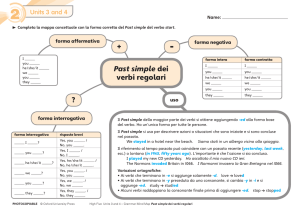
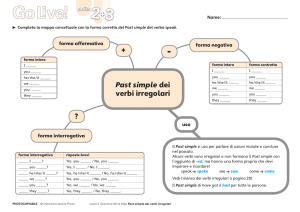
Università degli Studi di Bari Laboratorio di Lingua Inglese Dott. Gary Friel 1 THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di qualcosa che è vero in generale o di azioni o situazioni ricorrenti. TO BE (essere/stare) italiano POSITIVA CONTRATTA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA io sono I am I’m I’m not Am I? tu sei You are You’re You’re not / You aren’t Are you? lui è He is He’s He’s not / He isn’t Is he? lei è She is She’s She’s not / She isn’t Is she? esso/a è It is It’s It’s not / It isn’t Is it? noi siamo We are We’re We’re not / We aren’t Are we? voi siete You are You’re You’re not / You aren’t Are you? loro sono They are They’re They’re not / They aren’t Are they? TUTTI GLI ALTRI VERBI * per esempio, TO WORK (lavorare) italiano POSITIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA io lavoro I work I don’t work Do I work? tu lavori You work You don’t work Do you work? lui lavoro He works He doesn’t work Does he work? lei lavora She works She doesn’t work Does she work? esso/a lavora It works It doesn’t work Does it work? noi lavoriamo We work We don’t work Do we work? voi lavorate You work You don’t work Do you work? loro lavorano They work They don’t work Do they work? ✎ LA FORMA INTERROGATIVA A + S + V = ? (ausiliario + soggetto + verbo = domanda) ✎ 3° PERSONA He works. He doesn’t work. Does he work? 2 * vedi: Modal Verbs pagina 24 1. La risposta breve usa l’ausiliario DO (o DOES) per ogni verbo (tranne il verbo TO BE): Do you like pop music? Does your girlfriend live in Bari? Ø Yes, I do. Ø Yes, she does. Ø No, I don’t. Ø No, she doesn’t. 2. Nelle forme negative e interrogative il verbo TO HAVE (avere) può essere formato, come qualsiasi verbo, con il verbo ausiliario DO/DOES (preferito negli Stati Uniti) o con GOT (più comune in Gran Bretagna): USA: Do you have a car? Does he have a sister? I don’t have a pen. She doesn’t have a book. GB: Have you got a car? Has he got a sister? I haven’t got a pen. She hasn’t got a book. 3. Se una domanda inizia con una preposizione in italiano finisce con la preposizione in inglese: Ø Di dove sei? = Where are you from? Ø Con chi vive? = Who does he live with? Ø A cosa riferisce? = What does it refer to? Ø Fino a che ora lavorano? = What time do they work until? 4. Quando il soggetto non è conosciuto non si usa il verbo ausiliario nella forma interrogativa: Ø Chi abita qua? = Who lives here? Ø Che succede dopo? = What happens after? Ø Quanti studenti sanno la risposta? = How many students know the answer? 5. La forma positiva della terza persona si forma cosi: verbo à
+ s She plays tennis. Eccezione: do / go à
+ es He does nothing. / She goes to church. ____s à
+ es She passes all the tests. ____ch à
+ es She watches TV. ____sh à
+ es It washes floors. consonante + y à
+ ies He studies a lot. have à
has He has a car. 3 perché? ……………………………….. chi? ……………………………….. quando? ……………………………….. di chi? ……………………………….. TRADUZIONE 1. Di dove sei? 2. Dove vivi? 3. Con chi vivi? 4. Con chi vive il tuo amico? 5. Come si chiama lui? 6. È difficile. 7. Non avete molto tempo. 8. Quanti anni hanno? * 9. Perché Stefania è arrabbiata? 10. Mi piacciono i film. 11. Rita va al lavoro in macchina. 12. A che ora ti alzi? 13. Lui non fuma. 14. Sono le nove meno dieci. 15. Che cosa fa tuo padre? dove? ……………………………….. quale? ……………………………….. cosa? ……………………………….. come? ……………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. ……………………………………………………………………………................. *Numero 8: Si usa il verbo TO BE in inglese. 4 THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE Per parlare di azioni o situazioni in corso in questo momento, o questo periodo. TO BE + …...ING TO STUDY (studiare) italiano POSITIVA io sto studiando I am tu stai studiando You are lui sta studiando He is lei sta studiando She is studying esso/a sta studiando It is noi stiamo studiando We are loro stanno studiando They are NEGATIVA io non sto studiando I’m not You’re not / You aren’t He’s not / He isn’t She’s not / She isn’t studying It’s not / It isn’t We’re aren’t / We’re not They’re not / They aren’t INTERROGATIVA io sto studiando? Am I Are you Is he Is she studying? Is it Are we Are they 5 ESERCIZIO A What are they doing? 