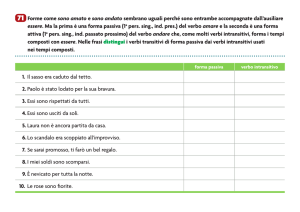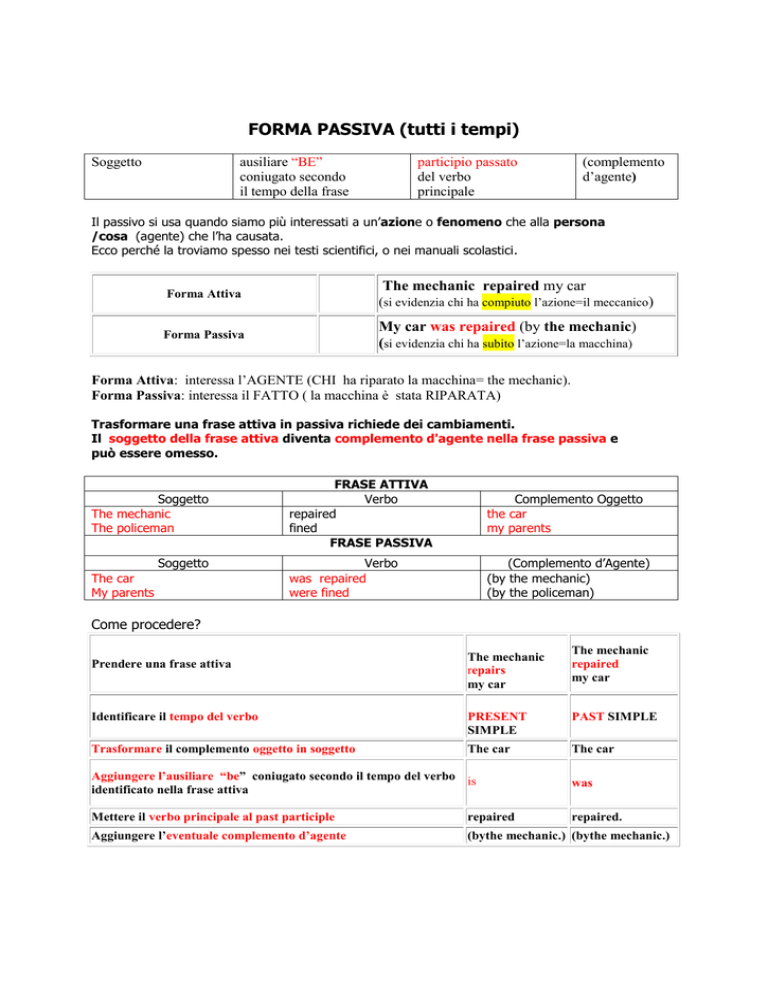
FORMA PASSIVA (tutti i tempi)
ausiliare “BE”
coniugato secondo
il tempo della frase
Soggetto
participio passato
del verbo
principale
(complemento
d’agente)
Il passivo si usa quando siamo più interessati a un’azione o fenomeno che alla persona
/cosa (agente) che l’ha causata.
Ecco perché la troviamo spesso nei testi scientifici, o nei manuali scolastici.
The mechanic repaired my car
Forma Attiva
(si evidenzia chi ha compiuto l’azione=il meccanico)
My car was repaired (by the mechanic)
(si evidenzia chi ha subito l’azione=la macchina)
Forma Passiva
Forma Attiva: interessa l’AGENTE (CHI ha riparato la macchina= the mechanic).
Forma Passiva: interessa il FATTO ( la macchina è stata RIPARATA)
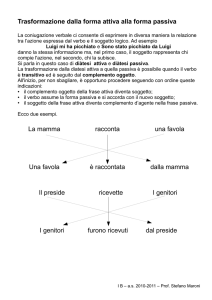
Trasformare una frase attiva in passiva richiede dei cambiamenti.
Il soggetto della frase attiva diventa complemento d'agente nella frase passiva e
può essere omesso.
Soggetto
The mechanic
The policeman
Soggetto
The car
My parents
FRASE ATTIVA
Verbo
repaired
fined
FRASE PASSIVA
Complemento Oggetto
the car
my parents
Verbo
was repaired
were fined
(Complemento d’Agente)
(by the mechanic)
(by the policeman)
Come procedere?
