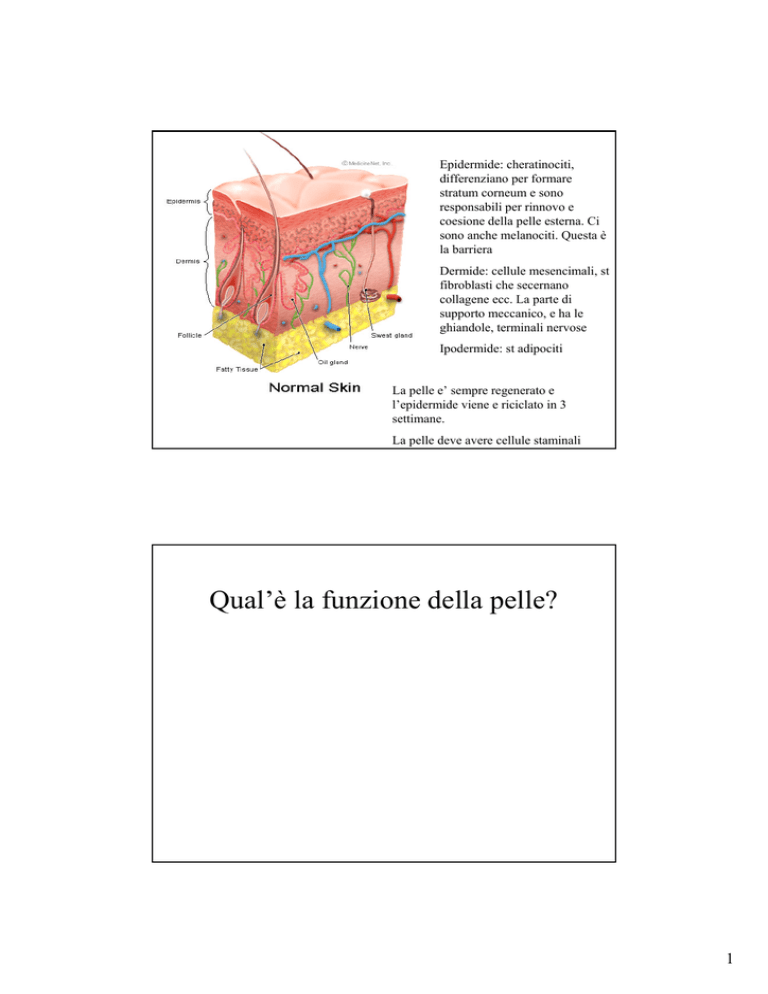
Epidermide: cheratinociti,
differenziano per formare
stratum corneum e sono
responsabili per rinnovo e
coesione della pelle esterna. Ci
sono anche melanociti. Questa è
la barriera
Dermide: cellule mesencimali, st
fibroblasti che secernano
collagene ecc. La parte di
supporto meccanico, e ha le
ghiandole, terminali nervose
Ipodermide: st adipociti
La pelle e’ sempre regenerato e
l’epidermide viene e riciclato in 3
settimane.
La pelle deve avere cellule staminali
Qual’è la funzione della pelle?
1
Ferite di terzo e secondo grado profondo non
rigenerano senza graft.
Altri problemi:ulcere, vitiligine, ferite profonde,
epidermolysis bullosa, psoriaisi, melanoma
Le cellule staminali della pelle identificate sono unipotenti o multi
potenti. Cellule staminale del epidermide sono unipotenti, mentre quelli
nella follicola multipotenti, e migrane nel epidermide dove diventano
unipotenti.
Si dividono molto lentamente (madre fa due figlie di cui solo una resta
staminale). Sono le figlie non staminali che replicano velocemente. Si
pensa che con solo 1 cellula staminale epidermale se riesce a generare
tutto il epitelio del epidermide necessaria per un adulto.
Quelli del derma sono multipotenti e possono formare epidermide,
follicoli, ghiandole. Non è chiaro come i diversi tipi (almeno 6)
migrano al epidermide e quale sono i segnali morfogenetici che li fanno
diventare una cosa o un altro.
Le terapia genica- trapianto di cellule staminali del epidermide- non e’
in grado - fino ad ora -di regenerare follicoli, ghiandole sebacei e
sudorifere. (ne la pelle ingegnerizzzato).
