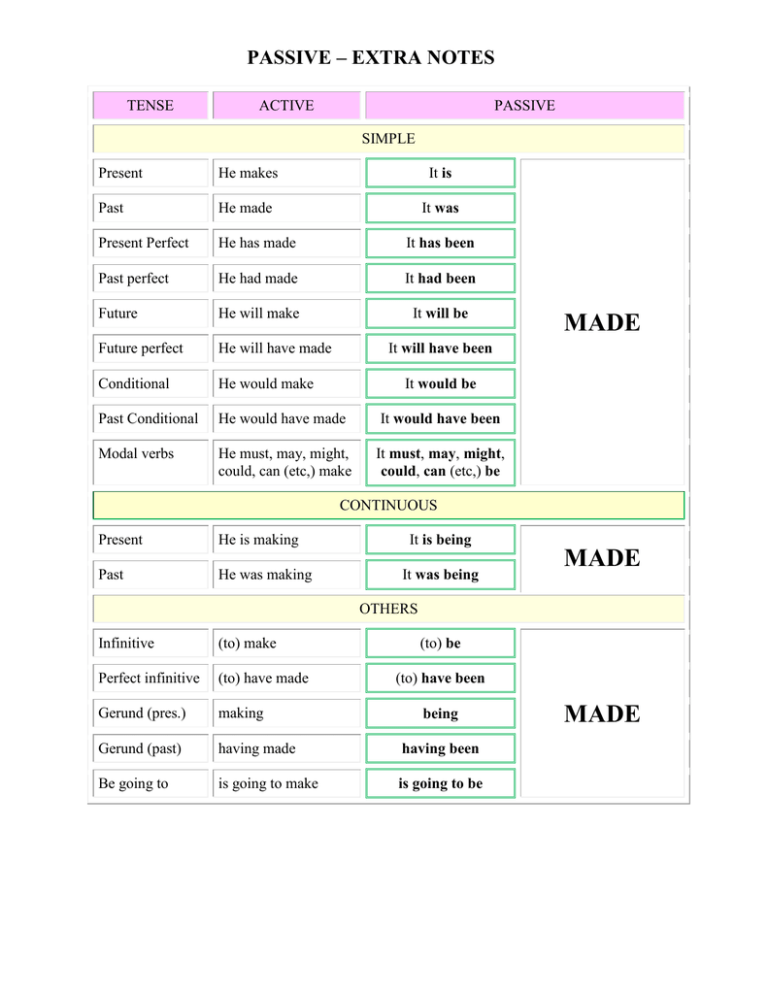
PASSIVE – EXTRA NOTES
TENSE
ACTIVE
PASSIVE
SIMPLE
Present
He makes
It is
Past
He made
It was
Present Perfect
He has made
It has been
Past perfect
He had made
It had been
Future
He will make
It will be
Future perfect
He will have made
Conditional
He would make
Past Conditional
He would have made
It would have been
Modal verbs
He must, may, might,
could, can (etc,) make
It must, may, might,
could, can (etc,) be
MADE
It will have been
It would be
CONTINUOUS
Present
He is making
Past
He was making
It is being
It was being
MADE
OTHERS
Infinitive
(to) make
(to) be
Perfect infinitive
(to) have made
Gerund (pres.)
making
Gerund (past)
having made
having been
Be going to
is going to make
is going to be
(to) have been
being
MADE
Nel trasformare una frase dalla forma attiva a quella passive, il verbo to be è coniugato allo
stesso tempo e modo della forma attiva.
Notate in particolare le forme del passato prossimo e del presente e passato progressivi.
The whale ate Jonah. Jonah was eaten by the whale.
They have broken the window. The window has been broken.
They are laying the table. The table is being laid.
They were serving dinner. Dinner was being served.
Il complemento d'agente è introdotto dalla preposizione by.
This picture was painted by a friend of mine
Naturalmente l'agente non è espresso se è indeterminato o irrilevante o ovvio.
