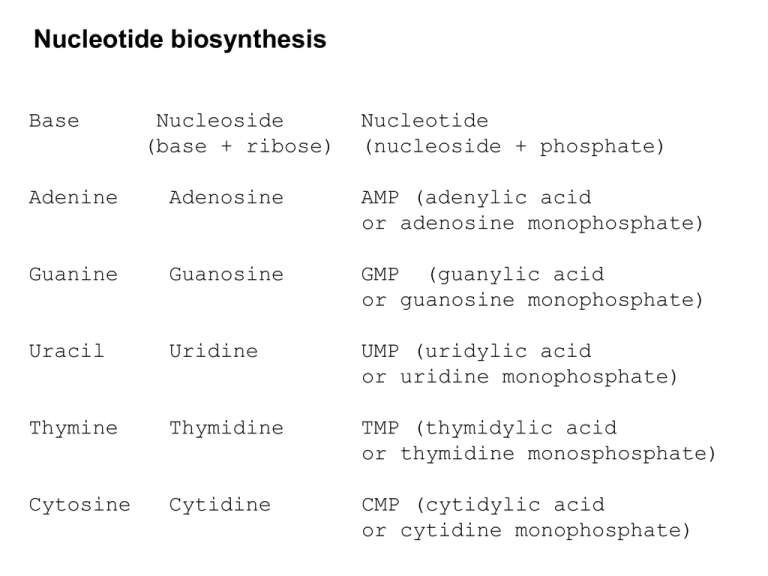
Nucleotide biosynthesis
Base
Nucleoside
(base + ribose)
Nucleotide
(nucleoside + phosphate)
Adenine
Adenosine
AMP (adenylic acid
or adenosine monophosphate)
Guanine
Guanosine
GMP (guanylic acid
or guanosine monophosphate)
Uracil
Uridine
UMP (uridylic acid
or uridine monophosphate)
Thymine
Thymidine
TMP (thymidylic acid
or thymidine monosphosphate)
Cytosine
Cytidine
CMP (cytidylic acid
or cytidine monophosphate)
CAD
Orotico aciduria
Malattia genetica rara caratterizzata da anemia per difetto di
maturazione degli eritrociti e per la presenza di acido orotico
nelle urine. I soggetti affetti sono incapaci di convertire l’acido
orotico in UMP
Tipo 1: carenza dell’enzima UMP sintasi (sia orotato fosforibosile
transferasi che orotato monofosfato decarbossilasi)
Tipo 2: difetto a carico solo dell’ orotato monofosfato decarbossilasi
(terapia con uridina)
Dosaggio acido orotico nelle urine
HPLC 275 nm
Più specifico LC/MS/MS
Experiments with radioactive tracers showed that the purine
ring is assembled from 5 different types of building block
Amino group
of aspartate
CO2
N
C
N10-formyl-THF
C
Glycine
C
N
C
N10-formyl-THF
N C N
Amide N of
glutamine
(THF = tetrahydrofolate)
A common pathway of 11 steps beginning with phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) and glutamine leads to inosine monophosphate
(IMP). Separate branches then lead to AMP and GMP.
AMP
PRPP + Gln
IMP
GMP
1 PRPP sintasi
2 amidofosforibosile transferasi
3 GAR sintetasi
4 GAR transformilasi
5 FGAM sintasi
6 AIR sintasi
7 AIR carbossilasi
8 SACAIR sintetasi
9 Adenilsuccinatoliasi
10 AICAR transformilasi
11 IMP sintasi
Biosintesi dei deossiribonucleotidi
e catabolismo delle purine
ADP, GDP, CDP & UDP can be reduced to
the corresponding deoxyribonucleotides
ADP
dADP
H2O
GDP
dGDP
CDP
dCDP
UDP
X ribonucleotide
SH reductase
X
S
SH
S
Nucleoside diphosphates
are reduced by cysteines
in the enzyme,
ribonucleotide reductase.
dUDP
dTTP
NADP+
NADPH
Regeneration of the
reduced enzyme
requires several steps)
DNA replication also
requires thymine, which
is made from dUDP.
Primates oxidize purines to uric acid for excretion
O
NH2
C
N
C
HC
C
N
C
N
CH
N
ribose
adenosine
O
HN
H2N-C
C
N
C
C
N
CH
C
C
C
HO
N
ribose
HN
N
N
C OH
N
H
uric acid
OH
guanosine
C
Birds, reptiles and insects also excrete uric acid.
Fish and most terrestrial mammals oxidize uric
acid further before excreting the product.
HO
N
C
C
C
N
N
C OH
N
H
O
C
uric acid has several
tautomeric forms
HN
C
H
N
C
O C N
N
H
C O
Uric acid production from purines
adenosine
NH2
C
N
C
HC
C
N
H2O
inosine
O
NH4+
C
N
CH
adenosine
deaminase
N
C
HN
HC
N
ribose
N
C
C
guanosine
CH
N
ribose
C
C
HN
HC
CH
N
C
N
N
CH
N
H
O2 + H2O
C
N
O
ribose-1-P
O
C
N
Pi
ribose
O
HN
H2N-C
C
hypoxanthine
N
C
HN
CH
C
C
HO
N
N
H
xanthine
O2 + H2O
Xanthine oxidase contains FAD, a
Mo complex, and two Fe-S centers.
