COS'E' LA “FORMA BASE” DEL
VERBO?
E' IL VERBO SENZA SOGGETTO PRIMA, NE'
PREPOSIZIONI.
ex. swim, like, play
INFINITIVE form(tempo infinito)
Si costruisce con “TO+forma
base del verbo”.
TO sta per “-are/-ere/-ire”
ex. to sleep dormire, to eat
mangiare
TO traduce anche le
preposizioni italiane “di, a,
da, per”.
ex. to live per vivere,
to drink
da bere
LA FORMA NEGATIVA SI COSTRUISCE CON
“NOT+ TO+ FORMA BASE DEL VERBO”
ex We are here to study, not to play.
Siamo qui per studiare non per giocare.
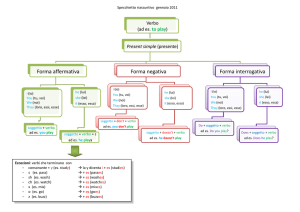
PRESENT SIMPLE
FORMA AFFERMATIVA:
Sogg+ forma base del verbo (tutte le persone)
ex. I play, we listen to, they study.
Sogg+ forma base del verbo+ -S/-ES/-IES
(terza persona singolare he/she/it)
ex. Susan plays, he listens to, Peter studies.
In genere alla terza persona si aggiunge -S
ex I eat
She eats
I verbi che terminano con -S,-SS,-SH,-CH,-O,-X
aggiungono -ES.
ex. We watch
He watches
I verbi che terminano in -Y preceduta da
consonante, perdono la y e aggiungono -IES.
ex. We study
Luke studies
I
EAT-WATCH-STUDY
YOU EAT-WATCH-STUDY
HE/SHE/IT EATS-WATCHES-STUDIES
WE EAT-WATCH-STUDY
YOU EAT-WATCH-STUDY
THEY EAT-WATCH-STUDY
FORMA INTERROGATIVA
In questo caso non basta fare l'inversione
soggetto verbo, come succedeva per il verbo to
be, to have got o to can, perchè NON parliamo di
verbi AUSILIARI.
Dobbiamo aggiungere noi un ausiliare, cioè
DO/DOES.
Questi ausiliari devono sempre essere messi
PRIMA del soggetto e NON hanno significato(non
si traducono!)
Con DOES il verbo perde -S, -ES, -IES.
Do+sogg.+ forma base verbo? (tutte le persone)
AFFERMATIVA: You play tennis.
INTERROGATIVA: Do you play tennis?
Does+sogg.+forma base verbo?
(terza persona singolare he/she/it)
AFFERMATIVA: Mary watches TV
INTERROGATIVA: Does Mary watch TV?
FORMA NEGATIVA
Anche per la forma negativa esistono due ausiliari
DON'T/DOESN'T.
Questi ausiliari devono sempre essere messi
DOPO il soggetto.
Con DOESN'T il verbo perde -S, -ES, -IES.
Sogg.+ don't+forma base verbo (tutte le persone)
AFFERMATIVA: You watch TV
NEGATIVA: You don't watch TV
Sogg.+doesn't+forma base verbo
(terza persona singolare he/she/it)
AFFERMATIVA: My mum cooks a cake
NEGATIVA: My mum doesn't cook a cake
SHORT ANSWER
YES+ SOGG.(pronome personale)+ do/does
NO+SOGG.(pronome personale)+don't/doesn't.
ex. Do you play tennis?
Yes, I do No, I don't.
Does your friend play tennis?
Yes, she does
No, she doesn't
QUANDO SI USA?
Per affermazioni di tipo generale
ex. I love English.
Per fatti che sono sempre veri.
ex. The sun rises from the East.
Per azioni di routine o che si compiono con una
certa frequenza (AZIONI ABITUALI)
ex. I wake up at 7.00, I have breakfast and I go
to school.
ADVERBS OF FREQUENCY
(Avverbi di frequenza)
Accompagnano il simple present e indicano la
frequenza con cui si fa un'azione.
La loro posizione nella frase è precisa: prima
del verbo principale e dopo il verbo to be. Se la
frase è negativa si trovano tra l'ausiliare ed i
verbo. Nella forma interrogativa, si trovano
dopo l’ausiliare e il soggetto.
Solo SOMETIMES si può trovare all'inizio o alla
fine della frase.
ALWAYS: SEMPRE
OFTEN: SPESSO
USUALLY: DI SOLITO
SOMETIMES: QUALCHE VOLTA
SELDOM/RARELY: RARAMENTE
NEVER:MAI (verbo alla forma affermativa)
EVER: MAI (nelle domande)
Examples
Your mum always cooks pasta.
Your mum doesn't always cook pasta.
Does your mum always cook pasta?
Your mum is often happy.
Your mum isn't often happy.
Is your mum often happy?
I never dance.
Do you ever dance?
ESPRESSIONI DI FREQUENZA
(all'inizio o al fondo della frase)
-ONCE: una volta
-TWICE: due volte
-THREE/FOUR etc. TIMES
tre/quattro volte
A MONTH al mese
A DAY
al giorno
A WEEK a settimana
A YEAR all' anno
-EVERY DAY: ogni giorno
-MANY TIMES: molte volte
-SEVERAL TIMES: diverse volte