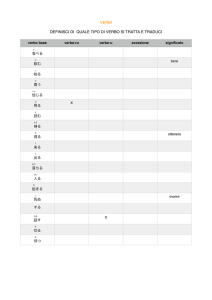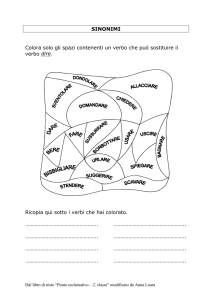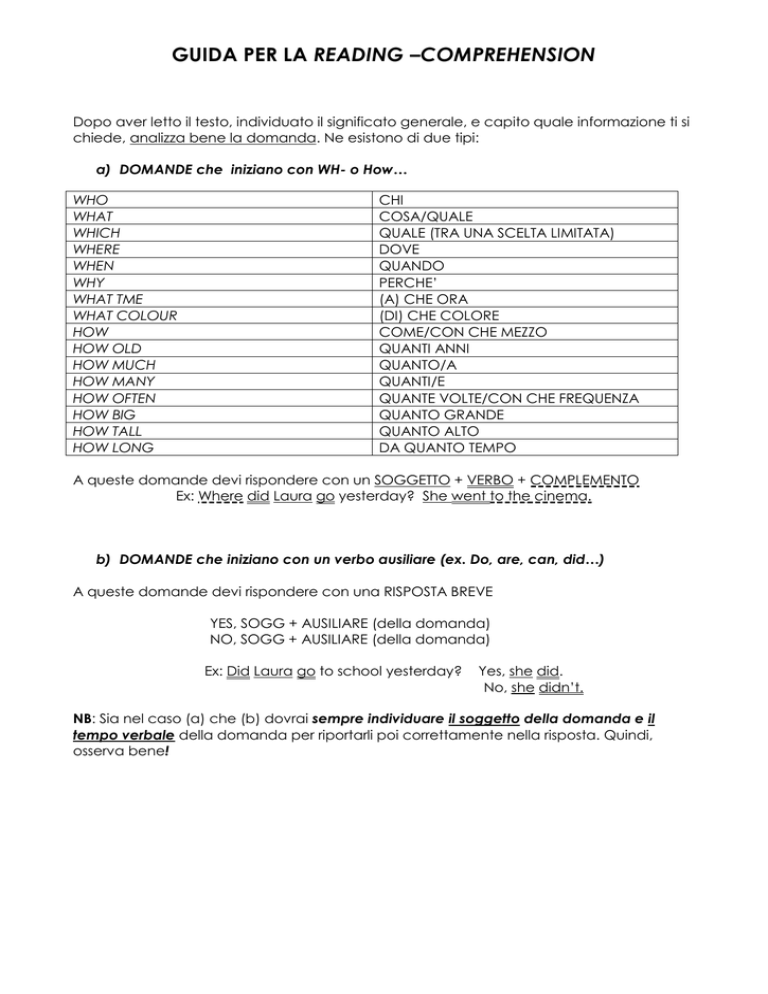
GUIDA PER LA READING –COMPREHENSION
Dopo aver letto il testo, individuato il significato generale, e capito quale informazione ti si
chiede, analizza bene la domanda. Ne esistono di due tipi:
a) DOMANDE che iniziano con WH- o How…
WHO
WHAT
WHICH
WHERE
WHEN
WHY
WHAT TME
WHAT COLOUR
HOW
HOW OLD
HOW MUCH
HOW MANY
HOW OFTEN
HOW BIG
HOW TALL
HOW LONG
CHI
COSA/QUALE
QUALE (TRA UNA SCELTA LIMITATA)
DOVE
QUANDO
PERCHE’
(A) CHE ORA
(DI) CHE COLORE
COME/CON CHE MEZZO
QUANTI ANNI
QUANTO/A
QUANTI/E
QUANTE VOLTE/CON CHE FREQUENZA
QUANTO GRANDE
QUANTO ALTO
DA QUANTO TEMPO
A queste domande devi rispondere con un SOGGETTO + VERBO + COMPLEMENTO
Ex: Where did Laura go yesterday? She went to the cinema.
b) DOMANDE che iniziano con un verbo ausiliare (ex. Do, are, can, did…)
A queste domande devi rispondere con una RISPOSTA BREVE
YES, SOGG + AUSILIARE (della domanda)
NO, SOGG + AUSILIARE (della domanda)
Ex: Did Laura go to school yesterday?
