XPath Injection
Alessandro ` jekil` Tanasi
Dati volubili
Un informazione (dato) può avere varie rappresentazioni
che non ne alterano il significato ma ne facilitano l'impiego
Infomazione che vengono memorizzate in file XML piuttosto
che in database tradizionali
Esempi:
Uso massiccio di middleware come soluzione ai problemi
del mondo(TM)
SQL Server e i dataset XML
XPath
“Mollare, non mollare. Spaghetti, non spaghetti.
Ti preoccupi troppo di cio` che era, e di cio`
che sara`. C’e` un detto: ieri e` storia, domani
e` un mistero, ma oggi e` un dono, per questo
si chiama presente” (Kung-fu Panda)
WTF XPath?
XPath è un linguaggio per porre interrogazioni in un modo
molto simile a SQL sui dati contenuti in file XML
Fornisce una sintassi standard per definire parti di un
documento e path expressions per scorrerne I suoi elementi
Come SQL implementa delle funzioni base ad es.
substring(), current-time()
E' uno standard W3C nella versione 1.0 (la più usata) e nella
versione 2.0 recentemente approvata
Viene usato standalone, all'interno di
trasformazioni XSLT o nell'utilizzo di XQuery
XPath
XPath viene impiegato quando c'e` bisogno di database light o
di particolari architetture ad es. Provisioning
Varie librerie forniscono supporto a database XML e integrano
XPath (dbXML, Xindice)
Viene usato nativamente (Java, .NET, Coldfusion)
Viene usato client side (Flash, Silverlight)
Terminologia
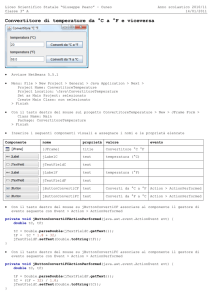
Relazioni di sangue
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO­8859­1"?>
<users>
<user>
<username id="1">root</username>
<password>OAhhgg</password>
</user>
</users>
✔
✔
<user> è padre di <username> e <password>
<username> e <password> sono parenti perchè hanno lo
stesso padre
✔
<users> è antenato di <user>
✔
<user> è discendente di <users>
Path Expressions
Sintassi basata su path: nodi di un documento XML hanno
analogie con directory e file di un file system
Expression
Description
nodename
Selects all child nodes of
the named node
/
Selects from the root node
//
Selects nodes in the
document from the current
node that match the
selection no matter where
they are
.
Selects the current node
..
Selects the parent of the
current node
Esempio
Expression
Result
users
Selects all the child nodes of
the users element
/users
Selects the root element
users
users/user
Selects all user elements that
are children of users
//users
Selects all users elements no
matter where they are in the
document
users//user Selects all user elements that
are descendant of the users
element, no matter where they
are under the users element
Predicati
Vengono utilizzato per trovare specifici nodi, sono sempre
indicati tra parentesi quadre
Expression
Result
/users/user[1]
Selects the first user element
that is the child of the users
element.
/users/user[last()]
Selects the last user element
that is the child of the users
element
/users/user[position()<3]
Selects the first two user
elements that are children of
the users element
//username[@id='1']
Selects all the username
elements that have an attribute
named id with a value of ‘1'
Location Path
Example
Result
child::user
Selects all user nodes that are children
of the current node
attribute::id
Selects the id attribute of the current
node
child::*
Selects all children of the current node
attribute::*
Selects all attributes of the current
node
child::text()
Selects all text child nodes of the
current node
child::node()
Selects all child nodes of the current
node
descendant::users
Selects all users descendants of the
current node
Funzioni
Le funzioni di XSLT e Xquery possono esser usate in Xpath
Le funzioni sono legate al datatype
Function Name
Description
substring(string,start,len)
Returns the substring from the start position to the specified length.
Index of the first character is 1. If length is omitted it returns the
substring from the start position to the end
string-length(string)
Returns the length of the specified string.
count((item,item,...))
Returns the count of nodes
starts-with(string1,string2)
Returns true if string1 starts with string2, otherwise it returns false
contains(string1,string2)
Returns true if string1 contains string2, otherwise it returns false
number(arg)
Returns the numeric value of the argument. The argument could be a
boolean, string, or node-set
string(arg)
Returns the string value of the argument. The argument could be a
number, boolean, or node-set
Xpath Injection
"Non aver paura di urtare i miei sentimenti, io
non mi preoccupo dei tuoi" (Leoni per agnelli)
WTF XPath Injection
Problema: uno sviluppatore doveva fuggire a casa e non ha
validato l'input utente che viene utilizzato per la creazione di
query XPath
Nel testing di un XPath Injection si prova ad alterare una
query XPath in modo da alterarne il suo significato
Senza conoscere la struttura dati
Senza conoscere la sintassi della query
XPath e` funny
Se XPath è standard esiste un unico dialetto per le query ogni
attack vector puo`essere applicato as-is su ogni
implementazione
L'accesso al foglio XML che contiene i dati non ha limitazioni
Mancanza di controllo d'accesso e di livelli di autorizzazione
Tecniche di Injection
Può darsi che nella rara occasione in cui per
seguire la giusta rotta ci voglia un atto di
pirateria, la pirateria stessa possa essere la
giusta rotta (La maledizione della prima luna)
Example page
XmlDocument XmlDoc = new XmlDocument();
XmlDoc.Load("...");
...