2
Prima di capire come fare la pelle ingegenrizzato, bisogna capire come avviene il processo
di guarigione dellea pelle, o “wound healing”. Sono 3 fasi principali, infiammazione,
remodellamento e proliferazione.
La prima fase, formazione di un trombo rechiede un interazone tra cellle endoteliali,
piastrine e fattori di coagulazione. Sono le piastrine che poi scatenano una risposta
infiammatoria, cosi importante per iniziare il processo.
Sembra che siano i macrofaghi che corrdinano la trasizione da inf a prof. attraverso il
rilascio di citchine e altri mediatori, st PDGF.
Per il fase della proliferazione, le cellule piu importanti sono i fibroblasti. Producono
collagnee, fn e proteglicani come HA.
Dopo avviene una fase di contrazione in cui il tessuto vecchio intorno al neo tessuto se ritira,
a causa della pulizia enzimatica atraverso le proteasi. Sono coinvolti anche i cheratinociti.
Remodellamento, l’ultima fase puo durare settimane o mesi. Consiste nel remodellamento
delal cicatrice attraverso una riduzione di conentuto cellulare e di vascolarizzazione.
Il problema piu grave è non tanto le ustioni, che problemi conessi con disturbi del processo
di guarigione. (neuropatia diabetica es).
I problemi sono: mancanza di fattori di crescità, attività ecessiva delle protease, perche
vengano spvvraespresse.
E cellule vecchie.
Da notare: l’embrione non forma cicatrici
ferita
coagulazione
paistrine
fibroblasti (no 1 per proliferazione)
resiste infezione e pulizia
infiammazione
Linfociti, macrofagi
epidermide
lisis collagene
crescità
neovascolare
contrazione
sintesi collagene
remodellamento
sintesi proteoglicani
ferita guarita
3
Si possono quasi dividere i problemi in 2: ustioni e problemi cronici
di guarigione.
Quello che hanno in commune è la necessità di fornire un
epitelizzazone veloce per evitare contaminazione e perdità di fluidi.
Approcio prima era di prendere epidermide (surface graft) o
epidermide + poco dermide (split thickness graft per ferite estese) da
altre zone e appicicarlo direttamente. L’epidermide prima andava
frullato e poi applicato per coprire grosse l’area. Problema: se
mancano siti, perche un sito non puo essere usato più di 2 volte.
Se mancavano siti si usava epidermide da cadveri (allograft).
Problemi: rigetto, infezione disponibilità e variabilità. Ad oggi questo
è l’approccio più diffuso per ustioni con grande area superficiale
E’ anche stato commercializzato un derma acellualre per auitare la
guarigione di autograft.
I requisiti
Un elemento dermal o mesenchimale capace di aiutare la
riparazione dermale e il supporto del epidermide
Un epidermdie capace di chiudere velocemente la ferita e
stabilire una barriera effettiva
Un sistema che permette poi la vascolarizzazione e
innervazione
Un sistema che permette la normalizzazione di altre strutture
e funzioni della pelle (fare sparire cicatrici, dare pigmento,
mobilità).
Un sistema in grado di guarire dopo
Per tutti i tessuti è importante
1. l’utilita e accettabilità per il paziente 2. sicurezza per il
paziente 3. conveniente da usare 3.
4
Approci
1) Graft autologhe, allogeniche, graft di cheratinociti, matrici (es
spugna di collagene e GAG (HA) su un supporto di silicone,
Integra, che funge da MEC, quando viene riassorbita il silicone
viene tolto e poi messo un autograft.) Non sono perfetti, ma
riducono infezione e dolore.
2) Folgi di cellule epidermdie
3) Substrato dermale
4) HSE –human skin equivalent (celle epidermde e dermide)
Graft epidermale bioingegnerizzato
Ricordiamo l’importanza del epidermide.
In 1975 Green et al svilupparono tecniche per la coltura di cheratinociti da una piccola
biopsia umana. Erano messo in coltura su un feeder layer di Fb di topo. (stemcells, air
etc).Potevano essere espansi per formare foglie di epidermide. In 1984, 2 pazienti usitionati
hanno avuto dei graft di epidermide ingegnerizzato (messo prima in coltura) con cellule
autologhe. La pelle era ancora molto giovane (tipo feto), ma e’ maturato dopo 2 settimane.
