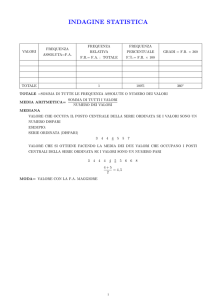
ADT Insieme
L'ADT Insieme è un contenitore di oggetti distinti.
non esistono due elementi uguali;
non esiste un ordinamento sugli oggetti.
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Metodi fondamentali dell'ADT Insieme
Metodi applicati all'insieme A (this):
void union (Set B): rimpiazza A con l'unione insiemistica di A e B
void intersect (Set B): rimpiazza A con l'intersezione insiemistica di A e B
void subtract (Set B): rimpiazza A con la differenza insiemistica A-B
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Interfaccia
public interface Set<E> {
public int size();
public boolean isEmpty();
/**Rimpiazza this con l'unione di this e B */
public void union(Set<E> B);
/**Rimpiazza this con l'intersezione di this e B */
public void intersect(Set<E> B);
/**Rimpiazza this con la differenza di this e B */
public void subtract(Set<E> B);
}
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
definire una relazione d'ordine totale (qualunque) sugli oggetti
usare una variabile istanza per la lista ed una per il comparatore
scrivere una classe astratta contenente un metodo merge,
una generica versione dell'algoritmo merge (usato nel mergesort)
scrivere tre sottoclassi distinte che specializzano merge
rispettivamente in:
- union
- intersect
- subtract
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
classe astratta Merge<E>
metodo merge
generico
sottoclasse
UnionMerge<E>
Strutture Dati
sottoclasse
IntersectMerge<E>
sottoclasse
SubtractMerge<E>
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
public class ListSet<E> extends Merge<E> implements Set<E>{
protected PositionList<E> A;
dell'insieme
protected Comparator<E> comp;
...
}
Strutture Dati
//la lista che contiene gli elementi
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
public abstract class Merge<E> {
private E a, b;
// elementi correnti in A e B
private Iterator<E> iterA, iterB;
// iteratori per A e B
//metodi ausiliari
private boolean advanceA()
if (iterA.hasNext()) { a
return false;
}
private boolean advanceB()
if (iterB.hasNext()) { b
return false;
}
...
}
Strutture Dati
{
= iterA.next(); return true; }
{
= iterB.next(); return true; }
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
public abstract class Merge<E> {
...
// metodi ausiliari da specializzare nelle sottoclassi
protected void aIsLess(E a, PositionList<E> C) { }
protected void bothAreEqual(E a, E b, PositionList<E> C) { }
protected void bIsLess(E b, PositionList<E> C) { }
}
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
public abstract class Merge<E> {
...
/** Metodo merge generico*/
public void merge(PositionList<E> A, PositionList<E> B, Comparator<E> comp,
PositionList<E> C) {
iterA = A.iterator();
iterB = B.iterator();
boolean aExists = advanceA();
boolean bExists = advanceB();
//ciclo principale del metodo merge generico
while (aExists && bExists) {
int x = comp.compare(a, b);
if (x < 0) { aIsLess(a, C); aExists = advanceA(); }
else if (x == 0) {
bothAreEqual(a, b, C); aExists = advanceA(); bExists = advanceB(); }
else { bIsLess(b, C); bExists = advanceB(); }
}
while (aExists) { aIsLess(a, C); aExists = advanceA(); }
while (bExists) { bIsLess(b, C); bExists = advanceB(); }
}
...
}
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di union (classe UnionMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a < b
B
b
C
Strutture
Dati
Laboratorio
di Algoritmi e Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di union (classe UnionMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a < b
B
b
metodo aIsLess(a,C) :
C
a
Strutture Dati
- aggiunge a C l'elemento a
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di union (classe UnionMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a = b
B
b
C
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di union (classe UnionMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a = b
B
b
metodo bothAreEqual(a,b,C) :
C
a
Strutture Dati
- aggiunge a C l'elemento a e non il suo duplicato b
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di union (classe UnionMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a > b
B
b
C
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di union (classe UnionMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a > b
B
b
metodo bIsLess(b,C) :
C
b
Strutture Dati
- aggiunge a C l'elemento b
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di intersect (classe IntersectMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a < b
B
b
C
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di intersect (classe IntersectMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a < b
B
b
metodo aIsLess(a,C) :
C
Strutture Dati
...non fa nulla!
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di intersect (classe IntersectMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a = b
B
b
C
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di intersect (classe IntersectMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a = b
B
b
metodo bothAreEqual(a,b,C) :
C
a
Strutture Dati
- aggiunge a C l'elemento a
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di intersect (classe IntersectMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a > b
B
b
C
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Implementazione di intersect (classe IntersectMerge<E>)
A
a
caso a > b
B
b
metodo bIsLess(b,C)
C
Strutture Dati
...non fa nulla!
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
public class UnionMerge<E> extends Merge<E>{
protected void aIsLess(E a, PositionList<E> C) {
C.addLast(a);// aggiunge a
}
protected void bothAreEqual(E a, E b, PositionList<E> C) {
C.addLast(a);
// aggiunge a (ma non il suo duplicato b)
}
protected void bIsLess(E b, PositionList<E> C) {
C.addLast(b);
// aggiunge b
}
}
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
public class IntersectMerge<E> extends Merge<E>{
protected void aIsLess(E a, PositionList<E> C) { }
protected void bothAreEqual(E a, E b, PositionList<E> C) {
C.addLast(a);
// aggiunge a (ma non il suo duplicato b)
}
protected void bIsLess(E b, PositionList<E> C) { }
}
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
public class SubtractMerge<E> extends Merge<E>{
protected void aIsLess(E a, PositionList<E> C) {
C.addLast(a);
// aggiunge a
}
protected void bothAreEqual(E a, E b, PositionList<E> C) { }
protected void bIsLess(E b, PositionList<E> C) { }
}
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
public class ListSet<E> extends Merge<E> implements Set<E>{
protected PositionList<E> A;//lista che contiene gli elementi dell'insieme
protected Comparator<E> comp;
/**Costruttore che crea un insieme vuoto*/
public ListSet() {
A = new NodePositionList<E>();
comp = new DefaultComparator<E>();
}
public void union(Set<E> B) {
PositionList<E> C = new NodePositionList<E>();
Merge<E> op = new UnionMerge<E>();
op.merge(A, B.elements(),comp,C);
A=C;
}
...
}
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Implementazione con lista ordinata
Complessità
●
merge: O(nA + nB)
(nA : numero di elementi in A; nB : numero di elementi in B)
Le operazioni union, intersect e subtract possono essere implementate in
tempo O(n).
(n : numero di elementi totale degli insiemi coinvolti)
Strutture Dati
ADT Insieme
Completare l' implementazione di Set aggiungendo anche
l'implementazione dei seguenti metodi:
elements(): restituisce la lista degli elementi dell'insieme;
iterator(): restituisce un iteratore sugli elementi dell'insieme;
insert(e): inserisce un nuovo elemento e nell'insieme;
Strutture Dati