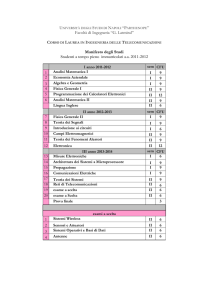
Corso di Laurea: Scienze e Tecnologie Agrarie
Corso Integrato: Principi di Economia agraria
Modulo: Principi di Economia agraria (6 CFU) (4 CFU Lezioni + 2 CFU Esercitazioni)
Docente
Dott. Francesco Bozzo – email: [email protected] - Tel. 080 544 2902
Obiettivi Formativi
Obiettivo del corso è consentire di conoscere la micro e macro economia:
- Microeconomia: Domanda, offerta, mercati dei prodotti. Elasticità e sue applicazioni. La teoria della
produzione. La teoria dei costi. Forme di mercato: concorrenza perfetta, monopolio, oligopolio e
concorrenza monopolistica.
- Macroeconomia: Formazione del reddito e crescita economica. Spesa aggregata. Moltiplicatore. Bilancio
dello Stato. Politica Monetaria e Politica Fiscale. Disoccupazione. Inflazione.
Competenze acquisibili
Le competenze sono propedeutiche per affrontare lo studio degli aspetti economici, gestionali ed
organizzativi dell’azienda agraria.
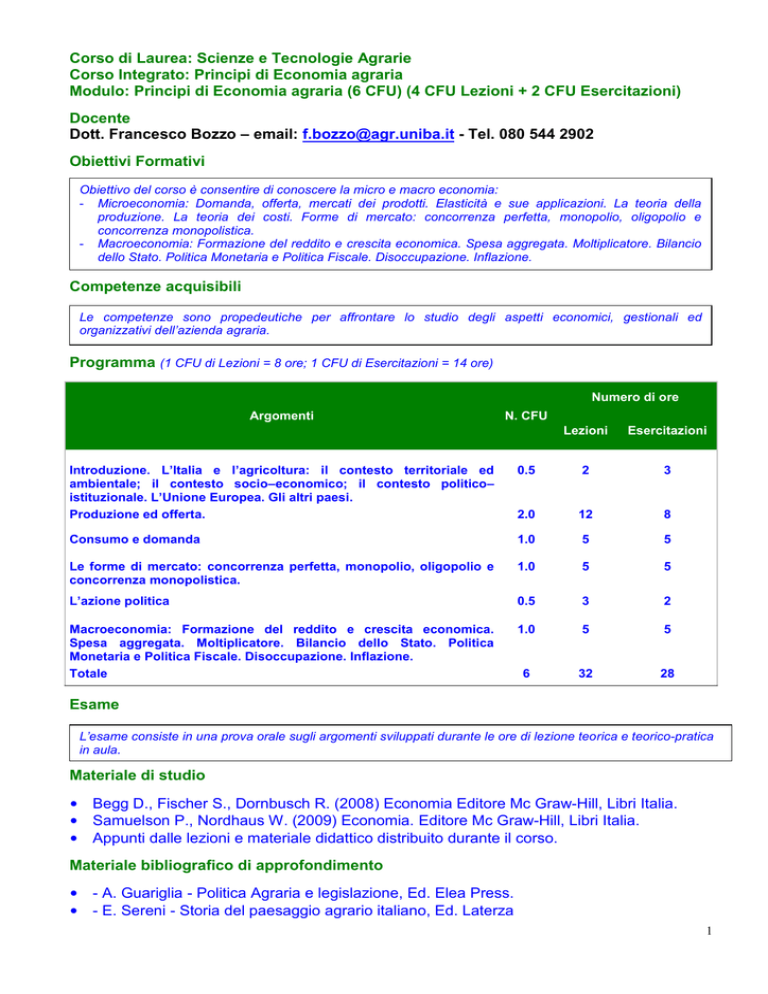
Programma (1 CFU di Lezioni = 8 ore; 1 CFU di Esercitazioni = 14 ore)
Numero di ore
Argomenti
N. CFU
Lezioni
Esercitazioni
Introduzione. L’Italia e l’agricoltura: il contesto territoriale ed
ambientale; il contesto socio–economico; il contesto politico–
istituzionale. L’Unione Europea. Gli altri paesi.
Produzione ed offerta.
0.5
2
3
2.0
12
8
Consumo e domanda
1.0
5
5
Le forme di mercato: concorrenza perfetta, monopolio, oligopolio e
concorrenza monopolistica.