Ci sono sempre probemi con cictrici e contrazione. Sono sottili e fragile e si pensa che sono
limitate dalla mancanza della componente dermale.
Ad oggi il metodo utilizzato per la coltura di queste cellule è fb topo e siero bovina
Adesso ci sono tanti prodotti, il prima era Epicel, 1987, Genzyme.
Vengono usato per ustioni di 3 grado quando almeno 50% del corpo e ferito. Si parte con
una biopsia di 5 cm2, e dopo 16 giorni si riesce a produrre tutta l’area necesaria.
Le cellule vengono messe in coltura sempre con il feeder layer, in fiasche. Dopo alcuni
pasaggi vengono attacato a una garza (gel di fibrina, HA ecc) e trasportati al ospedale.
Devono essere usati entro 24 ore
I pazienti che hanno ricevuto
trattamento stanno bene.
5
I prodotti epiteliali
• Epicel cellule sul garza
• Myskin cellule su scaffold sub confluente
• Epidex : piccole quantita dai follicoli (era
per trapianti di capelli)
• Cell Spray.Cellule autologhe in
sospensione. Sospetto lo stato di didifferenziamento.
Sostituo Dermale
• Il dermide ha gli elementi necessari per la
guarigione. Mentre la funzione del epid puo essere
sostituita da una copertura bioloigica o non, non è
possibile farlo per il dermide.
• Quindi se manca il dermide, il graft epidernale
non e’ sufficiente.
• Si fornisce un dermide con un epidermide
sintetico (o anche senza). Dopo alcune settimane
l’epidermide sintetico veine sostituito con un auto
graft epidermide.
6
Integra DRT, Integra 1996
Integra® Dermal Regeneration Template is a two-layer skin regeneration system.
The outer (epidermal) layer is made of a thin silastic membrane.
The inner (dermal) layer is constructed of a complex matrix of cross-linked fibers of bovine tendon collagen
and shark GAG. This porous material acts as a scaffold for regenerating dermal skin cells, which enables the
re-growth of a functional dermal layer of skin. Once dermal skin has regenerated, the silastic outer layer is
removed and replaced with a thin epidermal skin graft.
Integra Template can be used to treat life-threatening burn injuries when donor skin is not available for a skin
graft or when a skin graft is not desirable due to a person's condition. It is also available for the
reconstruction of scar tissue resulting from prior burn injuries.
Since June 1999, Integra is exclusively marketed and distributed by Johnson & Johnson Medical, around the
world.
Uno dei problemi è che le cellule del derma non aderiscono bene sullo scaffold. Quindi il processo di
guarigone è lento.
Alloderm, LifeCell, 1994
Alloderm is donated human tissue that is processed to remove all epidermal and dermal cells while
preserving the dermal matrix. The Alloderm does not have an epidermal layer.
Donor tissue is recovered by U.S. Tissue Banks. Donors' medical histories are reviewed and blood and tissue
samples are screened for pathogens.
The tissue is put through a 3-step process:
Step 1: Epidermis removal.
The epidermis is completely removed by uncoupling the bond with the dermis, while the basement
membrane is retained.
Step 2: Cell solubilization.
Dermal cells are removed with low molecular weight non denaturing detergents while the matrix is stabilized
through the inhibition of metalloproteinases. Failure to remove all cells marks the tissue as damaged, which
may lead to tissue rejection.
Step 3: Dry preservation.
The tissue is freeze-dried using a patented process which preserves the integrity of the biological dermal
matrix, eliminating the formation of ice crystals, accompanied to standard freeze-drying.
The recovery of donated tissue by U.S. Tissue Banks is supervised by the American Association of Tissue
Banks (AATB) and the FDA. The rest of the procedure does not require FDA approval.
But, at least once, in January 2001, the company recalled 18 pieces, when a donor's HIV-1 PCR testing
detected HIV DNA.
Uno dei problemi è che le cellule del derma non aderiscono bene
sullo scaffold. Quindi il processo di guarigone è lento.
7
Dermagraft, prima Ats poi Smith and Nephew (ora fallito)
FDA approval: Ulcers: 2001.
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB): 2003.