Its substrates are the free purines,
not nucleosides or nucleotides.
H2O2
xanthine H2O2
oxidase
xanthine
oxidase
O
uric acid
C
HN
C
C
C
HO
N
N
C OH
N
H
Mutations in adenosine deaminase cause
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease
SCIDS
NH2
deoxyadenosine
C
N
C
HC
C
N
H2O
C
N
CH
adenosine
deaminase
N
deoxyribose
dATP
O
NH4+
C
HN
HC
N
C
N
uric
acid
CH
N
deoxyribose
In the absence of adenosine deaminase, dATP accumulates to high levels.
The dATP inhibits ribonucleotide reductase, preventing synthesis of the
other deoxynucleotides and cutting off DNA synthesis. Lymphocytes are
particularly susceptible to this inhibition. Untreated SCID is fatal. SCID
was one of the first disorders to be addressed by gene therapy.
ribonucleotide
reductase
ribonucleotides
deoxyribonucleotides
DNA
Deposition of sodium urate
crystals in tissues causes gout
Impaired excretion of uric acid results in high levels of uric acid in body fluids. Crystals
of sodium urate form in the toe, kidney and other tissues, causing painful inflamation.
O
O
C
C
HN
HC
N
C
N
xanthine
oxidase
C
C
N
O
xanthine
oxidase
C
C
O
C
C
HN
HC
C
O
H
C
N
H
allopurinol
N
N
HN
HN
CH
C OH
C
C
C
C
HO
HO
N
N
N
N
H
H
O2 + H2O H2O2
O2 + H2O H2O2
CH
N
H
uric acid
xanthine
hypoxanthine
N
Gout can be treated with
allopurinol, an analog of
hypoxanthine that
inhibits xanthine oxidase.
C
HN
C
C
C
HO
sodium urate
N
N
N
H
Na+
C O-
• Gotta: dal latino «gutta » (= goccia)
• Già descritta da Ippocrate (ca. 460 – ca. 370 a.C.),
Galeno
(130 – 201 d.C.) e Paracelso (1493 – 1541)
• Definizione:
– Artropatia cristallina con deposito intra- ed
extrarticolare di cristalli di
acido urico, in presenza di un difetto del metabolismo
delle purine
• Deposito di cristalli di acido urico:
– Nelle articolazioni → «vera» artropatia urica
– Nei tessuti → possibile formazione di tofi (noduli)
• Spesso associata ad una nefropatia urica, disturbi del
metabolismo del glucosio e/o dei grassi
Diagnostica
• Laboratorio
– Puntato: tipici cristalli di acido urico,
evidenziati al microscopio con luce
polarizzata (rifrazione neg.)
– Escissione di tofi delle parti molli: valutazione
al microscopio del materiale biancastro
estratto e dimostrazione di cristalli di acido
urico in massa
– Sangue: nell’attacco acuto di gotta nel 90%
dei casi vi è un’iperuricemia. Inoltre aumento
dei parametri fiammatori (VES e PCR↑,
leucocitosi)
Esami necessari per chiarire la causa di
un’iperuricemia
– Acido urico sierico
– Creatinina sierica
– Eliminazione dell’acido urico e della
creatinina nelle urine delle 24 h
(clearance)
“Salvage” pathways capture free purine and
pyrimidine bases and regenerate nucleotides
adenine
phosphoribosyl
transferase
NH2
adenine
C
N
C
HC
N
C
N
O-CH2
O
OH
C
CH
N
C
HC
C
N
N
H
P
O-
P
NH2
O-CH2
N
CH
N
O
PPi
O-
OPOPOO
O
OH
OH
AMP
OH
5-phosphoribosyl-1pyrophosphate (PRPP)
Another enzyme (hypoxanthine-guanine
phosphoribosyl transferase) works on
hypoxanthine and guanine. Mutations in
this enzyme lead to Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
Lesch-Nhyan syndrome, an X-linked disorder that
results from a mutation in the gene for
hypoxanthine-guanine ribosylphosphotransferase,
is characterized by severe neurological defects.
• mental retardation
• self-mutilation
• cerebral palsy
• elevated uric acid (gout)
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome can be diagnosed prenatally
Fetal fibroblasts obtained by amniocentesis are
cultured in the presence of 3H-hypoxanthine.
Cells from normal individuals convert
hypoxanthine into IMP, which procedes to AMP
and GMP and is incorporated into DNA.
O
O
C
C
HN
HC
C
PRPP
N
PPi
C
CH
P
O-CH2
N
C
HN
HC
N
H
hypoxanthine
N
normal
CH
C
N
N
O
Lesch-Nyhan
IMP
Blocked in
Lesch-Nyhan
syndrome
OH
OH
AMP
DNA
GMP