Yes, she did.
No, she didn’t.
NB: Sia nel caso (a) che (b) dovrai sempre individuare il soggetto della domanda e il
tempo verbale della domanda per riportarli poi correttamente nella risposta. Quindi,
osserva bene!
Se nella domanda c’è…
il tempo è…
…e nella risposta…
DO +S +INF
PRESENT SIMPLE
Riporti il verbo che vedi dopo il soggetto.
(Ex. What subjects do you like?)
(abitudini)
(Ex. I like music)
DOES +S +INF
PRESENT SIMPLE
Riporti il verbo che vedi dopo il soggetto +
(Ex. What subjects does she like?)
(abitudini)
S della terza persona (Ex. She likeS music)
DID +S +INF
PAST SIMPLE
Riporti il verbo che vedi dopo il soggetto o
(Ex. Where did she go?)
(azioni terminate)
alla forma –ed (verbi regolari) o alla forma
che trovi nella seconda colonna del
paradigma (Ex. She went to the cinema)
AM / IS / ARE + S + …ING
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Riporti l’ausiliare ed il verbo in ing. (Ex. She
(Ex. What is she doing?)
(azioni in corso o futuro
is going to the cinema)
programmato)
WAS/WERE + S + …ING
PAST CONTINUOUS
Riporti l’ausiliare ed il verbo in ing. (Ex. She
(Ex. What was she doing?)
(azioni in corso nel
was going to the cinema)
passato)
HAVE/HAS + S + PART. PASSATO
PRESENT PERFECT
Riporti l’ausiliare HAVE o HAS ed il participio
(Ex. Where have you been?)
(azioni recenti,
passato. (Ex. I have been to London)
esperienze, durata
R.E.D.)
AM/IS/ARE + S + GOING TO +INF
GOING TO FUTURE
Riporti l’ausiliare, going to e il verbo. (Ex.
( Ex. What is she going to do?)
(futuro intenzionale o
She is going to buy a car)
previsioni certe)
WILL +S +INF
WILL FUTURE
Riporti will e un verbo infinito. (Ex. I will study
(Ex. What will you do next year?)
(previsioni incerte,
in Vicenza)
decisioni prese ora)
AM / ARE / IS + S
AM-IS-ARE
Rispondi con il verbo essere. (Ex. Yes, she
(Ex. Is your sister a student?)
(verbo essere)
is.)
HAVE / HAS + S + GOT
HAVE GOT
Riporti il verbo avere. (Ex. I have got a lot
(Ex. How many CDs have you got?)
(verbo possedere)
of CDs.)
WAS-WERE + S
WAS-WERE
Riporti il verbo was/were. (Ex. They were at
(Ex. Where were they yesterday?)
(verbo essere –passato)
the cinema)
CAN + S
MODALE CAN
Riporti il verbo can e l’infinito. (Ex. I can
(Ex. What languages can you speak?)
(sapere-potere)
speak English and German)
COULD + S
MODALE COULD
Riporti could e un infinito (Ex. No, but I
(Ex. Could you swim 5 years ago?)
(potere – condizionale)
could ride a bike)
WOULD + S
MODALE WOULD
Riporti il would e l’infinito. (Ex. Yes, I would
(Ex. Would you buy a new house?)
(condizionale)
buy a new mobile phone)
SHOULD + S
MODALE SHOULD
Riporti il should e l’infinito. (Ex. You should
(Ex. What should I do?)
(dovere- condizionale)
study more)
MUST + S
MODALE MUST
Riporti must e l’infinito (Ex. No, she must go
(Ex. Mustshe go to work tomorrow?)
(dovere –obbligo)
to the dentist’s.)