Many buildings were damaged during the war.
The flight to Bombay has been cancelled.
Nelle frasi interrogative la preposizione by è generalmente posta dopo il verbo.
Who was that film directed by?
È possibile usare get in alternativa all'ausiliare to be in genere quando si parla di avvenimenti che accadono in modo improvviso o inaspettato.
Did anybody get hurt in the accident?
The thieves got caught red-handed.
Uso del passivo
Il passivo è un modo comune di rendere il "si" passivante italiano.
The days of the week are written with a capital letter in English.
In inglese, I giorni della settimana si scrivono con la lettera maiuscola.
Come in italiano, il passivo è inoltre usato:
quando si vuole dare più risalto all'azione che non all'autore della stessa o quando l'autore
è ignoto o irrilevante
When will the goods be delivered?
These photos of the Earth were taken from a satellite.
in scritti scientifici o formali in genere per rendere il testo più impersonale.
Acid rain is caused by pollution.
It has been noted that... (invece di We have noted that...)
Passivo con verbi che reggono una preposizione
I verbi che reggono una preposizione la mantengono anche nella forma passiva (ad
esempio listen to, send for, laugh at...)
They didn't listen to me. I wasn't listened to.
We have already sent for an ambulance. An ambulance has already been sent for.
I hate people laughing at me. I hate being laughed at.
They don't speak very well of him. He is not very well spoken of.
Particolari significati passivi
Alcuni verbi, tra cui sell, wash, iron, open, close possono essere usati con significato
passivo ("si" impersonale in italiano).
Is your book selling well?
This window doesn't open.
Dopo i verbi need, require e want (= necessitare) la forma in -ing ha significato passivo.
The fence needs repairing. (oppure to be repaired)
The curtains want/require washing. (oppure need to be washed)
EX 1. Volgete al passivo le seguenti frasi. Esprimete il complemento d'agente solo quando necessario.
1. They make this digital camera in South Korea.
2. Penguin published the first paperback book in 1935.
3. They didn't return the book to the library.
4. Did they steal the Picasso painting?
5. We must find a solution as quickly as possible.
6. They cannot repair the damage.
7. Nobody informed him.
8. Did they arrest all the suspects?
9. You should take this medicine three times a day.
10. I didn't write that report.
11. They will perform the play only once.
12. They do not provide meals during the flight.
EX 2. Formulate domande riferite alle parole sottolineate usando una forma passiva.
e.g. Leonardo da Vinci painted the Mona Lisa. WHO WAS THE MONA LISA PAINTED BY?
1. Lewis Carrol wrote "Alice in Wonderland" for a little girl.
Who __________________________________________________________?
Who __________________________________________________________?
2. We use this instrument for detecting radiation.
What __________________________________________________________?
3. The Mayas built those pyramids. Who...
__________________________________________________________?
4. My son drew this picture. Who...
__________________________________________________________?
5. They hit him with a stone. What...
__________________________________________________________?
6. Doctor Pringle treated me with acupuncture.
Who __________________________________________________________?
How__________________________________________________________?
EX 3. Completate le frasi seguenti inserendo gli ausiliari be o have nei tempi appropriati.
1. The performance ____ just ended, but few people are applauding. In fact while the most dramatic scenes
were ____ performed, whistles and laughing ____ heard among the audience.
2. Dr Sinclair isn't here. He ____ just gone out. There ____ been an accident and he ____ called to the
hospital urgently.
3. This drug (not) ____ tested yet.
4. When we got back from our holiday, we found that all the plants ____ died.
5. This road (not) ____ built yet when I last came here.
6. The whole area ____ changed in the past few years: the old houses in Clifford Street ____ demolished
and they ____ built a shopping centre in their place.
7. The last scenes of the film are now ____ shot in a studio.
8. New measures to limit traffic in urban areas are ____ studied. For the moment the city centre ____ been
closed to cars.
