Fondamenti di Java
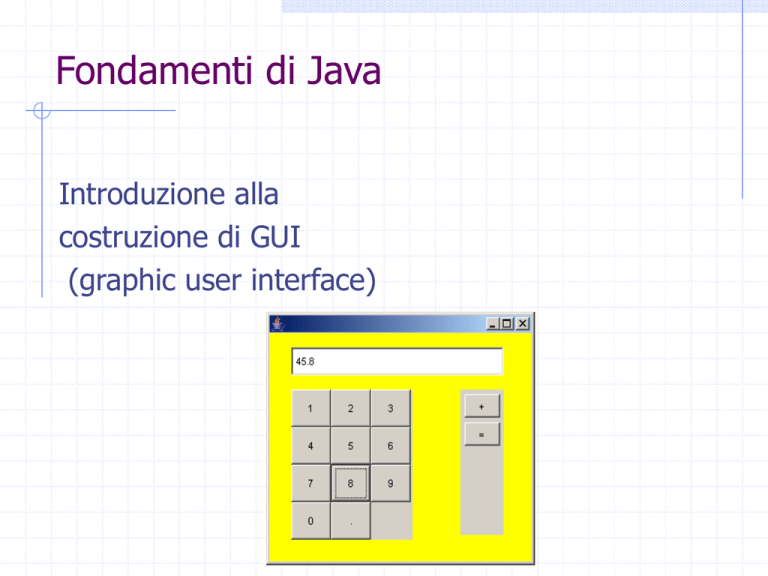
Introduzione alla
costruzione di GUI
(graphic user interface)
component - container - layout
Un Container contiene [0 o +] Components
Il Layout specifica come i Components sono disposti nel Container
Un Container è un Component (quindi il contenimento è ricorsivo)
Un Component ha una Graphics associata
Component
Graphics
posiziona
Container
Layout
awt component hierarchy
Component
Button
Canvas
List
Checkbox
Scrollbar
Choice
TextComponent
Label
TextArea
TextField
awt container hierarchy
Container
Panel
A pplet
Window
Frame
ScrollPanel
Dialog
FileDialog
Swing component hierarchy
Component
java.awt
Container
JComponent
JPanel
Swing “containers”
javax.swing
JButton
Swing “components”
Top Level Containers
TUTORIAL:
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/
General Purpose Containers
Special Purpose Containers
Basic Controls
Uneditable Information
More complex structures
Prima applicazione
JFrame
App
YellowWindow
JFrame
class YellowWindow
package it.unitn.science.prog2.guiApp;
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*;
public class YellowWindow extends JFrame
{
private JPanel contentPane;
public YellowWindow()
{
try { jbInit(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
private void jbInit() throws Exception
{
contentPane=(JPanel)this.getContentPane();
this.setSize(new Dimension(400, 300));
contentPane.setBackground(Color.YELLOW);
}
}
class App
package it.unitn.science.prog2.guiApp;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class App
{
JFrame finestra=null;
public static void main(String[ ] a){
new App();
}
public App() {
// aggiungere qui: set look&feel (vedi oltre)
this.setupGraphicEnvironment();
}
class App
private void setupGraphicEnvironment() {
finestra = new YellowWindow(); //new CalculatorWindow
// trova le dimensioni dello schermo e della finestra
Dimension screenSize =
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize();
Dimension frameSize = finestra.getSize();
// assicurati che la finestra non sia più grande dello schermo
if (frameSize.height > screenSize.height)
frameSize.height = screenSize.height;
if (frameSize.width > screenSize.width)
frameSize.width = screenSize.width;
class App
// centra la finestra nello schermo
finestra.setLocation((screenSize.width - frameSize.width) / 2,
(screenSize.height - frameSize.height) / 2);
// fai in modo che la chiusura della finestra
// termini l'applicazione
finestra.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE
);
// rendi la finestra visibile
finestra.setVisible(true);
}
}
18
Event Listeners
Some Events and Their Associated Event Listeners
Act that Results in the Event
Listener Type
User clicks a button, presses Enter while typing
in a text field, or chooses a menu item
ActionListener
User closes a frame (main window)
WindowListener
User presses a mouse button while the cursor is
over a component
MouseListener
User moves the mouse over a component
MouseMotionListener
Component becomes visible
ComponentListener
Component gets the keyboard focus
FocusListener
Table or list selection changes
ListSelectionListener
Any property in a component changes such as
the text on a label
PropertyChangeListener
19
ActionListener
public interface ActionListener extends EventListener
The listener interface for receiving action events. The
class that is interested in processing an action event
implements this interface, and the object created with
that class is registered with a component, using the
component's addActionListener method.
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
Invoked when an action occurs
20
ActionEvent
ActionEvent extends AWTEvent
A semantic event which indicates that a componentdefined action occured. This high-level event is
generated by a component (such as a Button) when
the component-specific action occurs (such as being
pressed). The event is passed to every every
ActionListener object that registered to receive such
events using the component's addActionListener
method.
21
ActionEvent
Method Summary
String getActionCommand()
Returns the command string associated with this action.
int getModifiers()
Returns the modifier keys held down during this action event.
long getWhen()
Returns the timestamp of when this event occurred.
