Esercizio 1
Inserisci i nomi corrispondenti alle varie parti del corpo, in base all’immagine qui sotto:
Esercizio 2.
Con l’aiuto del vocabolario, scegli la risposta esatta tra le seguenti:
1. Could you lend me a handkerchief please? I have ……………………
a) hiccups,
b) goose pimples,
c) a runny nose;
2. I fell off my bike yesterday and ……………… my hands and knees. I cleaned them and put on Band-Aids.
a) scratched,
b) sprained,
c) broke;
3. Patricia is allergic to pollen; she has been .......................... all day.
a) sneezing,
b) hiccupping,
c) bleeding;
4. ...................... results from involuntary spasms of the diaphragm. To stop it, try to breathe into a paper
bag five times in a row.
a) a cough,
b) a hiccup,
c) a sneezing;
5. ...................is a contagious disease that causes fever and swollen salivary glands.
a) Flu
b) Mumps
c) Measles
6. Betty has a fever; it makes her feel ............... all over her body.
a) sore
b) dizzy
c) ache
7. When she is very hungry, Lucy feels sick and ............. as if she was about to faint.
a) dizzy
b) scratched
c) bruised
8. ...........can strike more easily than you might think. Use a special cream to protect yourself from the
dangerous rays of the sun.
a) A Sunburn
b) A splinter
c) A shiver
9. ............... are those black and blue marks you get after you take a punch to your body.
a) Blisters
b) Bruises
c) Bumps
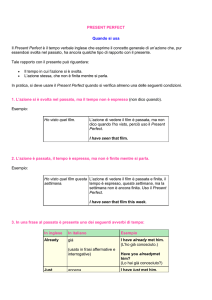
IL PRESENT PERFECT
Il Present Perfect è il tempo verbale inglese che esprime il concetto generale di un’azione che, pur
essendosi svolta nel passato, ha ancora qualche tipo di rapporto con il presente.
Esempio: I can’t go on holiday because I have broken my leg
Tale rapporto con il presente può riguardare:
Il tempo in cui l’azione si è svolta.
L’azione stessa, che non è finita mentre si parla o ha ancora un effetto sul nostro presente.
In pratica, si deve usare il Present Perfect quando si verifica almeno una delle seguenti condizioni.
1. L’azione si è svolta nel passato, ma il tempo non è espresso (non dico quando).
Esempio: I have seen that film. (Ho visto quel film)
L’azione di vedere il film è passata, ma non dico quando l’ho visto, perciò uso Il Present Perfect.
2. L’azione è passata, ma il tempo a cui si riferisce non è finito mentre si parla.
Esempio: I have seen that film this week. (Ho visto quel film questa settimana)
L’azione di vedere il film è passata e finita, il tempo è espresso, questa settimana, ma la settimana non è
ancora finita. Uso il Present Perfect.
3. L’azione è iniziata nel passato ma non è ancora finita nel momento in cui si parla.
Sono frasi in cui in italiano si usa il presente indicativo ed un'espressione di tempo introdotta dalla
preposizione da:
Esempio: Vivo in Inghilterra da quattro anni, oppure: Lo conosco dal 1995, oppure: Da quanto tempo lo
conosci? oppure: Ho la tosse da due settimane.
In inglese il verbo viene messo al Present Perfect, mentre l'espressione di tempo è introdotta da:
- SINCE quando è espresso il momento di inizio dell’azione: "da quando?"
Esempio: I have known him since 1995. (Lo conosco dal 1995).
- FOR quando è espressa la durata dell’azione: "da quanto tempo?"
Esempio: I have known him for three years. (Lo conosco da tre anni). oppure: I’ve had the cough for two
weeks. (Ho la tosse da due settimane).
Nelle domande l’espressione "da quanto tempo / da quando…?" si esprime in inglese con HOW LONG?
Esempio: How long have you known him? (Da quanto tempo lo conosci?) oppure: How long have you had
these symptoms? (Da quanto tempo ha questi sintomi?)
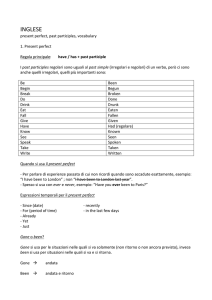
4. In una frase al passato c’è uno dei seguenti avverbi di tempo:
In inglese
In italiano
Esempio
Already
Già
I have already met him.
(usato in frasi affermative e (L'ho già conosciuto.)
interrogative)
Have you already met him?
(Lo hai già conosciuto?)
Just
Appena
Ever
mai
Have you ever met him?
(usato in frasi interrogative) (Lo hai mai conosciuto?)
Never
mai
I have never met him.
