caricato da
common.user5394
Grinberg's Theorem: Planar Graphs & Hamiltonian Cycles
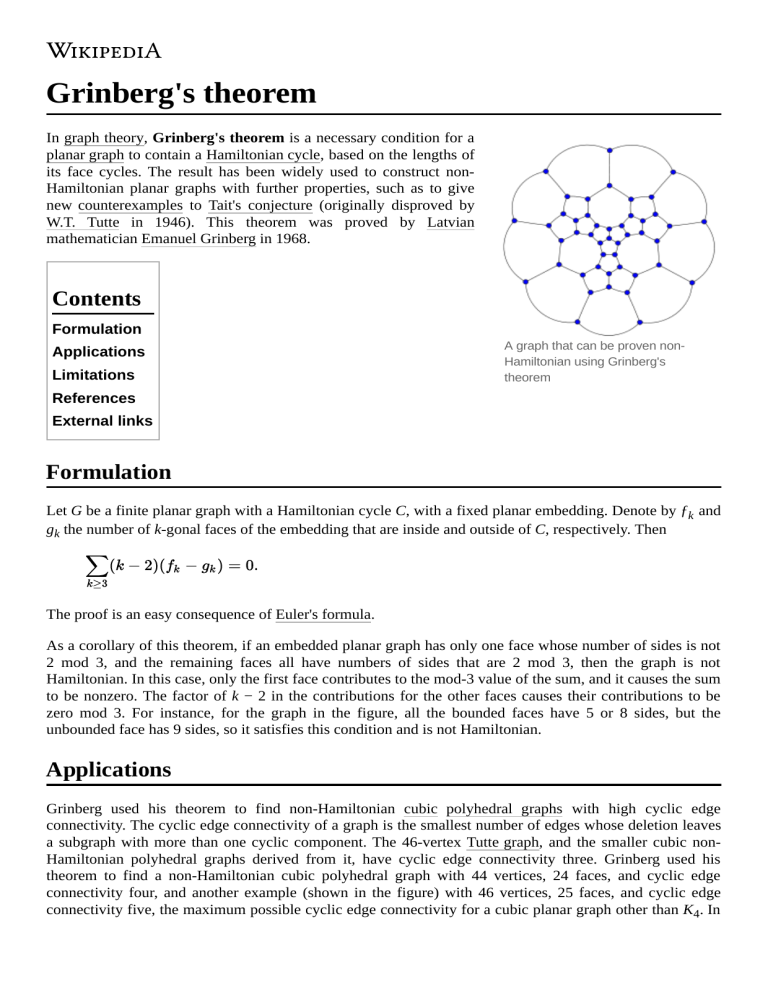
Grinberg's theorem In graph theory, Grinberg's theorem is a necessary condition for a planar graph to contain a Hamiltonian cycle, based on the lengths of its face cycles. The result has been widely used to construct nonHamiltonian planar graphs with further properties, such as to give new counterexamples to Tait's conjecture (originally disproved by W.T. Tutte in 1946). This theorem was proved by Latvian mathematician Emanuel Grinberg in 1968. Contents Formulation Applications Limitations A graph that can be proven nonHamiltonian using Grinberg's theorem References External links Formulation Let G be a finite planar graph with a Hamiltonian cycle C, with a fixed planar embedding. Denote by ƒk and gk the number of k-gonal faces of the embedding that are inside and outside of C, respectively. Then The proof is an easy consequence of Euler's formula. As a corollary of this theorem, if an embedded planar graph has only one face whose number of sides is not 2 mod 3, and the remaining faces all have numbers of sides that are 2 mod 3, then the graph is not Hamiltonian. In this case, only the first face contributes to the mod-3 value of the sum, and it causes the sum to be nonzero. The factor of k − 2 in the contributions for the other faces causes their contributions to be zero mod 3. For instance, for the graph in the figure, all the bounded faces have 5 or 8 sides, but the unbounded face has 9 sides, so it satisfies this condition and is not Hamiltonian. Applications Grinberg used his theorem to find non-Hamiltonian cubic polyhedral graphs with high cyclic edge connectivity. The cyclic edge connectivity of a graph is the smallest number of edges whose deletion leaves a subgraph with more than one cyclic component. The 46-vertex Tutte graph, and the smaller cubic nonHamiltonian polyhedral graphs derived from it, have cyclic edge connectivity three. Grinberg used his theorem to find a non-Hamiltonian cubic polyhedral graph with 44 vertices, 24 faces, and cyclic edge connectivity four, and another example (shown in the figure) with 46 vertices, 25 faces, and cyclic edge connectivity five, the maximum possible cyclic edge connectivity for a cubic planar graph other than K4. In the example shown, all of the bounded faces have either five or eight edges, both of which are numbers that are 2 mod 3, but the unbounded face has nine edges, unequal to 2 mod 3. Therefore, by the corollary to Grinberg's theorem, the graph cannot be Hamiltonian. Grinberg's theorem has also been used to find planar hypohamiltonian graphs, graphs that are not Hamiltonian but that can be made Hamiltonian by removing any single vertex. The construction again makes all but one face have a number of edges congruent to 2 mod 3 (Thomassen 1976, Wiener & Araya 2009). Thomassen (1981) uses the theorem in a somewhat more complicated way to find a planar cubic hypohamiltonian graph: the graph he constructs includes a 4-edge face adjacent to four 7-edge faces, and all other faces have five or eight edges. In order to satisfy Grinberg's theorem, a Hamiltonian