GENOMICA
Uso di Genome Browser per l'annotazione
di sequenze genomiche.
UCSC
University of California Santa Cruz
Genome Browser
Dott.ssa Inga Prokopenko
1
Sequenziamento del genoma –
assemblaggio delle sequenze disponibili
Una sequenza viene detta “finita” quando presenta un
livello di errore inferiore a 1/10000 basi e non ha gaps.
Il Progetto Genoma Umano era complesso dal punto di
vista tecnico ma anche dal punto di vista
computazionale.
L’output di una singola reazione di sequenza (read) =
500-800 bp Tutti i singoli frammenti dovevano essere
assemblati in una singola stringa lineare.
2
Biological Databases
L’annotazione del genoma è un’area di investigazione
attiva ed include molte organizzazioni che pubblicano i
risultati nella data banche biologiche disponibili per tutta
la comunità:
ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements (ENCODE)
Entrez Gene
Ensembl
Gene Ontology Consortium
GeneRIF
RefSeq
Uniprot
Vertebrate and Genome Annotation Project (Vega)
3
Browser genomici
aiutano a visualizzare genomi annotati completi (inclusi
geni e loro strutture, proteine, espressione, regulazione,
variazione ed analisi comparative)
Le risorse di annotazione sono multiple.
Genome Browsers
UCSC Genome Bioinformatics Genome Browser and
Tools (UCSC)
NCBI-UniGene (National Center for Biotechnology
Information)
Ensembl The Ensembl Genome Browser (Sanger
Institute and EBI)
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
4
3 milioni di basi in formato testo = nessuna utilita’
Servono:
•Annotazione dell’informazione sulla sequenza
•Possibilita’ di recuperare velocemente la sequenza di
regioni specifiche del genoma in base a criteri di
• Contenuto di informazione
• Caratteristiche di sequenza
UCSC Genome Browser
Sistema per la “navigazione” della sequenza e
dell’annotazione di genomi, che permette la
visualizzazione dell’informazione a “diverso
ingrandimento” ed il recupero di porzioni di sequenza
con associate le informazioni di annotazione, come:
Geni noti e geni predetti
ESTs, mRNAs
Isole CpG
assembly gaps e coverage, bande cromosomiche
Omologia con altri genomi
…
Genomi
disponibili
Human
Homo sapiens
assembly
• 99% delle regioni
contenenti geni
• accuratezza 99.99%
• 2.84 Gb finite “highly
contiguous”
Species
A. gambiae
A. mellifera
C. briggsae
C. elegans
C. intestinalis
Chicken
Chimp
Cow
D. ananassae
D. erecta
D. grimshawi
D. melanogaster
D. mojavensis
D. persimilis
D. pseudoobscura
D. sechellia
D. simulans
D. virilis
5
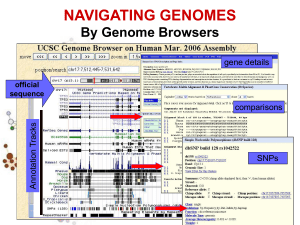
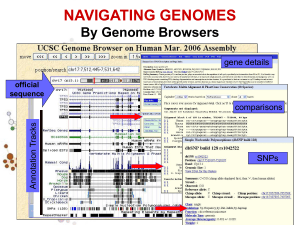
Organizazione dei dati genomici…
Annotation Tracks
sequenza Genome backbone: base position number
chromosome band
sts sites
gap locations
known genes
Links out to
more data
predicted genes
microarray/expression data
evolutionary conservation
SNPs
repeated regions
more…
6
The UCSC Home page: genome.ucsc.edu
navigate
General information
navigate
Specific information—
new features, current status, etc.
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
7
A sample of what we will find:
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
8
The Genome Browser Gateway
start page, basic search
text/ID
searches
,
les
p
m
xa w
e
h
o
arc bel
se stions
l
u
pf ugge
l
e
s
H
Use this Gateway to search by:
Gene names, symbols
Chromosome number: chr7, or region: chr11:1038475-1075482
Keywords: kinase, receptor
IDs: NP, NM, OMIM, and more…
9
UCSC Genome Browser
Molte possibilita’ per la ricerca di una regione specifica:
• chr7
un cromosoma intero
• 20p13
una regione (banda p13 del cr. 20)
• chr3:1-1000000
il primo milione di basi del cr. 3 dal ptel
• D16S3046
regione intorno al marcatore (100,000 basi per lato)
• RH18061;RH80175 regione tra i due marcatori
• AA205474
regione genomica che si allinea con la sequenza con
questo GB accession number
• PRNP
regione del genoma che comprende il gene PRNP
• NM_017414
regione del genoma con indificatore di RefSeq
• NP_059110
regione del genoma con “protein accession number”
• 11274 (LLID)
Oppure di liste di regioni:
• pseudogene mRNA Lists transcribed pseudogenes, but not cDNAs
• homeobox caudal
Lists mRNAs for caudal homeobox genes
• zinc finger
Lists many zinc finger mRNAs
• huntington
Lists candidate genes associated with Huntington's
disease
10
11
The Genome Browser Gateway
start page choices, February 2005
1
2
3
4
5
6
Make your Gateway choices:
1.
