Algoritmi e Strutture Dati
Laurea in Informatica
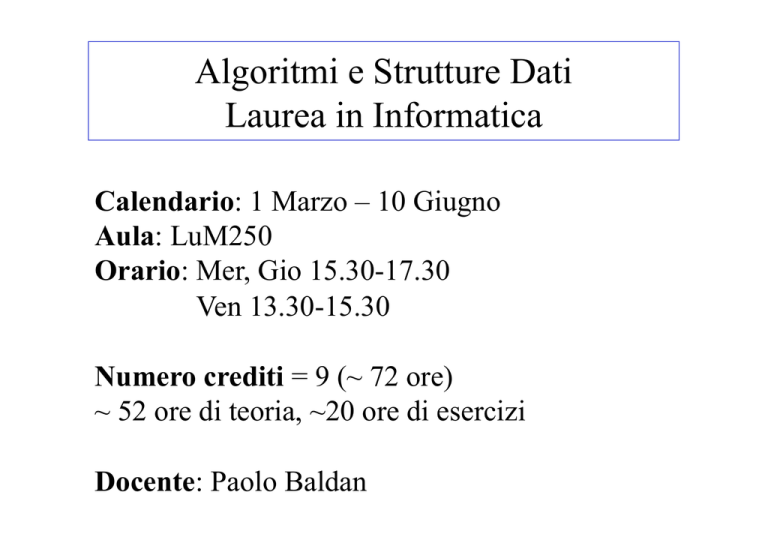
Calendario: 1 Marzo – 10 Giugno
Aula: LuM250
Orario: Mer, Gio 15.30-17.30
Ven 13.30-15.30
Numero crediti = 9 (~ 72 ore)
~ 52 ore di teoria, ~20 ore di esercizi
Docente: Paolo Baldan
Modalità d’Esame
a. Prova intermedia
per l’assegnazione di un bonus fino a 2 punti
(che si somma al voto dell’esame finale)
b. Prova scritta
(5 appelli - indispensabile iscriversi nella lista
di esame che verrà attivata su UNIWEB)
c. Registrazione, con possibile orale (su base
volontaria). Indispensabile per conseguire la
lode.
Materiale didattico
Testo: Introduzione agli Algoritmi e Strutture Dati
(3° ed). T.H.Cormen, C.E.Leiserson, R.L.Rivest,
C.Stein. McGraw-Hill.
Trad. di: Introduction to Algorithms and Data
Structures (3° ed). T.H.Cormen, C.E.Leiserson,
R.L.Rivest, C.Stein. MIT Press.
Pagina del corso con altro materiale (note,
link, ecc.:
www.math.unipd.it/~baldan/Algoritmi
Programma
Le prime 5 parti del testo (con qualche omissione):
I. Fondamenti: notazione per gli algoritmi e primi
esempi di algoritmi e di analisi degli algoritmi
II. Ordinamento e statistiche d’ordine
III. Strutture dati fondamentali
IV. Tecniche avanzate di progettazione ed analisi
degli algoritmi
V. Strutture dati avanzate
INTRODUZIONE
I problemi computazionali, gli algoritmi che li
risolvono e le tecniche per sviluppare tali
algoritmi
Esempio1: problema dell’ordinamento
Input: a1,a2,...,an
Output: a'1,a'2,...,a'n permutazione (riarrangiamento)
di a1,a2,...,an tale che a'1 ≤ a'2 ≤ ... ≤ a'n
TECNICA
INCREMENTALE
InsertionSort
Soluzione1: Algoritmo Insertion-Sort.