Prendere una frase attiva
The mechanic
repairs
my car
The mechanic
repaired
my car
Identificare il tempo del verbo
PRESENT
SIMPLE
PAST SIMPLE
Trasformare il complemento oggetto in soggetto
The car
The car
Aggiungere l’ausiliare “be” coniugato secondo il tempo del verbo is
identificato nella frase attiva
was
Mettere il verbo principale al past participle
repaired
repaired.
Aggiungere l’eventuale complemento d’agente
(bythe mechanic.) (bythe mechanic.)
SPECCHIETTO DEI TEMPI PRINCIPALI della FORMA PASSIVA
Present
My car is repaired ( by the
The mechanic repairs my car
Simple
mechanic)*
The mechanic is repairing my car
Present
Progressive
My car is being repaired
The mechanic has repaired my car
Present
Perfect
My car has been repaired
The mechanic repaired my car
Past Simple
My car was repaired
The mechanic will repair my car
Future Simple My car will be repaired
The mechanic wants to repair my car
Infinitive
The mechanic can repair my car
The mechanich must repair my car
The mechanic may repair my car
The mechanic should repair my car
Verbi modali
+ Infinitive
I want my car to be repaired (by
the mechanic)
My car can be repaired
My car must be repaired
My car may be repaired
My car should be repaired
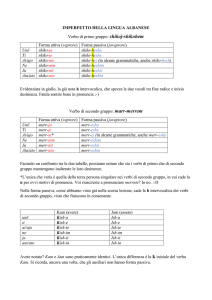
NOTA BENE: I verbi intransitivi non possono diventare passivi
Il passivo si costruisce trasformando un complemento oggetto in soggetto.
Ciò è possibile in presenza di verbi transitivi. Cioè quando l’azione espressa dal verbo passa da un soggetto a
un (complemento) oggetto.
“Spostare” una sedia è un verbo transitivo. (La sedia è stata spostata)
“Rompere” una finestra” è un verbo transitivo. (La finestra è stata rotta)
“Salutare” un amico è un verbo transitivo (L’amico è stato salutato)
Ciò non è possibile con i verbi intransitivi dove non c’è :
Si può dire “Piove”, non “E’ stato piovuto”
Si può dire “Dormee”, non “ E’ stato dormito?”
Pertanto i verbi intransitivi (verbi che non reggono un complemento oggetto) non possono
essere usati nella forma passiva. Alcuni esempi di verbi intransitivi sono arrive, sleep, die,
walk, rain, snow e smile.
Nemmeno alcuni verbi di stato (verbi che descrivono uno stato o una condizione, e che non
hanno le forme progressive) possono essere usati nella forma passiva. Alcuni esempi sono
have (=possedere), belong to, resemble, suit e fit (=essere della misura giusta).
EXERCISES
1. Present Simple passive: Scrivi frasi alla forma passiva.
1.
the documents / print = The documents are printed
2.
the window / open
3.
the shoes / buy
4.
the car / wash
5.
the litter / throw away
6.
the letter / send
7.
the book / read / not
8.
the songs / sing / not
9.
the food / eat / not
10.
the shop / close / not
2. Past Simple passive. Scrivi frasi alla forma passiva.
0. the test / write = The test was written
1. the table / set
2. the cat / feed
3. the lights / switch on
4. the house / build
5. dinner / serve
6. this computer / sell / not
7. the car / stop / not
8. the tables / clean / not
9. the children / pick up / not
3. Present Perfect passive. Scrivi frasi alla forma passiva.
0. the postcard / send = The postcard has been sent
1. the pencils / count
2. the door / close
3. the beds / make
4. the mail / write
5. the trees / plant
6. the money / spend
7. the room / book / not
8. the rent / pay / not
9. the people / inform / not
4. Future Simple passive. Scrivi frasi alla forma passiva.
1
the exhibition / visit = The exhibition will be visited
2.
the windows / clean
3.
the message / read
4.
the thief / arrest
5.
the photo / take
6.
these songs / sing
7.
the sign / see / not
8.
a dictionary / use / not
9.
credit cards / accept / not
10.
the ring / find / not
5. ATTIVO O PASSIVO?
Usa il Simple Present o il Simple Past.