1. She _____ __________ 2. She _____ __________ 3. She _____ __________ on the phone. dinner. football. 4. He _____ __________ ESERCIZIO B Present Simple or Present Continuous? 1. Look at that dog. It plays / is playing with a cat! 2. My mother always drives / is driving to work. 3. I can hear a baby. It cries / is crying. 4. I hate my neighbour. He listens / is listening to loud music all night, every night. 5. He’s not in his office today. He works / is working at home. TRADUZIONE 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Cosa stai facendo? Sta piovendo. Suo marito non lavora oggi perché sta male. Sto leggendo un libro molto interessante. “Dove vai?” ............................................................................................... ............................................................................................... ............................................................................................... ............................................................................................... ............................................................................................... “Vado a casa. Sono stanco” ............................................................................................... 1. fare 2. piovere 3. marito male 4. leggere 5. stanco 6 = to do = to rain = husband = ill = to read = tired THE PAST SIMPLE TENSE Per parlare di azioni o situazioni successe in un periodo finito. TO BE (essere/stare) POSITIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA I was I wasn’t Was I? You were You weren’t Were you? He was He wasn’t Was he? She was She wasn’t Was she? It was It wasn’t Was it? We were We weren’t Were we? They were They weren’t Were they? TUTTI GLI ALTRI VERBI ...ed/didn’t/did? Positiva: Yesterday I cooked lasagne. Negativa: He didn’t have much time. Interrogativa: Did they study yesterday? Solo i verbi regolari. Tutti i verbi. ✎ LA PRONUNCIA – VERBI REGOLARI Solo quando il verbo finisce con T o D si pronuncia l’ultimo sillabo (-­‐ED). – “d” – loved – “t” – cooked – “tid” – wanted – “did” – needed 7 questo/a ……………………………….. quello/a ……………………………….. TRADUZIONE questi/e ……………………………….. quelli/e ……………………………….. 1. Cosa hai detto? ............................................................................................................. 2. Non ho sentito. ............................................................................................................. 3. Siamo andati al cinema ieri. ............................................................................................................. 4. Con chi sei andata in vacanza? ............................................................................................................. 5. Dove sei stato ieri sera? ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 7. Abitavano a Bari da 2009 a 2012. ............................................................................................................. 8. Il suo ragazzo venne in taxi. ............................................................................................................. 9. Quanto avete pagato? ............................................................................................................. 10. Loro sono andati via alle 9. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 12. Siamo stati a casa di John sabato. ............................................................................................................. 6. Hai visto la partita domenica? 11. Mi è piaciuta la torta. 13. Paul uscì per telefonare a sua moglie. 14. Quanti anni avevi? ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 15. Mio padre non aveva una televisione in casa quando era bambino. ......................................................... ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 1. dire = to say 8. venire = to come 2. sentire = to hear 9. pagare = to pay 3. andare = to go 10. via = away 4. in vacanza = on holiday 11. la torta = the cake 5. ieri sera = yesterday evening 12. la casa di John = John’s house 6. vedere = to see 13. uscire = to go out la partita = the match moglie = wife 7. abitare = to live 15. bambino = little boy 8 THE PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE TENSE 1. Per parlare di azioni successe nel passato, ma in un periodo che continua. L’informazione non è definitiva ma è vero solo finora. 