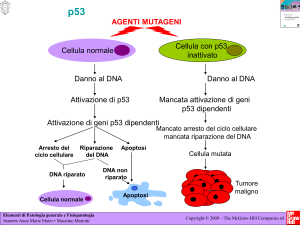
Le mutazioni sono dei
cambiamenti ereditabili della
sequenza di basi che
modificano l’informazione
contenuta nel DNA
Le mutazioni che osserviamo sono in sostanza danni al DNA che
non sono stati riparati. Molti errori vengono corretti perché:
1. La DNA
polimerasi ha un
sistema di
correzione degli
errori (attività
esonucleasica 3’ →
5’)
2. Ci sono altri sistemi di riparazione per correzione diretta
che ripristinano le condizioni iniziali della doppia elica
3. Ci sono sistemi di riparazione per escissione che
rimuovono la regione danneggiata producendo un gap che
viene in seguito colmato per nuova sintesi di DNA
Riparazione per correzione diretta
Tramite fotoriattivazione: In vari procarioti ed Eucarioti, dimeri di timina
vengono riparati grazie all’enzima fotoliasi, che scinde il dimero grazie
all’energia rilasciata da un fotone (λ=320-370 nm). (Nell’uomo esiste un
meccanismo simile, ma non l’enzima fotoliasi).
Tramite metiltransferasi: In molti procarioti, l’effetto degli agenti alchilanti
viene annullato da un enzima (metilguanina-metiltransferasi) che rimuove
il gruppo metilico dalla guanina
Molti ceppi di E. coli sono in grado
di correggere i dimeri di timina
anche al buio. Perciò devono
disporre di un sistema di
riparazione non attivato dalla luce:
riparazione per escissione.
Il sistema comprende, oltre a DNA
P I e ligasi, 4 enzimi: UvrA, UvrB,
UvrC e UvrD e opera tagliando una
sola elica intorno al dimero di
timina.
Figura 7.16
Peter J Russell, Genetica © 2010 Pearson Italia S.p.A
Types of DNA Damage Summarised
G
A
T
dsDNA Break
C
Mismatch
C-U deamination
ss Break
Thymidine dimer
Covalent X-linking
AP site
Sistema di riparazione dell’appaiamento errato in
E. coli
Il sistema di riparazione dell’appaiamento errato consiste
nell’escissione del segmento di DNA che contiene il
nucleotide sbagliato e nella successiva sintesi del nuovo
filamento
riparato.
In E. coli il taglio viene effettuato sul filamento ipo-metilato in
corrispondenza della sequenza GATC più vicina al sito di
errore. Un’esonucleasi rimuove i nucleotidi successivi fino al
sito dell’errore. La porzione che ne risulta a singolo filamento
viene prontamente riparata. Ogni filamento può essere
tagliato e corretto, ma lo stato di ipo-metilazione del
filamento neosintetizzato ne favorisce l’escissione.
Gli Eucarioti hanno gli omologhi di mutS e mutL ma non
mutH.
Single strand repair
•
Base excision repair
–
–
–
A base-specific DNA
glycosylase detects an altered
base and removes it
AP endonuclease and
phosphodiesterase remove
sugar phosphate
DNA Polymerase fills and DNA
ligase seals the nick
Action of DNA glycosylases
These enzymes hydrolyze the glycosidic bond of their
corresponding altered base (red) to yield an AP site.
Page 1177
O
N
O
O
O
N
NH
N
H2O
NH2
O
O
O
Abasic site
OH
Structure of human uracil–DNA glycosylase (UDG)
in complex with a 10-bp DNA containing a U·G
base pair.
Double strand repair
• Nonhomologous endjoining
– two broken ends of DNA
are joined together
– some nucleotides are cut
from both of the strands
– ligase joins the strands
together
DSB repair by Non Homologous End Joining
A single Ku heterodimer binds to each free
DNA end of a DSB and recruits DNA-PKcs,
resulting in the formation of the DNA-PK
complex. Subsequently, Xrcc4 /Ligase IV
complex binds to each of the DNA ends and
interacts to form a tetramer that may serve to
bridge the DNA ends. Other repair proteins are
likely involved in this pathway, including the
Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 (Xrs2) complex.
Double strand repair
• Homologous
recombination
– damaged site is copied
from the other
chromosome by special
recombination proteins
Homologous recombination (HR)
Homologous
recombination (HR) is a
multistep process that is
mediated
by
the
sequential accumulation of
proteins. After detection
of the DNA double-strand
break (DSB) and resection
of the DNA in the 5'3'
direction, RAD51 binds to
single-stranded
(ss)DNA
and displaces replication
protein A (RPA), which
leads
to
RAD51
polymerization (this phase
is referred to as the
presynaptic phase).
Once the homology search
is successful, the duplex is
captured and the RAD51
filament invades it to form
the heteroduplex structure
(synaptic phase). RAD54,
a DNA-dependent ATPase,
stabilizes
the
RAD51–
ssDNA complex, thereby
promoting this process.
Heteroduplex DNA extension and branch migration normally occurs during the postsynaptic
phase of HR.
DNA polymerases use the intact copy to re-synthesize the deleted DNA sequences, DNA
ligases join the newly synthesized fragments and the junctions are resolved by specific
endonucleases that are known as resolvases.
Homologous recombination (HR) is a multistep process that is mediated by the
sequential accumulation of proteins. After detection of the DNA double-strand break
(DSB) and resection of the DNA in the 5'3' direction, RAD51 binds to single-stranded
(ss)DNA and displaces replication protein A (RPA), which leads to RAD51
polymerization (this phase is referred to as the presynaptic phase). Although RAD52
stimulates the polymerization of RAD51, wild-type p53 can control the process in
vivo (the steps in the HR process that are controlled by p53 are shown) by its direct
binding to RAD51. Once the homology search is successful, the duplex is captured
and the RAD51 filament invades it to form the heteroduplex structure (synaptic
phase). RAD54, a DNA-dependent ATPase, stabilizes the RAD51–ssDNA complex,
thereby promoting this process. RAD54 can itself bind to p53 and scan the
heteroduplex, a process that is probably regulated by p53 alone, or preferably
targeted by RAD51. Depending on the extent of the damage, the mismatch is either
corrected exonucleolytically by p53 or it can restrain the exchange of imperfectly
homologous sequences. Heteroduplex DNA extension and branch migration normally
occurs during the postsynaptic phase of HR, and wild-type p53 can inhibit the
RAD51-promoted branch-migration process. The effect of p53 on heteroduplex or
RAD51-mediated branch migration has been shown in in vitro studies. DNA
polymerases use the intact copy to re-synthesize the deleted DNA sequences, DNA
ligases join the newly synthesized fragments and the Holliday junctions are resolved
by specific endonucleases that are known as resolvases.


![mutazioni genetiche [al DNA] effetti evolutivi [fetali] effetti tardivi](http://s1.studylibit.com/store/data/004205334_1-d8ada56ee9f5184276979f04a9a248a9-300x300.png)

![(Microsoft PowerPoint - PCR.ppt [modalit\340 compatibilit\340])](http://s1.studylibit.com/store/data/001402582_1-53c8daabdc15032b8943ee23f0a14a13-300x300.png)