XPathNavigator nav = XmlDoc.CreateNavigator();
XPathExpression expr =
nav.Compile("string(//user[name/text()='"+TextBox1.Text+
"' and password/text()='"+TextBox2.Text+
"']/account/text())");
String account=Convert.ToString(nav.Evaluate(expr));
if (account=="")
{
// name+password pair is not found in the XML document –
// login failed.
...
}
else
{
// account found -> Login succeeded.
// Proceed into the application.
...
}
Authentication bypass
XPath non prevede delimitatori di commenti
L'utilizzo coretto del form di login fa eseguire una query simile
a:
//user[name/text()='antani' and
password/text()='tapioco']/account/text()
Tentativo di abuso fatto con ' or 1=1 or ''='
//user[name/text()='' or 1=1 or ''='' and
password/text()='']/account/text()
L'utente e` in grado di forzare un cambiamento alla semantica
della query XPath
Un'attacco di questo tipo garantisce il bypass di una form di
autenticazione
Node guessing
Leak dei dati contenuti nel database XML, ad esempio
enumerazione del primo nodo figlio
Utilizzando le funzioni per la selezione dei nodi si puo` tentare
l'enumerazione dello schema
Check sul nodo figlio:
//user[name/text()='antani' or name(//user/name[1]) = 'tapioco' or
'a=b' and password/text()='']/account/text()
Ritorna il primo elemento del node set P:
//user[name/text()='Foobar'] | p | //user[name/text()='NoSuchUser'
and password/text()='NoSuchPass']/account/text()
Xpath crawling
Vogliamo ottenere tutti i dati contenuti nel database XML
Utilizzando le funzioni per contare nodi, navigare nei nodi,
estrapolare il tipo di nodo e il suo valore
Xpath 1.0 permette l'enumerazione dei figli ma non di ricavare
dittamente il loro node type
XPath Crawling
Estrapolare il numero di nodi figli
Ci sono almeno 4 tipi di nodi che ci possono interessare
Contare gli elementi, reiterare il fetch per ogni elemento
count(path/child::node()) - Conta il numero di noti per un path
dato
count(path/child::text()) - Conta il numero di campi
count(path/child::comment()) - Conta il numero di commenti
count(path/child::*) - Conta il numero di figli
count(path/child::processing-instruction()) - Conta il numero di
nodi PI
L'algoritmo di crawl e` descritto da Amit Klein in Blind Xpath
Injection
Blind Xpath Injection
La query viene eseguita in un contesto booleano
Una query scalare deve essere booleanizzata
Bisezione e funzioni stringa string-length e substring
L'implementazione e` simile a quella usata per le blind SQL
injections
Lunghezza della seconda stringa del primo utente:
stringlength(//user[position()=1]/child::node()[position()=2])
Fetch del primo carattere:
substring((//user[position()=1]/child::node()[position()=2),1,1)
Injection in XPath 2.0
Xpath 2.0 puo` accedere a dati XML via URI e senza
limitazioni sul documento in uso
Retrive di qualsiasi documento XML sul file system, ad es.
file:///c:/data/database.xml
Aggiunta la funzione string-to-codepoints() che data una
stringa ritorna la sua rappresentazione di codici Unicode
Problematiche
Ricostruzione imperfetta del documento XML in caso di note
type particolari
Performance per il fetch dei dati
Gestione di eventuali simboli
Eventuale query size >65000
Mitigation
Ciambelle... esiste qualcosa che non riescono a
fare? (Homer Simpson)
Mitigation
Input validation
Filtraggio ed escaping degli input
Whitelisting / blacklisting
Parametrizzazione
Statement precompilati
Utilizzo di query XPath precompilate (se la tecnologia usaa
lo permette)
Future research
Il materiale disponibile non e` molto, rimangono scoperte alcune
tematiche:
Mappable Injections
Librerie che implementano XPath
Ricerca vulnerabilità
XPath 2.0
Riferimenti
XML Path Language (XPath) Version 1.0
http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath
OWASP http://www.owasp.org/index.php/XPATH_Injection
Blind XPath Injection - Amit Klein
http://packetstormsecurity.org/papers/bypass/Blind_XPath_Inj
ection_20040518.pdf
Acunetix
WSDigger
Domande