2. In Gran Bretagna, quando siamo più interessati alle conseguenze attuali di un’azione successa in passato, e non quando/dove ecc. è successa. (Negli Stati Uniti, però, il Past Simple è spesso usato invece del Present Perfect.) HAVE / HAS + Il PARTICIPIO PASSATO Positiva: I have written five emails this week. io ho scritto... Negativa: He hasn’t eaten anything today. lui non ha mangiato... Interrogativa: Have you seen the film ‘Lincoln’? avete visto... ✎ Nel Passato Prossimo italiano l’ausiliario può essere avere o essere. Nel Present Perfect inglese l’ausiliario è sempre avere (have o has). ✎ L’uso del Present Perfect inglese non corrisponde sempre al Passato Prossimo italiano. ✎ Sia il Past Simple che il Present Perfect vengono usati per descrivere azioni successe nel passato. Ma il Past Simple si riferisce ad azioni successe in un periodo di tempo finito, mentre il Present Perfect si riferisci ad azioni successe in un periodo di tempo che continua. Periodo di tempo finito Periodo di tempo che continua (Past Simple: ___ed/didn’t/did?) (Present Perfect: have/has +P.P.) Yesterday I smoked 3 cigarettes. Today I have smoked 3 cigarettes. Last week he didn’t call me. This week he hasn’t called me. Last month did you see any films? This month have you seen any films? Last year they didn’t write. This year they haven’t written. ✎ Il Present Perfect è usato con i seguenti avverbi di tempo: already (già –usato in frasi affermative e interrogative), yet (ancora –in frasi negative/già –in frasi interrogative), just (appena). 9 ESERCIZIO 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Past Simple or Present Perfect? a) I saw John yesterday. b) I have seen John yesterday. a) Did you ever eat Indian food? b) Have you ever eaten Indian food? a) Sara won £5,000 last month. b) Sara has won £5,000 last month. a) I didn’t read Harry Potter. b) I haven’t read Harry Potter. a) We got up at 6.30 today. b) We have got up at 6.30 today. 6.
7.
8.
9.
a) They weren’t here a few minutes ago. b) They haven’t been here a few minutes ago. a) Barack Obama studied Law at university. b) Barack Obama has studied Law at university. a) When did she call? b) When has she called? a) How many Oscars did Tom Cruise win? b) How many Oscars has Tom Cruise won? 10. a) How many Oscars did Frank Sinatra win? b) How many Oscars has Frank Sinatra won? TRADUZIONE 1. Ho fatto tre esami quest’anno. ............................................................................................... 2. Non ho letto il giornale oggi. ............................................................................................... 3. Non sono mai stato in America. ............................................................................................... 4. Quante volte hai visto questo film? ............................................................................................... 5. Abbiamo studiato l’inglese a scuola. ............................................................................................... 6. Non avete mai studiato questa regola. ............................................................................................... 7. Quando sei arrivato? ............................................................................................... 8. Justin Bieber non ha mai fatto un concerto ............................................................................................... a Bari. 9. Michael Jackson non ha mai fatto un concerto ............................................................................................... a Bari. 10. Oh no, ho perso le mie chiave! ............................................................................................... 1. fare un esame = to do an exam 2. leggere il giornale = to read the newspaper 4. vedere un film = to see a film 6. regola = rule 8. fare un concerto = to do a concert 10. p
erdere = to lose c
hiave = keys 10 COMPARATIVES AGGETTIVO ESEMPIO 1 sillaba poor COMPARATIVO poorer (than...) italiano più povero (di...) 2 sillabe + y happy happier (than...) più felice (di...) 2 sillabe o più boring interesting più noioso (di...) more boring (than...) more interesting (than...) più interessante (di...) ✎ Altre forme del comparativo: §