The Statue of Liberty
Esercizio: completa le frasi ( alla forma attiva o passiva);
1.
The Statue of Liberty (give)_was given _ to the United States by France.
2.
It (be) __was___ a present on the 100th anniversary of the United States.
3.
The Statue of Liberty (design)__________ by Frederic Auguste Bartholdi.
4.
It (complete)_________ in France in July 1884.
5.
In 350 pieces, the statue then (ship)_________ to New York, where it
(arrive) _________ on 17 June 1885.
6.
The pieces (put) _________together and the opening ceremony (take)
place on 28 October 1886.
7.
The Statue of Liberty (be) ____________ 46 m high (93 m including the
base).
8.
The statue (represent)_____________ the goddess of liberty.
9.
She (hold) ___________ a torch in her right hand and a tablet in her left
hand.
10. On the tablet you (see / can)______________ the date of the Declaration of
Independence (July 4, 1776).
11. Every year, the Statue of Liberty (visit) _______________ by many people
from all over the world
Check Answ ers
Mark wrong answers
Replace wrong by correct answers
Show all correct answers
6. Esercizi sul testo. Leggi i brani e svolgi le attività indicate .
Se non comprendi alcuni vocaboli, puoi consultare il dizionario multilingue online:
www.wordreference.com
Washington, DC
Washington, DC is the capital of the United States. DC stands for District of Columbia and
means that Washington is not part of any federal state , but a unique district. The citizens of
Washington, DC have no voting representation in Congress and are ) not at all represented in
the Senate.
White House
The White House is the working place and residence of the United States President. It was
built between 1792 and 1800 and has 132 rooms. There is also a swimming pool, movie
theater, tennis court and bowling lane.
United States Capitol
A long mall connects the White House and the Capitol home of the Congress). The House of
Representatives is in the south wing and the Senate in the north wing. On Inauguration Day
(January 20), the President holds his inaugural address on the steps of the Capitol and then
usually parades from the Capitol to the White House.
FORMA PASSIVA: Usiamo la forma passiva per enfatizzare un fatto. Chi/Cosa lo ha
causato non è altrettanto importante ( oppure è ignoto)
Esercizio: riscrivi le frasi seguenti, trasformandole da attive in passive e viceversa.
Attiva:
>Passiva:
Many people visit Washington.
Washington is visited by many people
Passiva:
>Attiva:
The White House was built by James Hoban.
Passiva:
>Attiva:
The White House and the Capitol are connected by Pennsylvania Avenue.
Attiva:
>Passiva:
In the Capitol, workers are building a visitors center.
Attiva:
>Passiva:
They will probably finish it in 2006.
7. Hadrian's Wall (il vallo di Adriano)
Completa il testo con il tempo corretto. Usa la forma attiva o passiva.
1.
2.
In the year 122 AD, the Roman Emperor Hadrian (visit)
Britain.
On his visit, the Roman soldiers (tell)
Britain's north (attack)
3.
his provinces in
him that Pictish tribes from
them.
So Hadrian (give)
narrowest parts of the country.
the order to build a protective wall across one of the
4.
After 6 years of hard work, the Wall (finish)
5.
It (be)
6.
The Wall (guard)
in 128.
117 kilometres long and about 4 metres high.
by 15,000 Roman soldiers.
7.
Every 8 kilometres there (be)
(find)
8.
a large fort in which up to 1,000 soldiers
shelter.
The soldiers (watch)
over the frontier to the north and (check)
the people who (want)
9.
In order to pass through the Wall, people (must go)
forts that (serve)
10.
milecastles because the distance from one fort to
one Roman mile (about 1,500 metres).
Between the milecastles there (be)
(guard)
12.
to one of the small
as gateways.
Those forts (call)
another (be)
11.
to enter or leave Roman Britain.
two turrets from which the soldiers
the Wall.
If the Wall (attack)
by enemies, the soldiers at the turrets (run)
to the nearest milecastle for help or (light)
a fire that (can / see)
by the soldiers in the milecastle.
13.
In 383 Hadrian's Wall (abandon)
14.
Today Hadrian's Wall (be)
England.
15.
In 1987, it (become)
.
the most popular tourist attraction in northern
a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Check answ ers
Changed: 07th Nov 2006 01:32
URL: http://www.ego4u.com/en/cram-up/tests/hadrians-wall