EX 4. Volgete al passivo le seguenti frasi.
1. A car has run over a lady.
2. Somebody's watching us.
3. They will have to re-examine the case.
4. A dog has bitten Tim recently.
5. They ought to have warned us of the danger.
6. When we arrived, they hadn't laid the table yet. When we arrived,
7. We have not paid the bill yet.
8. Look! That man is stealing your bike!
9. They were evacuating the town because of the hurricane.
10. They were still decorating the house when we moved in.
11. They are going to put a new model on the market.
12. We have already sent for a doctor.
13. Our agent will take care of everything.
14. You never listen when they speak to you.
15. An inspector from the insurance company is looking into the matter.
EX 5. Un villaggio in Transilvania. Mr Mortimer sta camminando per le strade deserte. quando un vecchio
si avvicina e lo avverte che quella sera nessuno deve uscire dopo il tramonto. Riscrivete le sue frasi
volgendole al passivo.
1. We haven't seen Dracula for a long time, / DRACULA HASN'T BEEN SEEN for a long time, 2. but
yesterday we heard strange noises in his castle. 3. Somebody predicted that the howl of a wolf would wake
him up 4. and yesterday we heard a wolf howling repeatedly in the night. 5. The women are putting garlic
on front doors 6. and the people have already put iron bars on the windows. 7. They are barring the doors
for the night. 8. Don't walk through the streets tonight Sir, or the shadow of Dracula will follow you.
COSTRUZIONI PASSIVE PERSONALI E IMPERSONALI
I was told / given….
Con verbi come ask, answer, tell, give, send, bring, hand, show, teach, offer, promise, pay,
grant, award (assegnare) owe (dovere; essere debitore di), .. di norma la persona (il complemento di
termine) diventa soggetto della frase passiva. La normale forma passiva esiste, ma è
poco usata.
Somebody sent me a bunch of roses. I was sent a bunch of roses.
(meno comune: A bunch of roses was sent to me.)
They asked us for our documents. We were asked for our documents.
They'll give you instructions later. You'll be given instructions later.
They have offered her a new job. She has been offered a new job.
Ian is teaching/showing us how Internet works. We are being taught/shown how Internet works by Ian.
After they had given Tom the prize, he... After Tom had been given the prize, he...
After being given the prize, Tom...
He is said / thought to be...
Verbi di "dire" e "pensare" come say, report (riferire), think, know, believe, suppose,
consider, expect (aspettarsi, prevedere, immaginare)... possono avere due costruzioni passive.
Nella costruzione personale il verbo è seguito dall'infinito presente o passato. Si usa:
l'infinito presente se la situazione è o era attuale nel momento in cui viene riferita;
l'infinito passato se la situazione è o era antecedente.
COSTRUZIONE IMPERSONALE
COSTRUZIONE PERSONALE
It is thought that certain computer games
Certain computer games are thought
are dangerous.
to be dangerous.
It was known that that airport was unsafe.
That airport was known to be unsafe.
It is reported that 60 people died in the air crash. Sixty people are reported to have died in the air crash.
It was said he had spent a few years in prison. He was said to have spent a few years in prison.
L'infinito può anche essere nella forma progressiva.
It is believed that extra-terrestrials are watching us. Extra-terrestrials are believed to be watching us.
Si crede che extraterrestri ci stiano osservando.
They suppose he was working for CIA at the time. He is supposed to have been working for CIA at the time.
Si suppone che stesse 1avorando per 1a CIA a quell'epoca.
EX 1. Riportate questa esperienza di viaggio usando La forma passiva personale.
1. They had told us that those tribes people were very unfriendly.
We 'D/HAD BEEN TOLD THAT those tribes people were very unfriendly.