The FDA approved Dermagraft as a Humanitarian Use Device for the
treatment of DEB.
When is it used: Full-thickness diabetic foot ulcers. Ulcers that do not involve tendon,
muscle, joint capsule or bone. Wounds of patients suffering from DEB.
Dermagraft is a cryopreserved human fibroblast-derived dermal substitute that is composed of fibroblasts,
extracellular matrix, and a bioabsorbable scaffold.
Dermagraft does not contain an outer layer, and is produced in a 3-step process:
Step 1: Human fibroblast cells are expanded and then seeded on a bioabsorbable polyglactin (vicryl) scaffold.
The cells are tested throughout the process for bacteria, viruses, fungi, and mycoplasma.
Step 2: Cells attach to the scaffold and multiply to fill the spaces within the scaffold.
Step 3: Cells continue to divide and grow, secreting human growth factors, cytokines, extracellular matrix
proteins, and GAGs.
The end result is a cryopreserved three-dimensional human dermal substitute containing metabolically active
living cells. (non è condiviso)
When Dermagraft is applied, the wound is covered with a non-adherent dressing. After 3 to 4 weeks, the
scaffold dissolves and an epithelial natural layer is grown.
A former version of this product, Dermagraft TC (Transcyte), was approved for marketing as a temporary
wound covering for partial-thickness burns in March, 1997.
The Dermagraft TC was composed of a silicone polymer epidermal layer, on top of the dermal layer
described above. It was used as a temporary wound coverage for excised burn wounds, and the outer silicone
layer was eventually removed and replaced by a split thickness autograft.
(Transcyte stessa ditta, le cellule sono su una matrice di silicone, serve come copertura temporanea)
8
Full skin replacement
• Dato i problemi incontrati (non adesione e lenta
vascolarizzazione) con i sostituiti dermale e
epdiermali, si è cercato di fare co colture di
cheratinociti e fibroblast su strati di collagene.
• E stato visto che sostituti maggiore di 0.4 mm di
spessore non vengono vascolarizzati in maniera
efficace
HSE: tutti e due –epidermide e derma
Orcel, Ortec
FDA approval: Donor site wounds in burn victims: August 2001.
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB): February 2001.
The FDA approved Orcel as a Humanitarian Use Device for the
treatment of DEB.
When is it used: Treatment of donor site wounds in burn victims. Treatment of Dystrophic
Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) in reconstructive hand surgery and donor
site wounds resulting from these surgeries.
Orcel is a bi-layered cellular matrix, manufactured from human neonatal foreskin tissue.
Epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts from the same donor are cultured in two separate layers into a
Type I bovine collagen sponge scaffold.
Safety precautions:
The donor’s mother is tested for syphilis and for human viruses, including CMV, HSV I & II, HTLV I & II,
Hepatitis B&C, HIV 1&2, EBV and HHV-6. The donor’s fibroblast and keratinocyte cells are tested for
viruses and retroviruses (including HTLV I&II, Hepatitis B, HIV 1&2, EBV, and HHV-6), bacteria, fungi,
yeast, mycoplasma, and tumorigenicity. The donor cells are tested using karyology, isoenzyme, growth and
morphological analyses. Animal derived reagents are tested for: viruses, bacteria, fungi, yeast, and
mycoplasma before use.
Manufacturing process:
Prior to cell seeding, the matrix is cross-linked and then coated on one side with a thin gel layer prepared
from acid-soluble collagen.
Donor dermal fibroblasts are cultured on and within the porous sponge side of the collagen matrix while
keratinocytes are cultured on the coated, non-porous side of the collagen matrix.
9
The final product:
Orcel does not contain Langerhans cells, melanocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, blood vessels or hair
follicles. DNA analysis performed on two Orcel treated donor site patient showed no trace of allogeneic
DNA after three weeks.
On the other hand, Orcel has been shown to contain the following cell-expressed cytokines and growth
factors: FGF-1 (βFGF), NGF, GM-CSF, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, HGF, KGF-1 (FGF-7), M-CSF, PDGF-AB,
TGF-α, TGF-β1, TGF-β2, and VEGF.
Orcel is then tested for morphology, cell density, cell viability, sterility, mycoplasma, and physical container
integrity.