A
A
A
1
n
1j
n
1
j
n
1
i j
n
j
n
j
n
j
n
key
A
key
A
key
A
i1
A
A
1
1
1
i
n j
Insertion-Sort(A)
n = A.length
for j = 2 to n
key = A[j]
// inseriamo A[j] nella sequenza
// ordinata A[1..j-1]
i=j-1
while i > 0 and A[i] > key
A[i+1] = A[i]
i=i–1
A[i+1] = key
Insertion-Sort(A)
n = A.length
for j = 2 to n
key = A[j]
// inseriamo A[j] nella
// sequenza ordinata
// A[1..j-1]
i=j–1
while i > 0 and A[i] > key
A[i+1] = A[i]
i=i–1
A[i+1] = key
void Insertion-Sort(vector<T> A)
{
int i, j, n = A.size(); T key;
for (j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
key = A[j];
// inseriamo A[j] nella
// sequenza ordinata
// A[0..j-1]
i = j – 1;
while (i >= 0 && A[i] > key)
{
A[i+1] = A[i];
i--;
}
A[i+1] = key;
}
}
5
5
#
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
#
5
5
5
5
5
5
#
4
4
4
4
8
8
8
8
#
#
8
8
5
5
5
5
5
A
4 7
4 7
4 7
4 7
4 7
4 7
4 7
# 7
8 7
8 7
8 #
# 8
7 8
key
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
2
8
4
7
Insertion-Sort(A)
n = A.length
for j = 2 to n
// inserisce A[j] nella
// sequenza ordinata
// A[1..j-1]
key = A[j]
i=j–1
while i > 0 and A[i] > key
A[i+1] = A[i]
i=i–1
A[i+1] = key
2
2
#
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
4
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
5
5
4
4
4
#
3
3
3
3
A
7 8
7 8
5 7
5 7
5 7
4 5
4 5
4 5
4 5
4 5
key
1
#
8
8
8
7
7
7
#
6
3
3
3
3
#
8
8
8
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
#
8
8
1
3
6
Insertion-Sort(A)
n = A.lenght
for j = 2 to n
// inserisce A[j] nella
// sequenza ordinata
// A[1..j-1]
key = A[j]
i=j–1
while i > 0 and A[i] > key
A[i+1] = A[i]
i=i–1
A[i+1] = key
Analisi di Insertion-Sort: correttezza
Insertion-Sort(A)
n = A.length
for j = 2 to n
A
1
key = A[j]
i=j-1
while i > 0 and A[i] > key
A
j
n
1
i
j
n
1
i
j
n
j
n
A[i+1] = A[i]
i=i–1
A
i 1
A[i+1] = key
j
n
A
A
1
Correttezza InsertionSort
Analisi di Insertion-Sort: complessità
Insertion-Sort(A)
n = A.length
for j = 2 to n
key = A[j]
i = j -1
while i > 0 and A[i] > key
A[i+1] = A[i]
0 ≤ tj
i=i–1
A[i+1] = key
<j
//
//
//
//
//
//
//
//
//
c0
c1
c2 n
c3 (n − 1)
c4 (n − 1)
n
c5 ∑ j = 2 (t j + 1)
n
c6 ∑ j = 2 t j
n
c7 ∑ j = 2 t j
c8 (n − 1)
T IS (n) = c0 + c1 + c2 n + (c3 + c4 + c8 )(n − 1)
n
n
+ c5 ∑ j =2 (t j + 1) + (c6 + c7 )∑ j =2 t j
caso migliore:
tj = 0
0 ≤ tj < j
IS
min
T (n) = c0 + c1 + c2 n + (c3 + c4 + c8 )(n − 1)
n
n
+ c5 ∑ j = 21 + (c6 + c7 )∑ j =2 0
IS
Tmin
(n) = (c2 + c3 + c4 + c5 + c8 )n + (c0 + c1 − c3 − c4 − c5 − c8 )
= bn + a
caso peggiore:
t j = j −1
0 ≤ tj < j
IS
Tmax
(n) = c0 + c1 + c2 n + (c3 + c4 + c8 )(n − 1)
n
n
+ c5 ∑ j =2 j + (c6 + c7 )∑ j =2 ( j − 1)
IS
max
T
1
(n) = (c5 + c6 + c7 )n 2
2
1
1
1
+ (c2 + c3 + c4 + c5 − c6 − c7 + c8 )n
2
2
2
+ (c0 + c1 − c3 − c4 − c8 )
= c ' n 2 + b' n + a '
caso medio: t j =
IS
med
T
T
0 ≤ tj < j
(n) = c0 + c1 + c2 n + (c3 + c4 + c8 )(n − 1)
+ c5 ∑
IS
med
j −1
2
n
j +1
j =2 2
n
+ (c6 + c7 )∑ j =2 j2−1
1
(n) = (c5 + c6 + c7 )n 2
4
3
1
1
+ (c2 + c3 + c4 + c5 − c6 − c7 + c8 )n
4
4
4
+ (c1 − c3 − c4 − c5 − c8 )
2
= c" n + b" n + a"