that all the equipment used for samples storage and/or the system is in
perfect working order. The storage at different suggested temperature may
cause biological material denaturation (samples and/or reagents). Ensure that
the equipment used is in perfect working order and periodically check the
recorded temperature.
− Utilise a suitable method for the correct identification of patient samples.
Incorrect identification may cause a specificity losses of the system and wrong
clinical results.
In order to avoid personal and environmental contamination, the following
precautions must be observed:
− Use disposable gloves while handling potentially infectious material and while
performing the assay.
− Do not pipette reagents by mouth.
− Do not smoke, eat, drink or apply cosmetics during the assay.
− Chromogen and Blocking Reagent should be handled with care. Avoid contact
with skin, eyes and mucous membranes. In case of accident rinse thoroughly
with running water.
− All material of human origin used for the preparation of this kit tested negative
for HBsAg, anti-HIV and anti-HCV. Since no test at present can guarantee
complete absence of these viruses, all samples and reagents containing
biological material used for the assay must be considered potentially
infectious.
− Avoid splashing and aerosol formation; in such cases, carefully wash with a
3% sodium hypochlorite solution. Any such cleaning material must be treated
as potentially infectious and disposed of accordingly.
− Some reagents contain sodium azide as preservative; to prevent build-up of
explosive metal azides in lead and copper plumbing, reagents should be
discarded by flushing the drain with large amounts of water.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 14/24
− According to Italian decree D.L. no. 22 dated 05.02.97, in compliance with
EEC directives (91/156/EEC, 91/689/EEC, 94/62/EEC), all waste products
originating from either manual and/or automated processing are classified as
hazardous special waste material (European classification code180103). As
such, they must be eliminated by delegating to special enterprises, qualified for
waste collection and disposal.
6. SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND PREPARATION
The assay can be performed in serum or plasma samples. Moderately lipemic
samples do not influence the results; highly lipemic or hemolyzed samples may
affect the results. The presence of fibrin filaments could interfere with the assay;
make sure that samples are always perfectly clear before testing. Keep samples
properly stored at 2-8°C for 1 week; for longer periods it is advisable to freeze
samples at -20°C. Repeated freezing and thawing of samples should be avoided.
Before use, dilute samples 1:300 with diluted Sample Diluent (see REAGENTS).
Example: 10 µL sample + 2990 µL diluent.
7. ASSAY PROCEDURE*
− Allow the reagents and samples to warm up at room temperature.
− Mix samples by inversion before use.
7.1
Prepare the wells in duplicate for Controls and in single for Blank and
Samples.
7.2 Pipette 100 µL of Controls and diluted Samples into the corresponding
wells.
Note: Controls must not be diluted.
7.3 Pipette 100 µL of diluted Sample Diluent into the Blank well.
7.4 Cover the microplate with adhesive sheet (supplied with the kit) and
incubate the wells for 60±5 minutes at 37±2°C.
7.5 Wash the wells 4 times with 350 µL of diluted Washing Solution. Aspirate all
liquid from the wells.
7.6 Add 100 µL of Enzyme Conjugate into all wells.
7.7 Cover the microplate with adhesive sheet (supplied with the kit) and
incubate the wells for 30±2 minutes at 37±2°C.
7.8 Wash the wells as described in point 7.5.
7.9 Pipette 100 µL of Chromogen into all wells.
7.10 Incubate the wells for 10 minutes at 37±2°C or 15 minutes at room
temperature (18-25°C). Avoid direct light exposure.
7.11 Pipette 100 µL of Blocking Reagent into all wells.
7.12 Read the absorbance of the wells with a preferably bichromatic
spectrophotometer at 450 nm, with reference wavelength at 620 nm (setting
the instrument at zero with the Blank well). In case of overflow absorbance
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 15/24
values, read at 405 nm. Reading must be completed within 15 minutes from
the end of the assay.
* While using for the procedure a RADIM and/or SEAC automatic instrument for
microplates, refer to its relative manual.
8. ASSAY SCHEME: see p. 23
9. CALCULATION OF RESULTS*
The optical density of each negative, positive and cut-off control must be
considered. The presence or absence of anti-HSV type 1 IgG antibodies is
defined by comparing the sample absorbance with the absorbance of the Cut-off
Control (threshold value). Samples with optical density lower than the cut-off
control are to be considered non-reactive for anti-HSV type 1 IgG antibodies.
Samples with optical density higher than the cut-off control are to be considered
reactive for anti-HSV type 1 IgG antibodies.
Samples with absorbance values ranging within ± 10% of the cut-off control are to
be considered questionable and should be retested for confirmation.
* While using a RADIM and/or SEAC automatic instrument for microplates, the
spectrophotometric reading will be performed automatically at 3 different
wavelengths: 450, 405 and 620 nm, thereby allowing a wider curve range.
