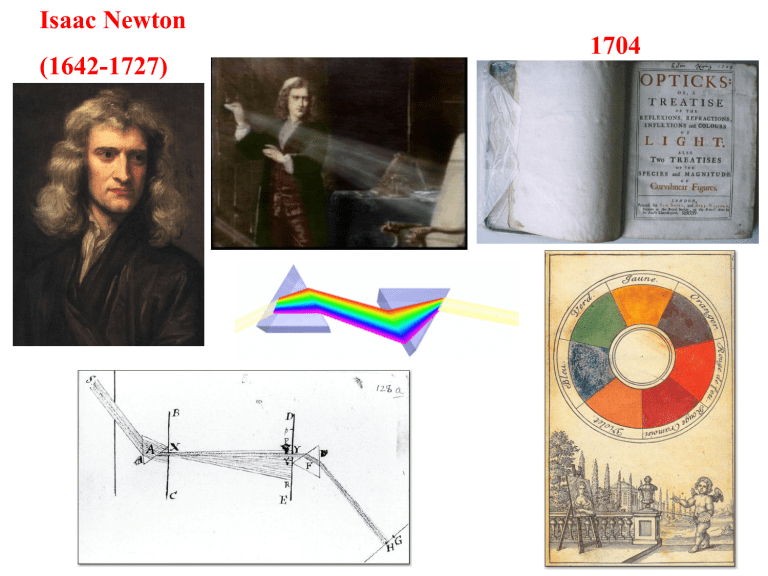
Isaac Newton
(1642-1727)
1704
Oltre i limiti dello
spettro visibile
IR: 1800 (Herschel)
UV: 1801 (Ritter)
Frederick William Herschel
(1738-1822)
Ultravioletto: effetti fotochimici
Infrarosso: effetti termici
Joseph von Fraunhofer (1787-1826)
The Wave Nature of Light
Saggi alla fiamma
Litio
Sodio
Potassio
Cesio
Calcio
Stronzio
Bario
Rame
Franz Schmidt & Haensch, Berlin, ca. 1916
Franz Schmidt&Haensch, Berlin S., 1902
Origine delle righe di Fraunhofer nello spettro solare
The Wave Nature of Light
Line Spectra and the Bohr Model
Bohr Model
• Colors from excited gases arise because electrons move between energy states in
the atom. (Electronic Transition)
Cavità assorbente (corpo nero)
Distribuzione
spettrale della
radiazione di cavità
Max Planck (1858 -1947)
E nh
n 0,1,2...
Formula di Planck (1900)
8 h 3
u ( , T )
c3
1
h
e kT
u ( , T )
1
8 hc
5
1
hc
e kT
1
Rydberg
1 1
R 2 2
2 n
1
n2
Rhc
En 2
n
Bohr
1 1
R 2 2
2 n
1
1
1
E Rhc 2 2
n
n
iniziale
finale
1 E
hc
La formula di Bohr è in accordo all’ esperimento
Diffrazione di onde meccaniche
The Wave Behavior of Matter
• Knowing that light has a particle nature, it seems
reasonable to ask if matter has a wave nature.
• Using Einstein’s and Planck’s equations, de Broglie
showed:
h
mv
• The momentum, mv, is a particle property, whereas is a
wave property.
• de Broglie summarized the concepts of waves and
particles, with noticeable effects if the objects are small.
Equazione di Schroedinger
dV
2
Densità di probabilità
Probabilità di trovare una particella tra V e V+dV
2
2
dV 1
E 1 / n
2
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Orbitals
Orbitals and Quantum Numbers
Representations of Orbitals
The s-Orbitals
Representations of Orbitals
The p-Orbitals
d-orbitals
+
+
-
-
+
+
-
-
+
-
+
+
-
+
-
-
+
+
d-orbitals
Many-Electron Atoms
Electron Spin and the Pauli Exclusion
Principle
Probabilità radiale
dP 2 dV 2 4r 2
Zeff = Z-s
Z eff
2
n
2
E~
Orbitals and Their Energies
Orbitals CD
Many-Electron Atoms
Figure 6.27
Orbitals CD
Figure 6.27
Figure 6.28
Orbitals CD
Periodic Trends
Two Major Factors:
•principal quantum number, n, and
•the effective nuclear charge, Zeff.
Figure 7.6
Periodicità del raggio atomico
Potenziale di ionizzazione
X
X+ + e-
Figure 7.10
IE clip
Figure 7.9
Affinità elettronica
X + e-
X-
EA
Elettronegatività
IP EA
2