Un solo genoma con una molteplicità
impressionante di varianti di espressione
Corteccia cerebrale
Fegato
Muscolo liscio
Il Trascrittoma è l’insieme completo dei trascritti e
dei loro livelli di espressione in un dato tipo
cellulare ed un determinato stato fisiologico.
Transcriptome studies
a)Mappare “sequence reads” onto a reference
genome.
b) De novo transcriptome assembly uses software
to infer transcripts directly from short sequence
reads.
c) Differential expression
•A eukaryotic cell contains a total mass of ∼100 000
mRNAs with ∼15.000–30.000 distinct mRNAs.
Prevalence ranging from one to several thousands.
•About 50% of the transcript population is made up of a
relatively small number (some hundreds) of abundant
transcripts, representing only 1% of the different mRNA
species.
•The other 50 % half contains the ‘rare’ mRNAs.
•The difficulty of fishing out a gene responsible for a
specialized function in a certain biological program often
originates from the fact that the gene is expressed at low
levels whereas the bulk of a cell’s mRNA is made up of
highly abundant transcripts.
Analisi di espressione
differenziale
Screening for differentially expressed genes is one of the most
straightforward approaches to unravel the molecular basis of
a biological system
Le cDNAteche
sono uno strumento prezioso per gli studi di
espressione genica
Conversione dei trascritti in cDNA
Selection /Isolation of specific messenger RNA
Identification of novel messenger RNA with degenerated oligo/probes
Studies on differentially expressed messenger RNA
Differential Hybridization Technique
Differential hybridization o ibridazione sottrattiva
driver
cDNAteca
Driver
Marcata con biotina
Biotina: cofattore
Avidina
ne è ricco il bianco d’uovo
essa lega “avidamente la
Biotina” e ne previene
l’assorbimento intestinale;.
tester
Differential Dysplay Technique
RT-PCR to increase mRNA abundance
AAAAAAAA
AAAAAAAA
AAAAAAAA
AAAAAAAA
AAAAAAAA
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
AAAAAAAA
TTTTTTTTT
RNAsi
Primer sequenza specifico
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
Primer
hybridization
high stringency
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
PCR
Oligo dTTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
PCR
Oligo dTTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
PCR
TTTTTTTTT
Oligo dTTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTTTA3’OH
TTTTTTTTTTT
TTTTTTTTTTG
TTTTTTTTTTC
TTTTTTTTTTCG
TTTTTTTTTTCC
Differentially expressed gene
Misure di espressione genica:
1980 Northern Blot/Dot Blot
Misure di espressione genica:
1990 Differential dysplay e tecniche sottrattive /PCR
1995 Arrays/ SAGE/RealTime PCR
wide”)
(analisi “genome
The complexity of
transcriptome
http://neomorph.salk.edu/human_methylo
me/data.html
DNA
Transcription
20.929
Protein coding
RNA
Translation
23.218
Non-coding
RNA
No Translation
Protein
More than 70% of the genome is transcribed and 50% is
non-coding RNA
Complex splicing pattern
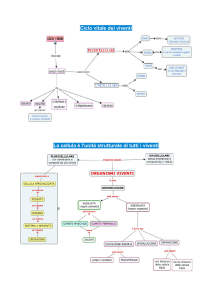
La complessità del trascrittoma
Alternative promoters
Complex splicing patterns
Messenger RNA
Tissue-specificity of promoters
Corteccia somato-sensitiva
Ippocampo
Corteccia visiva
Cervelletto
Differentiation stage-specificity of promoters
XM (mRNA)
XR (non-coding RNA)
transcript from genome annotation
NM
NR
XP( protein) NCBI predicted
NP from RNA sequencing and may differ from XP files
Fantom 5 project: Alternative
Transcription Starting Sites (TSS)
Proteina fibrillare acida della glia
Actin B