9.1 Calculation example
The following values must be taken as an example and should not be used in
place of experimental data.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 16/24
Description
O.D. 450 nm
Negative Control
0.082
Cut-off Control
0.504
Positive Control
1.992
Sample
0.889
The tested sample comes out positive for anti-HSV type 1 IgG antibodies.
9.2 Validation Criteria
Before proceeding to calculation of results, make sure the control absorbances
are included within the following ranges:
Description
Expected values
Negative Control
< 0.200
Positive Control
> 0.700
If the values obtained are not within the expected range, it will be necessary to
repeat the assay.
9.3 Interpretation of Results
− Non-reactive samples are to be considered negative for anti-HSV type 1 IgG
antibodies.
− Reactive samples are to be considered positive for anti-HSV type 1 IgG
antibodies.
− Questionable samples must be critically evaluated or repeated for confirmation.
Subsequent blood-drawls of the same patient can be compared only if tested in
the same assay. In this case, a 60% absorbance increase in the 2nd sample can
be considered a significant indication of a recent or in progress infection. If so, test
for specific IgM.
10. PERFORMANCES OF THE ASSAY
10.1 Diagnostic Specificity
The diagnostic specificity of the method was evaluated over a representative
group of individuals with no immunity against HSV type 1 IgG infection. The result
was 100%.
10.2 Diagnostic Sensitivity
The diagnostic sensitivity of the method was evaluated over a representative
group of individuals having undergone past HSV type 1 IgG infection. The result
was 97.6%.
10.3 Precision
Precision was evaluated determining the repeatability and the reproducibility of
the assay (intra- and inter-assay variability), on 3 sera at different anti-HSV type 1
IgG concentrations.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 17/24
Repeatability (Intra-assay)
Serum
Mean
a
b
c
570
1027
2718
±
(O.D. 450 nm)
±
±
±
S.D.
27.6
63.5
103.6
C.V.
%
4.8
6.2
3.8
Replicates
no.
12
12
12
C.V.
%
13.8
15.3
11.1
Assays
no.
10
10
10
Reproducibility (Inter-assay)
Serum
Mean
a
b
c
0.431
1.870
3.547
±
(O.D. 450 nm)
±
±
±
S.D.
59.8
286
397
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 18/24
11. LIMITS OF THE ASSAY
In defining the immunity level of a patient against HSV type 1, the presence of IgG
class antibodies, at any level, does not exclude the possibility of an ongoing
infection. Therefore, specific IgM antibody testing is essential for an early
diagnosis of acute infections. In case of illness, a rapid intervention will
considerably reduce the risks. However the results of the assay must be carefully
interpreted and confirmed by clinical evaluations and further diagnostic tests.
12. SYMBOLS LEGEND: see p. 20
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 19/24
SIMBOLI, SYMBOLS, SYMBOLES,
ΣΥΜΒΟΛΑ, SYMBOLIT, SYMBOLER
SÍMBOLOS,
SÍMBOLOS,
SYMBOLE,
EN 980 - EDMA
REF
Codice di riferimento o di ordine / reference or order code / Référence ou
numéro de commande / referencia o número de pedido / referência ou
número da encomenda / Referenz oder Bestellnummer / κωδικός
προϊόντος ή παραγγελίας / Refarans veye sipariş numarsı / referenční
nebo objednací číslo
LOT
Lotto / lot / Lot / lote / lote / charge / παρτίδα / parti / šarže
Data di scadenza / expiry date / date d’expiration / Fecha de caducidad /
Data de vencimento / Verfallsdatum / Ηµεροµηνία λήξης / Son kullanma
targhi / datum expirace
IVD
Per uso diagnostico in-vitro / For in-vitro diagnostic use / Pour diagnostic
in-vitro / Para uso diagnóstico In-vitro / aplicação do diagnóstico In-vitro /
Für den Gebrauch in der IN-VITRO-DIAGNOSTIK / για in vitro
διαγνωστική χρήση / in –vitro diagnostik kullanım / pro použití in-vitro
Marcatura CE secondo le direttive IVD 98/79/CE / CE marking according
to IVD guidelines 98/79/EC / marquage CE conforme aux directives IVD
98/79/EC / marcado CE según directiva de IVD 98/79/CE / marcação-CE
segundo a directriz-IVD 98/79/CE / CE-Markierung bei Erfüllung der IVD
Richtlinie 98/79/EG / Σηµανση CE βάσει κοινοτικής οδηγίας IVD