2. But in fact they welcomed us. But in fact we ______________________ .
3. They showed us round their village. We ______________________ their village.
4. They offered us something to eat and drink. We ______________________ something to eat and drink.
5. Of course they asked us a lot of questions. Of course we ______________________ a lot of questions.
6. And they also asked us for some presents. And we ______________________ some presents.
7. In return they gave us some souvenirs. In return we ______________________ some souvenirs.
8. The only person who could speak some English taught us a few words in their language.
We ______________________ in their language ______________________ could speak some English.
EX 2. Volgete al passivo le seguenti frasi. Usate la forma passiva più comune.
1. They promised me a reward.
2. Didn't they tell you that the meeting was postponed?
___________________________________ the meeting was postponed?
3. Have they sent you the extracts of the conference?
___________________________________ of the conference?
4. First they told us we didn't need a visa and now they're telling us we need one.
5. We will show you the documentary in a minute.
___________________________________ in a minute.
6. They'll request us to leave the room if you keep talking.
___________________________________ the room if you keep talking.
7. We'll give you a reply by post.
8. Miss O'Sullivan gave me your name.
9. My neighbour has given me this recipe.
10. We shouldn't tell children frightening stories.
___________________________________ frightening stories.
11. My Brazilian friend taught me how to dance the samba.
___________________________________ dance the samba ___________________________________.
12. They didn't grant us any discount.
13. Who gave you this information?
14. Haven't they offered you anything yet?
15. They may tell you strange stories about cousin George. In fact he's a nice guy.
___________________________________ about cousin George. In fact he's a nice guy.
EX 3. Riscrivete le frasi come nell'esempio.
e.g. I like it when they give me presents. I LIKE BEING GIVEN PRESENTS.
1. Everybody dislikes it if you criticise them. Everybody ___________________________________
2. Cats like it if you stroke them. Cats ___________________________________
3. She loves the fact that people admire her. She ___________________________________.
4. I hate it when people ignore me. I ___________________________________.
5. I can't stand it when they give me orders. I can't ___________________________________.
EX 4. Riscrivete le seguenti frasi iniziando con le parole date in corsivo.
1. I can't open this door easily. This door ________________ easily.
2. This book is very easy to read. This book ________________ easily.
3. I prefer ironing damp clothes. It's easier. Damp clothes ________________ more easily.
4. We sold thousands of copies of this book. This book ________________ thousands of copies.
5. We need to cut the grass. The grass ________________.
7. I don't want you to tell me what I should do. I don't want to ________________ I should do.
8. There's nothing we can do now. There's nothing to ________________.
9. Nobody invited him. He came to the meeting without ________________.
10. Mr Reed was burnt in a fire in his house. Mr Reed is still critically ill after _______________________
in his house.
EX 5. Riscrivete Le frasi usando una forma passiva alternativa. Iniziate le frasi con le parole sottolineate.
e.g. Once it was believed that the earth was flat.
ONCE THE EARTH WAS BELIEVED TO BE FLAT.
1. It is supposed that the fugitive is armed. ____________________________________________
2. It is said that we are in for a cold winter.
3. It is reported that three people lost their lives in the gas explosion.
____________________________________________in the gas explosion.
4. It is expected that we'll be landing in half an hour.
5. It is believed that the disease is caused by a virus.
6. Once it was thought that being left-handed was a deficiency.
7. It was known that the area was dangerous.
8. It is expected that the rate of inflation will go up again.
9. It is said that a ghost is haunting that castle.
EX 6. Traducete usando una forma passiva.
1. Si parla inglese in tutto (= all over) il mondo.
2. Stanno costruendo un nuovo ponte.
3. Mi hanno mandato uno strano messaggio.
4. La cerimonia si terrà (= hold) domani pomeriggio.
5. Da chi fu inventato l'aereo?
6. Stanno servendo la colazione.
7. Il mio appuntamento è stato posticipato.
8. Ci avevano detto che era un buon albergo, ma non ci è piaciuto affatto.
9. Si crede che qualche forma di vita esista su Marte.
10. Si ritiene (= report) che almeno 30 persone siano morte a causa dei bombardamenti. (= because of the
bombings)