cycle would have to separate one of the 4- or 7-edge faces from the other four, which is not possible. Limitations There exist planar non-Hamiltonian graphs in which all faces have five or eight sides. For these graphs, Grinberg's formula taken modulo three is always satisfied by any partition of the faces into two subsets, preventing the application of his theorem to proving non-Hamiltonicity in this case (Zaks 1977). It is not possible to use Grinberg's theorem to find counterexamples to Barnette's conjecture, that every cubic bipartite polyhedral graph is Hamiltonian. Every cubic bipartite polyhedral graph has a partition of the faces into two subsets satisfying Grinberg's theorem, regardless of whether it also has a Hamiltonian cycle (Krooss 2004). References Grinberg, È. Ja. (1968), "Plane homogeneous graphs of degree three without Hamiltonian circuits", Latvian Math. Yearbook 4 (in Russian), Riga: Izdat. “Zinatne”, pp. 51–58, MR 0238732 (https://www.ams.org/mathscinet-getitem?mr=0238732). English translation by Dainis Zeps, arXiv:0908.2563 (https://arxiv.org/abs/0908.2563). Krooss, André (2004), "Die Barnette'sche Vermutung und die Grinberg'sche Formel", Analele Universităţii din Craiova. Seria Matematică-Informatică (in German), 31: 59–65, MR 2153849 (https://www.ams.org/mathscinet-getitem?mr=2153849). Malkevitch, Joseph (January 2005), Euler's Polyhedral Formula: Part II (http://www.ams.org/fe aturecolumn/archive/eulers-formulaII.html), Feature Column, American Mathematical Society. Thomassen, Carsten (1976), "Planar and infinite hypohamiltonian and hypotraceable graphs", Discrete Mathematics, 14 (4): 377–389, doi:10.1016/0012-365X(76)90071-6 (https://doi.org/1 0.1016%2F0012-365X%2876%2990071-6), MR 0422086 (https://www.ams.org/mathscinet-get item?mr=0422086). Thomassen, Carsten (1981), "Planar cubic hypo-Hamiltonian and hypotraceable graphs", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B, 30 (1): 36–44, doi:10.1016/0095-8956(81)90089-7 (https://doi.org/10.1016%2F0095-8956%2881%2990089-7), MR 0609592 (https://www.ams.or g/mathscinet-getitem?mr=0609592). Wiener, Gábor; Araya, Makoto (2009), The ultimate question, arXiv:0904.3012 (https://arxiv.or g/abs/0904.3012), Bibcode:2009arXiv0904.3012W (https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2009arX iv0904.3012W). Tutte, W. T. (1998), "Chapter 2: Knights Errant", Graph theory as I have known it, Oxford Lecture Series in Mathematics and its Applications, 11, New York: The Clarendon Press Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-850251-6, MR 1635397 (https://www.ams.org/mathscinetgetitem?mr=1635397). Zaks, Joseph (1977), "Non-Hamiltonian non-Grinbergian graphs", Discrete Mathematics, 17 (3): 317–321, doi:10.1016/0012-365X(77)90165-0 (https://doi.org/10.1016%2F0012-365X%28 77%2990165-0), MR 0460189 (https://www.ams.org/mathscinet-getitem?mr=0460189). External links Grinberg Graphs (http://mathworld.wolfram.com/GrinbergGraphs.html), from MathWorld. Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Grinberg%27s_theorem&oldid=951466086" This page was last edited on 17 April 2020, at 09:02 (UTC). Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.