Less aggettivo than... Florence is less beautiful than Rome. Firenze è meno bella di Roma. §
As aggettivo as... Florence is as beautiful as Rome. Firenze è bella quanto Roma. §
Not as aggettivo as... Florence is not as beautiful as Rome. Firenze non è bella quanto Roma. SUPERLATIVES AGGETTIVO ESEMPIO 1 sillaba poor SUPERLATIVO the poorest italiano il più povero 2 sillaba + y happy the happiest il più felice 2 sillaba o più boring interesting the most boring the most interesting il più noioso il più interessante ✎ Altra forma del superlativo: §
The least aggettivo It’s the least expensive. È il meno costoso.. ✎ Ci sono tre eccezioni a queste regole: AGGETTIVO COMPARATIVO SUPERLATIVO good better (than...) meglio (di...) the best il migliore bad worse (than...) peggio (di...) the worst il peggiore far further (than...) più lontano (di...) the furthest il più lontano 11 THE FUTURE 1. PRESENT CONTINUOUS -­‐ Per esprimere un programma preciso per il futuro, per realizzare il quale si è già fatto qualcosa. Positiva: I’m having a party on Saturday. Negativa: We aren’t staying in a hotel. Interrogativa: Are you getting married in church? 2. TO BE + GOING TO + VERB -­‐ Per esprimere l’intenzione di fare qualcosa. -­‐ Per esprimere una previsione che si fa sulla base di una constatazione. Positiva: I’m going to get up early. Negativa: She isn’t going to cook this evening. Interrogativa: Are they going to come with us? 3. WILL -­‐ Previsioni*: I don’t think he will win. * particolarmente dopo i verbi to suppose (supporre), to expect (aspettarsi), to think (pensare), to believe (credere) ecc. -­‐ Offerte: -­‐ Promesse: I’ll help you. I won’t tell anyone. -­‐ Suggerimenti: Shall we go to the cinema? Yes! Let’s go now! -­‐ Decisioni prese nel momento in cui si parla: I’ll have a beer, please. Positiva I’ll You’ll He/She/It’ll We’ll You’ll They’ll Negativa I won’t You won’t He/She/It won’t We won’t You won’t They won’t 12 Interrogativa Shall I? / Will I? Will you? Will he? Shall we? / Will we? Will you? Will they? Match the questions with the answers collegare le domande con le risposte TO BE (essere/stare) 1. ______________________________________________________________ ? My name is Ben. 2. ______________________________________________________________ ? I’m 23 years old. 3. ______________________________________________________________ ? I’m from Dublin. 4. ______________________________________________________________ ? I’m a student. 5. ______________________________________________________________ ? No, I’m not. 6. ______________________________________________________________ ? I’m fine, thanks. §
§
§
§
§
§
Are you married? How are you? How old are you? What’s your job? What’s your name? Where are you from? OTHER VERBS (altri verbi) 7. ______________________________________________________________ ? London. 8. ______________________________________________________________ ? With two friends. 9. ______________________________________________________________ ? One brother. His name is Steven. 10. _____________________________________________________________ ? Yes, I have. Her name is Tina. 11. _____________________________________________________________ ? Jazz. 12. _____________________________________________________________ ? Every evening. 13. _____________________________________________________________ ? My mother is a housewife. My father is retired. §
§
§
§
§
§
§
Have you got a girlfriend? Have you got any brothers or sisters? What do your parents do? Where do you live? What music do you like? Who do you live with? How often do you watch television? 13 1.
What ____________________ your name? My name is... 2.
How old ____________________ you? I am... 3.
Where ____________________ you from? I am from... I live in... I go to university in... 6.
____________________ you got any brothers or sisters? Yes, I have. I’ve got... / No, I haven’t. 7.
What type of music ____________________ you ____________________ to? I listen to... 4.
Where ____________________ you live? 5.
Where ____________________ you go to university? 8.
What television programs ____________________ you ____________________? I watch... 9.