(vuole sempre il verbo nella (Non l'ho mai conosciuto.)
forma affermativa)
Recently
Lately
Recentemente
Yet
a) ancora (in frasi negative) a) I haven't met him yet.
(Non l'ho ancora conosciuto.)
b) già (in frasi interrogative)
b) Have you met him yet?
(Lo hai già conosciuto?)
I have just met him.
(L'ho appena conosciuto.)
I have met him recently.
(L'ho conosciuto recentemente.)
Nota:
Already, just, ever, never si collocano tra l'ausiliare have/has e il verbo.
Esempio: I have just finished, (ho appena finito) oppure: I have never seen him, (non l'ho mai visto).
Yet, recently, lately si mettono alla fine della frase.
Esempio: I haven’t finished yet. (Non ho ancora finito).
Come si costruisce
Il Present Perfect è un tempo composto che utilizza l’ausiliare TO HAVE al Simple Present ed il Participio
Passato (3° voce del paradigma, vedi tabella dei verbi irregolari della lezione 7) del verbo della frase.
Essendo un tempo composto, è l’ausiliare have a prendere la forma interrogativa e negativa, il verbo
rimane al suo posto al participio passato.
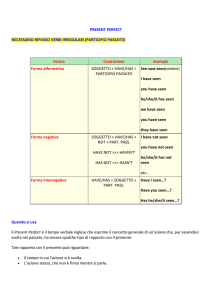
Forma affermativa
I have seen
you have seen
he/she/it has seen
we have seen
you have seen
they have seen
Forma negativa
I have not seen
you have not seen
he/she/it has not seen
we have not seen
you have not seen
they have not seen
Forma interrogativa
Have I seen
Have you seen
Has he/she/it seen
Have we seen
Have you seen
Have they seen
forma contratta: I’ve forma contratta: I
seen, you’ve seen,
haven’t seen, you
he’s seen, etc.
haven’t seen, he hasn’t
seen, etc.
Esercizio 3:
Completa le seguenti frasi con uno dei verbi del box qui sotto, coniugato al present perfect:
buy
decide
forget
go
see
not see
take
tell
finish
invite
1. “Can I have this newspaper?” “Yes, I ……………………..with it.”
2. I ……………………………………some new shoes. Do you want to see them?”
3. “Where’s Liz?” “She …………………….. out”.
4. I’m looking for Paula. ………………… you …………………….. her?”
5. Does Lisa know you’re going away?” “Yes, I ……………………………her.”
6. I can’t find my umbrella. Somebody …………………………… it.
7. Sue is having a party tonight. She ………………..a lot of people.
8. What are you going to do? ……………………… you ……………………………?
9. I know that woman but I ……………………………..her name.
10. “Where are my glasses?” “I don’t know, I ………………………………………….them.”
Esercizio 4:
Fai delle domande con: “How long….?” come nell’esempio qui sotto:
Jill is on holiday.
Domanda: How long has she been on holiday?
1.I know Sarah.
Domanda: ……………………………………………………………………………..………
2.Diana works in a restaurant .Domanda: ……………………………………………………………………………………….
3.My brother lives in Canada. Domanda:…………………………………………………………………………………………
4.I’m a teacher.
Domanda:……………………………………………………………………………………….
5. I have a sore throat.
Domanda:……………………………………………………………………………………….
Esercizio 5:
Completa le seguenti frasi scegliendo tra le parole del box qui sotto:
already
already
for
for
ever
ever
just
since
yet
yet
1. My aunt has lived in Australia ……………. 15 years.
2.Margaret is in her office. She has been there ……………7 o’clock.
3. It’s only nine o’clock and Anna has ………………..gone to bed.
4. Have you …………………played golf?
5. “Has Linda started her new job ………………….?”
6. “Are Diana and Paul here?” “Yes, they’ve ……………….arrived.”
7. “John this is Mary.” “Yes. I know. We’ve ………………..met.”
8. “Does John know that you’re going away?” “No, I haven’t told him ……….”
9. The bus is late. We have been waiting ……………. 20 minutes.
10.Have you ………………..eaten Chinese food?
Esercizio 6:
In ognuna delle seguenti frasi c’è un errore. Trovalo.
1) Ten years ago Ted has asked Rosie to marry him.
2)Mr. Brown broughted me some work to do yesterday.
3) We’ve gone swimming last week. The sea was calm.
4) When I were at college, lessons began at 8 o’clock.
5) Did you ever been to Rome?
6) They never saw a tiger before.
7) I worked for Mr. Cooper since I left school.
8) I lived here for six years.
9) She has met Tom three days ago.
10) Have he arrived yet?