98/79/EC / 98/79/EC IVD tüzüğüne göre CE işareti / CE označení dle IVD
98/79/EU
Conservare a 2-8°C / keep at 2-8°C / conserver à 2-8°C / Conservar a 28°C / conservar a 2-8°C / Lagerung bei 2-8°C / φύλαξη στους 2-8°C / 28°C da saklayınız / skladovat při 2-8°C
Fabbricante / Manufacturer / Fabriquant / produzido por / Fabricante /
produkt der / κατασκευάζεται από / tarafından üretilmiştir / výrobce
Rischio biologico / Biohazard / Risque Biologique / Riesgo Biológico /
Risco Biológico / Bιολογικός κίνδυνος / Riziko tehlike biyolojik/ Biologicky
nebezpečné
Consultare la metodica operativa / consult instructions for use / consulter
le mode opératoire / consultar las instrucciones de uso / consultar as
instruções de uso / Schauen Sie die Arbeitsanleitung an / συμβουλευτείτε
τις οδηγίες χρήσης / kullanımda başvurulacak bilgiler / Sledujte návod k
použití
96
Sufficiente per 96 test / sufficient for 96 tests / suffisant pour 96
déterminations / suficiente para 96 determinaciones / Componentes para
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 20/24
96 testes / genügend für 96 Tests / επαρκεί για 96 τεστ / 96 test için
yeterli / dostačující pro 96 testů
192
Sufficiente per 192 test / sufficient for 192 tests / suffisant pour 192
déterminations / suficiente para 192 determinaciones / Componentes
para 192 testes / genügend für 192 Tests / επαρκεί για 192 τεστ / 192 test
için yeterli / dostačující pro 192 testů
RDATE Data di Riferimento / Reference date / Date de référence / Fecha de
referencia / Data de refêrencia / Referenzdatum / ημερομηνία
βαθμονόμησης / Referans Targhi / referenční datum
RCNS
Ricostituire con / reconstitute with / reconstituer avec / reconstituir con /
reconstituir com / rekonstituiren mit / ανασυστάται με / ile karıştırma /
rekonstituovat
H2O
Acqua distillata o deionizzata / deionized or distilled water / eau deionisée
ou distillée / agua destilada o desionizada / água destilada ou deionizada
/ Deionisiertes oder Destilliertes Wasser / απιονισμένο -απεσταγμένο
νερό / deiyonize veya distile su / deionizovaná nebo destilovaná voda
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 21/24
BIBLIOGRAFIA - REFERENCES
1 - Frame, B., J. B. Mahony, N. Balachandran, W. E. Rawls, and M. A.
Chernensky. 1984. Identification and typing of Herpes simplex virus by
enzyme immunoassay with monoclonal antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 20:162166.
2 - Davis W. B., J. A. Taylor, and J. E. Oakes. 1979. Ocular infection with Herpes
simplex virus type 1: prevention of acute herpetic encephalitis by systemic
administration of virus- specific antibody. J. Infect. Dis. 140:534-539.
3 - E. Kaufman, D. M. Drylic, S. L. Deardourff, and Centifanto, Y. M. 1972.
Herpes virus type 2 in male genito-urinary tract. Science 178:318-319.
4 - Alexander, I., C. R. Ashley, K. J. Smith, J. Harbour, A. P. Roome, and J. M.
Darville. 1985. Comparison of ELISA with virus isolation for the diagnosis of
genital Herpes. J. Clin. Pathol. 38:554-557.
5 - Pereira, Coleman R.M., P.D. Bailey, D. Dondero, C. Wickliffe and A.J.
Nahmias. 1983. Determination of Herpes simplex virus type-specific
antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 18:
287-291.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 22/24
8. SCHEMA DEL DOSAGGIO - ASSAY SCHEME
Prediluizione del campione, Sample predilution: 1/300
Pozzetti
Wells
Reag.
NEG
POS
C/O
Campioni, Samples
DIL
Bianco,
Blank
NEG
POS
C/O
Campioni,
Samples
-----
100 µL
-----
----100 µL
---------
100 µL
-----
100 µL
100 µL
− Incubare, Incubate: 37±2°C, 60±5 min.
− Aspirare e Lavare, Aspirate and Wash: 4 x 350 µL.
CONJ
100 µL
− Incubare, Incubate: 37±2°C, 30±2 min.
− Aspirare e Lavare, Aspirate and Wash: 4 x 350 µL.
TMB
100 µL
100 µL
100 µL
− Incubare, Incubate: 37±2°C, 10'; o, or T.A. / R.T. 15'
STOP
100 µL
100 µL
100 µL
− Leggere, Read: 450-405 nm.
KH1G/KH1GB – HSV 1 IgG EIA WELL
M72 – Rev.9 – 02/2006 – Pag. 23/24
RADIM S.p.A. -
Via del Mare, 125 - 00040 Pomezia (Roma) Italia
Tel.: +39 06 91.249.1 - Fax: +39 06 91.249.443
National Order Entry: +39 06 91.249.702
Export Department: +39 06 91.249.701
Customer Care: +39 06 91.249.700
[email protected] - www.radim.com