____________________ you ____________________ any musical instruments? Yes, I do. I play... / No, I don’t. 10. What languages ____________________ you ____________________? I speak... I play... / I go... / None. I like... 11. What sports ____________________ you practice? 12. What food ____________________ you ____________________? 13. Where ____________________ you usually ____________________ on holiday? I usually go to... / I stay at home. 14. What ____________________ your hobbies? My hobby is... / My hobbies are... 15. What time ____________________ you ____________________ in the morning? I get up at... 16. What ____________________ you ____________________ for breakfast? For breakfast I have... I come to university... I have lunch... In the evening I usually... I usually go to bed at... 17. How ____________________ you ____________________ to university? 18. Where ____________________ you ____________________ lunch? 19. What ____________________ you ____________________ in the evening? 20. What time ____________________ you ____________________ to bed? 14 TO
PAST
MINUTES
TO
PAST
HOUR
It’s three o’clock. It’s a quarter past six. It’s ten past seven. It’s half past ten. It’s a quarter to two. It’s five to four. Every day Ben gets up at 1)______________. He has a shower and he gets dressed. He has 2)______________ for breakfast and then he goes to the university by 3)______________. He arrives at the university at 4)
______________ and his first lesson starts at 5)______________. At 1.15 he 6)______________ with his 7)______________ in the 8)______________. In the afternoon he usually 9)______________ in the 10)______________. At 11)______________ he goes home. After dinner he usually 12)
______________. He goes to bed at 13)______________. 15 On Fridays I ____________________ home from work at about 5.30 in the afternoon and I just ____________________. On Friday evenings I don’t ____________________, but sometimes a friend ____________________ for dinner. He or she ____________________ some wine and I ____________________ dinner. I ____________________ cooking! We ____________________ to music or we just ____________________. On Saturday mornings I ____________________ at 9.00 and I ____________________ shopping. Then in the evenings I sometimes ____________________ to the cinema or to the theatre with a friend. Then we ____________________ in my favorite restaurant. On Sunday mornings I ____________________ in bed late. I don’t ____________________ until 11.00! Sometimes in the afternoon I ____________________ my sister. She ____________________ in the country and ____________________ two children. I ____________________ playing with my niece and nephew, but I ____________________ early because I ____________________ to bed at 10.00 on Sunday evenings. 1. Use the correct form of these verbs to complete the spaces. usare la forma giusta di questi verbi per riempire gli spazi to bring to get up (x2) to like to stay to chat to go (x3) to listen to visit to come (x2) to go out to live to cook to have to love to eat to leave to relax 2. Write about your weekends. scrivere delle tue fine settimane .......................................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................................... 16 YOU 1.
Where ____________________ you born? I was born in... 2.
When ____________________ you born? I was born on... 3.
Where ____________________ you live as a child? I lived in... 4.
Where ____________________ you live now? I live in... SCHOOL 5.
Where ____________________ you go to school? I went to school in... 6.
How ____________________ you go to school? I went to school on foot / by... 7.
What type of school ____________________ you go to? I went to a... 8.
____________________ you like school? Yes, I... / No, I... 9.
What ____________________ your favorite subject? My favorite subject was... YESTERDAY 10.
What time ____________________ you ____________________ yesterday? I got up at... 11.
____________________ you ____________________ to university? Yes, I... / No, I... 12.
Where ____________________ you ____________________ lunch? I had lunch... 13.
Who ____________________ you ____________________ lunch with? I had lunch with... 14.
What ____________________ you ____________________ for dinner? For dinner I had... 15.
What ____________________ you ____________________ in the evening? In the evening I... 16.
What time ____________________ you ____________________ to bed? I went to bed at... THE BEST HOLIDAY OF YOUR LIFE 17.
Where ____________________ you ____________________? I went to... 18.
Who ____________________ you ____________________ with? I went with... 19.
How ____________________ you get there? I went by... 20.
How long ____________________ you stay for? I stayed for... 21.
What ____________________ the weather like? It was... 22.