Alipigraf, Organogenesis
FDA approval: Venous ulcers: 1998
Diabetic foot ulcers:1998
When is it used: Treatment of noninfected partial and full-thickness skin ulcers.
Treatment of full-thickness neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers which extend through the
dermis but
without tendon, muscle, capsule or bone exposure.
Apligraf is bi-layered living skin substitute which is manufactured from human neonatal foreskin
tissue. The dermal layer is composed of fibroblasts in a bovine Type I collagen lattice while the
epidermal layer above is formed by keratinocytes and has a well-differentiated stratum corneum.
Safety precautions:
The foreskin donor’s mother is tested for human viruses, including antibodies to (HIV-1), (HIV-2),
(HTLV-1), hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg), and syphilis. The fibroblast
and keratinocyte cell banks are tested for human and animal viruses, retroviruses, bacteria, fungi,
yeast, mycoplasma, karyology, isoenzymes, and tumorigenicity. Product manufacture also includes
reagents derived from animal materials including bovine gland extract. All animal derived reagents
are tested for viruses, retroviruses, bacteria, fungi, yeast, and mycoplasma before use.
Manufacturing process:
Fibroblasts are placed on a semipermeable membrane along with bovine type I collagen. After a six
day period of incubation in which fibroblasts create matrix proteins and connect to the collagen
filaments, keratinocytes are seeded on the contracted matrix and for four more days go to incubation.
After ten more days in incubation exposed to an air-liquid-interface the keratinocytes form the stratum
corneum. There are 11 days in which the harvesting can take place and a 5 days shelf life from the day
of packaging.
Apligraf is supplied as a circular disk approximately 75 mm in diameter and 0.75 mm thick in an
agarose medium.
10
The final product:
Apligraf does not contain Langerhans cells, melanocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes,
blood vessels or hair follicles. In a 10 patient venous leg ulcer study to determine the
longevity of Apligraf cells, 2 of 8 patients evaluated at 4 weeks demonstrated Apligraf DNA.
Neither of these patients showed Apligraf DNA at 8 weeks.
Apligraf does contain matrix proteins, cytokines and growth factors found in human skin
such as: TGF-α, TGF-β1, TGF-β2, IL-1,-6, -8, -11, interferon-α,β, IGF-1 and PDGF.
The final product is tested for morphology, cell viability, epidermal coverage, sterility,
mycoplasma, and physical container integrity.
Prodotti Dermale
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Pelle del donatore cadavere
Integra
Alloderm
Dermagraft
Transcyte
Permacol: pelle porcina temporanea
Laserskin
11
Prodotti Dermale/epidermale
• Alpigraf cellule allogeniche su collagene
bovina per ulcere
• Orcel cellule allogeniche su collagene
bovina per ustioni
• Permaderm cellule autologhe su collagene
bovina
Sostiture la pelle: ok per ulcere e zone piccole. Non per ustioni perche troppo costoso.
Le due ditte piu grosse : Organogenesis e ATS sono fallite perche il processa di ingeg la
pelle ha un prezzo molto elevato.
I problemi sono tanti: mancanza di automazione del processo, sia Dermagraft che
Organogenesis avevano una forte componente umana
Sterilita. QC, proprieta meccaniche e quindi maneggiabilità, mancanza di pelli, lenta
vascolarizzazione, cicatrice non sparisce ecc. Per questo c’e sempre la ricerca,, costa
troppo avere approvazione FDA.
Costi:20,000 £ pa per alpigraf, 27,000 per tradizionali (garze ecc).
Altro grosso problema: inerzia medici
Quindi la pelle TE perfetta rimane ancora distante, ed e’ un campo molto competitivo
C’e piu attenzione a terapia alternative di tipo allopatiche (cioe medicine), forse piaccono piu
ai medici.
Fattori di crescita applicate localmente: PDGF (Regranem becaplermina).
Sono in fase di testing fattori per stimolare macrofagi, FGF, EGF, e per controllare la
degradazione e sintesi della MEC
12
Altri usi (in vitro) per la pelle
Studi fisiologici
Cellule staminali: marker ecc
Processo di guarigione
Malattie della pelle
Dermatofarmacologia
Tossicologia in vitro
Modello angiogenesi
Ma cosa hanno fatto a Roma? (Notizie Prof Nicolò Scuderi)
13
14