1.0
5
5
L’azione politica
0.5
3
2
Macroeconomia: Formazione del reddito e crescita economica.
Spesa aggregata. Moltiplicatore. Bilancio dello Stato. Politica
Monetaria e Politica Fiscale. Disoccupazione. Inflazione.
Totale
1.0
5
5
6
32
28
Esame
L’esame consiste in una prova orale sugli argomenti sviluppati durante le ore di lezione teorica e teorico-pratica
in aula.
Materiale di studio
• Begg D., Fischer S., Dornbusch R. (2008) Economia Editore Mc Graw-Hill, Libri Italia.
• Samuelson P., Nordhaus W. (2009) Economia. Editore Mc Graw-Hill, Libri Italia.
• Appunti dalle lezioni e materiale didattico distribuito durante il corso.
Materiale bibliografico di approfondimento
• - A. Guariglia - Politica Agraria e legislazione, Ed. Elea Press.
• - E. Sereni - Storia del paesaggio agrario italiano, Ed. Laterza
1
• - G.T. Padoa Schioppa - Europa forza gentile.
• - M. Rossi Doria - La questione meridionale, Monografia REDA
• - G. de Luca e altri - Dizionario di economia politica, Ed. Simone
Orario di ricevimento
Dal lunedì al venerdì, tutti i pomeriggi dalle 16.00 alle 20.00, previo appuntamento.
Ausili didattici
Gli argomenti del corso saranno trattati con l’ausilio di presentazioni in Power Point.
Per gli studenti a tempo parziale:
• Compendio di Economia Politica Micro e Macroeconomia. La nuova università. Edizioni
Simone.
Per gli studenti stranieri (LLP-Erasmus, Tempus, ecc.):
Begg D., Fischer S., Dornbusch R. (2008) Economics. McGraw-Hill Education.
2
Bachelor/Master Programme: Sciences and Technologies Agrarian
Integrated Course: Principles of agrarian economy
Module: Principles of agrarian economy (6 CFU)
(4 CFU Lectures + 2 CFU Laboratory or field classes)
Professor
Dott. Francesco Bozzo – email: [email protected] - Tel. 080 544 2902
Educational Goals
Objective some course is to allow to know the micro one and macro economy:
Microeconomics: Question, offered, markets of the products. Elasticity and its applications. The theory of the
production. The theory of the costs. Forms of market: perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly and
monopolistic competition.
Macroeconomics: Formation of the income and economic growth. United expense. Multiplier. Budget of the
State. Monetary politics and Fiscal Politics. Unemployment. Inflation.
Acquirable skills
Competences are preliminary to face the study of the economic, managerial and organizational aspects of
the agrarian firm.
Programme (1 ECTS of Lecture = 8 hours; 1 ECTS of Laboratory and field classes = 14 hours)
Number of hours
Topic/Subject
N. ECTS
Introduction. Italy and agriculture: the territorial and
environmental context; the context social-economics; the
context policy- institutional. The European Union.
0.5
2
Production and offer.
2.0
12
8
Consumption and question.
1.0
5
5
Forms of market: perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly
and monopolistic competition.
1.0
5
5
The political action.
0.5
3
2
Macroeconomics: Formation of the income and economic
growth. United expense. Multiplier. Budget of the State.
Monetary politics and Fiscal Politics. Unemployment.
Inflation.
Totale
1.0
5
5
6
32
28
Lecture
Lab & field cl.
3
Exam
The exam consists of an oral test with questions related to the programme.
Support materials
• Samuelson P., Nordhaus W. (2009) Economia. Editore Mc Graw-Hill, Libri Italia.
• Begg D., Fischer S., Dornbusch R. (2008) Economia Editore Mc Graw-Hill, Libri Italia.
• Notes of the lectures distributed during the course.
Additional readings
• - A. Guariglia - Politica Agraria e legislazione, Ed. Elea Press.
• - G.T. Padoa Schioppa - Europa forza gentile.
• - G. de Luca e altri - Dizionario di economia politica, Ed. Simone
Visiting hours
The instructor will be available to students every Tuesday, Wednesday from 10.30 to 13.30,
Thursday and Friday from 10.00 to 12.00 by previous agreement.
Teaching procedures
Lectures will be presented through PC assisted tools (Powerpoint, Adobe Acrobat, etc.), slide
projector.
For foreign students (LLP-Erasmus, Tempus, ecc.):
• Begg D., Fischer S., Dornbusch R. (2008) Economics. McGraw-Hill Education