____________________ you like the food? Yes, I... / No, I... 23.
____________________ it expensive? Yes, it... / No, it... 17 Have you ever been to America? Yes, I have. When did you go I went there two there? years ago. Use the verbs in the box to complete the conversations. usare i verbi nel box per completare le conversazione to break to live to buy to meet to drink to sing to drive to sleep to eat to spend to like to steal eaten sushi? 1. A: Have you ever _____________ 6. A: Have you ever _____________ your arm? B: Yes, I have. B: Yes, I have. like
A: Did you _____________ it? A: How did you _____________ it? liked it a lot. B: Yes, I _____________ B: I _____________ it skiing. 2. A: Have you ever _____________ a famous person? 7. A: Have you ever _____________ abroad? B: Yes, I have. Kate Moss. B: Yes, I have. A: Where did you _____________ her? A: When did you _____________ abroad? B: I _____________ her in Rome. B: I _____________ in France as a child. 3. A: Have you ever _____________ more than €5,000? 8. A: Have you ever _____________ a Ferrari? B: Yes, I have. B: Yes, I have. A: What did you buy? A: Whose Ferrari did you _____________? B: I _____________ a car. B: I _____________ my uncle’s Ferrari. 4. A: Have you ever _____________ too much tequila? 9. A: Have you ever _____________ in public? B: Yes, I have. B: Yes, I have. A: Where did you _____________ too much tequila? A: Where did you _____________? B: I _____________ too much tequila at my sister’s party. B: I _____________ in a karaoke bar. 10. A: Have you ever _____________ anything? 5. A: Have you ever _____________ in a hammock*? B: Yes, I have. B: Yes, I have. A: How did you _____________? A: What did you _____________? B: I _____________ very well. B: I _____________ some sweets when I was a child. * h ammock = amaca 18 COMPARATIVES Ben Ben and Steven are brothers. Steven 1. Ben is _____________________________________________ than Steven. (+ young) 2. Ben is _____________________________________________ than Steven. (+ handsome) 3. Ben is _____________________________________________ than Steven. (+ friendly) 4. Ben is _____________________________________________ as Steven. (= intelligent) 5. Steven is _____________________________________________ as Ben. (− tall) SUPERLATIVES 1. River _________________ (long) 2. University _________________ (old) 3. Building _________________ (tall) 4. Religion _________________ (ancient) 5. Man _________________ (rich) 6. City _________________ (populated) 7. Film _________________ (expensive) 8. Record _________________ (successful) 9. Planet _________________ (near) 10. _______________________________________________________________________________________ 19 PREDICTIONS During my lifetime... 1. Petrol __________ 2. Female President __________ 3. The moon __________ 4. Cash __________ 5. Cancer __________ 6. Nuclear war __________ 1. Catch a bus/train __________ 2. Cook __________ 3. Study __________ 4. Go out __________ __________ 6. Go to bed early __________ INTENTIONS This evening... 5. Watch a film 20 APPENDICE PRONOUNS Pronomi SOGGETTO OGGETTO ME AGGETIVO POSSESSIVO MY PRONOME POSSESSIVO MINE I YOU YOU YOUR YOURS HE HIM HIS HIS SHE HER HER HERS IT IT ITS ITS WE US OUR OURS YOU YOU YOUR YOURS THEY THEM THEIR THEIRS ADVERBS OF FREQUENCY gli avverbi di frequenza ALWAYS sempre USUALLY / NORMALLY di solito / normalmente FREQUENTLY / REGULARLY frequentemente / regolarmente OFTEN spesso SOMETIMES a volte OCCASIONALLY occasionalmente RARELY / SELDOM raramente HARDLY EVER / ALMOST NEVER quasi mai NEVER mai 21 APPENDICE IRREGULAR VERBS i verbi irregolari VERB BE BEAT BECOME BEGIN BITE BLOW BREAK BRING BUILD BURN BUY CATCH CHOOSE COME COST CUT DO DRAW DREAM DRINK DRIVE EAT FALL FEEL FIGHT FIND FLY FORGET GET GIVE GO GROW HANG HAVE HEAR HIDE HIT HOLD HURT KEEP KNOW LEARN essere/stare battere diventare incominciare/iniziare