String paramString()
Returns a parameter string identifying this action event.
Methods Inherited
…
public Object getSource()
Returns The object on which the Event initially occurred.
Seconda applicazione
JFrame
JPanel
ActionListener
ButtonPanel
Painter
3
Button
addActionListener
23
Esempio
package actionlistener;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class ButtonPanel extends JPanel {
public ButtonPanel() {
super();
JButton button1 = new JButton("Giallo");
JButton button2 = new JButton("Verde");
JButton button3 = new JButton("Rosso");
this.add(button1);
this.add(button2);
this.add(button3);
Painter azioneGiallo = new Painter(Color.YELLOW,this);
Painter azioneVerde = new Painter( Color.GREEN,this);
Painter azioneRosso = new Painter(Color.RED,this);
button1.addActionListener(azioneGiallo);
button2.addActionListener(azioneVerde);
button3.addActionListener(azioneRosso);
}
24
Esempio - continua
public static void main(String a[]) {
JFrame f=new JFrame();
f.setContentPane(new ButtonPanel());
f.setSize(300,300);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
class Painter implements ActionListener {
private Color colore;
private JPanel contenitore;
public Painter(Color colore, JPanel contenitore) {
this.colore = colore;
this.contenitore=contenitore;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
contenitore.setBackground(colore);
}
}
25
Esempio 2
public class ButtonPanel extends JPanel {
public ButtonPanel() {
super();
Painter p=new Painter(this);
String c[]={"Giallo","Verde","Rosso"};
for (int i=0;i<c.length;i++) {
JButton b=new JButton(c[i]);
this.add(b);
b.addActionListener(p);
// b.setActionCommand(c[i]);
}
}
public static void main(String a[]) {
JFrame f=new JFrame();
f.setContentPane(new ButtonPanel());
f.setSize(300,300);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
26
Esempio 2 - continua
class Painter implements ActionListener {
private JPanel contenitore;
private Color colore;
public Painter(JPanel contenitore) {
this.contenitore=contenitore;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
String s=((JButton)actionEvent.getSource()).getText();
//String s=actionEvent.getActionCommand();
if (s.equals("Giallo")) colore=Color.YELLOW;
else if (s.equals("Rosso")) colore=Color.RED;
else if (s.equals("Verde")) colore=Color.GREEN;
contenitore.setBackground(colore);
}
}
27
Esempio 3
public class ButtonPanel extends JPanel {
public ButtonPanel() {
super();
Painter p=new Painter(this);
this.setLayout(null);
String c[]={"Giallo","Verde","Rosso"};
for (int i=0;i<c.length;i++) {
JButton b=new JButton(c[i]);
b.setSize(100,50);
b.setLocation(i*100,i*50);
this.add(b);
b.addActionListener(p);
b.setActionCommand(c[i]);
}
}
NON CONSIGLIATO – LAYOUT NON LIQUIDO!
28
Compito
Scrivere un applicazione contenente un bottone
che quando viene premuto si sposta altrove
nella finestra.
Scrivere una applicazione contenente due
bottoni: uno ingrandisce la dimensione della
finestra, l’altro la rimpicciolisce
29
Mouse events
This low-level event is generated by a component object
for:
Mouse Events
a mouse button is pressed
a mouse button is released
a mouse button is clicked (pressed and released)
the mouse cursor enters the unobscured part of
component's geometry
the mouse cursor exits the unobscured part of
component's geometry
Mouse Motion Events
the mouse is moved
the mouse is dragged
30
Compito
Scrivere un applicazione contenente un TextField
il cui valore inizialmente è zero, e che viene
incrementato di uno ogni volta che il bottone
del mouse viene cliccato.
Scrivere un’applicazione contenente un bottone
che si posiziona dove viene cliccato il bottone
del mouse. Se invece viene cliccato il bottone
grafico, questo si riposiziona nella sua sede
iniziale.
Pluggable Look&Feel
Scelta del Look&Feel
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(
UIManager.getCrossPlatformLookAndFeelClassName());
} catch (Exception e) { }
new SwingApplication(); //Create and show the GUI.
}
UIManager.getCrossPlatformLookAndFeelClassName()
Returns the Java look and feel.
UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName()
Specifies the look and feel for the current platform.
Scelta del Look&Feel
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(
"com.sun.java.swing.plaf.gtk.GTKLookAndFeel");
} catch (Exception e) { }
new SwingApplication(); //Create and show the GUI.
}
UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName(String s)
Specifies the look and feel for the platform described by
“s”.
Available Look&Feel
"com.sun.java.swing.plaf.gtk.GTKLookAndFeel"
Specifies the GTK+ look and feel. Introduced in release
1.4.2.
"javax.swing.plaf.metal.MetalLookAndFeel"
Specifies the Java look and feel.
"com.sun.java.swing.plaf.windows.WindowsLookAndFeel"
Specifies the Windows look and feel. Currently, you can
use this look and feel only on Microsoft Windows
systems.
"com.sun.java.swing.plaf.motif.MotifLookAndFeel"
Specifies the CDE/Motif look and feel. This look and
feel can be used on any platform.