Select Clade
2.
Select species: search 1 species at a time
3.
Assembly: the official backbone DNA sequence
4.
Position: location in the genome to examine
5.
Image width: how many pixels in display window; 5000 max
6.
Configure: make fonts bigger + other choices
12
The Genome Browser Gateway
sample search for Human BRCA1
Sample search: human, May 2004 assembly, BRCA1
select
•Often you will have to select the
right gene from a results list
•Sometimes, you will go directly
to a browser image (use an ID)
•AF005068, breast cancer 1, early onset
13
Overview of the whole
Genome Browser page
(first day, new human release)
}
Genome viewer section
Track and image controls
(day 1 = 40 tracks)
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
14
Overview of the whole
Genome Browser page
(mature release)
}
Genome viewer section
Groups of data
Mapping and Sequencing Tracks
Genes and Gene Prediction Tracks
mRNA and EST Tracks
Expression and Regulation
Comparative Genomics
ENCODE Tracks
Variation and Repeats
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
15
Different species, different tracks, same software
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
16
Sample Genome Viewer image, BRCA1 region
Genome backbone
STS markers
Known genes
RefSeq genes
MGC clones
Gene predictions
GenBank mRNAs
GenBank ESTs
conservation
SNPs
repeats
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
17
Annotation Track options, defined
Hide: removes a track from view
Dense: all items collapsed into a single line
Squish: each item = separate line, but 50% height + packed
Pack: each item separate, but efficiently stacked (full height)
Full: each item on separate line
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
18
Clicking an annotation line,
new page of detailed information
You will get detail for that single item you click
Example: click on the BRCA1 Black “Known Genes” line
Click the line
New
web page
opens
Many details
and links
to more data
about BRCA1
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
19
informative
description
Click annotation track = BRCA1
“Known gene” detail page
other resource links
links to sequences
microarray data
Not all genes have
This much detail.
Different
annotation tracks
carry different detail
data.
mRNA secondary structure
protein domains/structure
homologs in other species
SNP
detail page
sample
Gene Ontology™ descriptions
mRNA descriptions
pathways
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
20
Getting the sequences
Get DNA, with Extended Options; or Details pages
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
Use the DNA link at
the top
Plain or Extended
options
Change colors,
fonts, etc.
21
Accessing the BLAT tool
BLAT = BLAST-like Alignment Tool
Rapid searches by INDEXING the entire genome
Works best with high similarity matches
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
22
BLAT: Blast-like alignment tool
Blat is really really fast—it has been optimized to search
the whole genomes more quickly than BLAST does.
UCSC have created an INDEX of all the unique 11mers if
it’s DNA, 4mers if protein (or stretches of 11nucleotides
or 4 amino acids).
it looks down its index of 11mers, finds a match and
works out from there.
Blast does it the other way—it indexes your query and
then runs your smaller index over everything…that’s the
essential difference in the algorithm.
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
23
BLAT
UCSC documentation:
“On DNA queries, BLAT is designed to quickly find
sequences with 95% or greater similarity of length 40
bases or more. It may miss genomic sequences that are
more divergent or shorter than these minimums, although
it will find perfect sequence matches of 33 bases and
sometimes as few as 22 bases. The tool is capable of
aligning sequences that contain large introns.
On protein queries, BLAT rapidly locates genomic
sequences with 80% or greater similarity of length 20
amino acids or more. In general, gene family members
that arose within the last 350 million years can generally
be detected.”
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
24
BLAT tool overview:
www.openhelix.com/sampleseqs.html
Make
choices
Paste one
or more
sequences
DNA limit 25000 bases
Protein limit 10000 aa
25 total sequences
Or
upload
Submit
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
25
BLAT results, with links
sorting
Results with demo sequences, settings default; sort = Query, Score
Score is a count of matches—higher number, better match
Click browser to go to Genome Browser image location (next slide)
Click details to see the alignment to genomic sequence (2nd slide)
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
26
BLAT results, alignment details browser
Click to flip frame
query
matches
From browser click in BLAT results
A new line with your Sequence from BLAT Search appears!
Watch out for reading frame! Click - - - > to flip frame
Base position = full and zoomed in enough to see
amino acids
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
27
BLAT results,
alignment details
Your query
Genomic match, color cues
Side-by-side alignment
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
28
In Silico PCR:
find genomic sequence using primers
Select genome
Enter primers
Minimum 15 bases
Flip reverse primer?
Submit
(note: the tool does not handle ambiguous bases at this time—don’t use Ns)
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
29
In Silico PCR: results
location
size
your primers
Tm for primers
Genomic location shown, links to Genome Viewer
Product size shown
Your primers displayed, flipped if necessary
Predicted genomic sequence shown
Primer melting temperatures provided
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
30
Proteome Browser
more
protein
data
Access from homepage or Known Gene pages
Exon diagram, amino acids
Many protein properties (pI, mw, composition, 3D…)
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
31
Gene Sorter
From homepage select ‘Gene sorter’
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
32
Gene Sorter interface
Sorts genes by several criteria
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
33
Gene Sorter interface
Choose from 11 sorting options
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
34
Gene Sorter results
Copyright OpenHelix. No use or reproduction without express written consent
35