mordere soffiare rompere portare costruire bruciare comprare prendere scegliere venire costare tagliare fare disegnare sognare bere guidare mangiare cadere sentire lottare trovare volare dimenticare ottenere dare andare crescere appendere avere sentire nascondere colpire tenere in mano ferire/fare male tenere sapere/conoscere imparare PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE was / were beat became began bit blew broke brought built burnt or burned bought caught chose came cost cut did drew dreamt or dreamed drank drove ate fell felt fought found flew forgot got gave went grew hung had heard hid hit held hurt kept knew learnt or learned been beaten become begun bitten blown broken brought built burnt or burned bought caught chosen come cost cut done drawn dreamt or dreamed drunk driven eaten told felt fought found flown forgotten got given gone grown hung had heard hidden hit held hurt kept known learnt or learned 22 VERB PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE lasciare/partire LEAVE prestare LEND permettere/lasciare LET stendersi/sdraiarsi LIE accendere/illuminare LIGHT perdere LOSE fare MAKE significare MEAN incontrare MEET pagare PAY mettere PUT leggere READ telefonare/squillare RING alzarsi/sorgere RISE correre RUN dire SAY vedere SEE vendere SELL mandare SEND splendere SHINE sparare SHOOT mostrare SHOW chiudere SHUT cantare SING sedersi SIT dormire SLEEP odorare SMELL parlare SPEAK spendere/passare SPEND stare in piede STAND rubare STEAL nuotare SWIM prendere/portare TAKE insegnare TEACH strappare TEAR dire/raccontare TELL pensare THINK gettare THROW capire UNDERSTAND svegliarsi WAKE indossare WEAR vincere WIN scrivere WRITE left lent let lay lit lost made meant met paid put left lent let lain lit lost made meant met paid put read (pronunciato “red”) rang rose ran said saw sold sent shone shot showed shut sang sat slept smelt or smelled spoke spent stood stole swam took taught tore told thought threw understood woke wore won wrote read (pronunciato “red”) rung risen run said seen sold sent shone shot shown shut sung sat slept smelt or smelled spoken spent stood stolen swum taken taught torn told thought thrown understood woken worn won written 23 APPENDICE MODAL VERBS I verbi modali I verbi modali esprimono il modo in cui il soggetto si pone nei confronti dell’azione che compie. I verbi modali in inglese sono: CAN, MUST, MAY, WILL, SHALL, WOULD, SHOULD, OUGHT • Tutti i verbi modali si comportano da verbi ausiliari, cioè seguono il modello del verbo to be per quanto riguarda la costruzione interrogativa e negativa, l’uso di forme contratte e le risposte brevi. • Nella forma negativa sono seguiti da not. • Nella forma interrogativa precedono il soggetto. • Il verbo che segue un verbo modale va nella Forma Base (l’infinito senza to) tranne ought. • Alla terza persona singolare del Present Simple non prendono la s. Positiva: I can swim. He can drive. Negativa: I can’t swim. He can’t drive. Interrogativa: Can you swim? Can he drive? -­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐ SITI UTILI englishgratis.com – spiegazioni in italiano della grammatica inglese. english-­‐grammar-­‐lessons.com – spiegazione della grammatica inglese con relativi esercizi. englishpage.com – spiegazione della grammatica inglese con relativi esercizi. bbc.co.uk/worldservice/learningenglish – notizia con spiegazione dei vocaboli usati. guardian.co.uk – giornale inglese independent.co.uk – giornale inglese telegraph.co.uk – giornale inglese italianinsider.it – giornale italiano in lingua inglese thelocal.it – giornale italiano in lingua inglese YouTube – lezioni video di lingua inglese youtube.com/bbclearningenglish youtube.com/user/BritishCouncilLE youtube.com/user/freeenglishlessons youtube.com/user/EnglishLessons4U youtube.com/user/duncaninchina youtube.com/user/MinooAngloLink youtube.com/user/JenniferESL 24