3
Unit 3
Name:
+
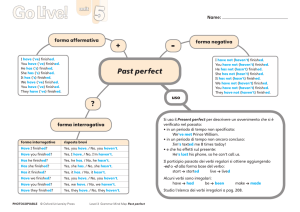
forma affermativa
I have (’ve) finished.
You have (’ve) finished.
He has (’s) finished.
She has (’s) finished.
It has (’s) finished.
We have (’ve) finished.
You have (’ve) finished.
They have (’ve) finished.
-
Present perfect
forma negativa
uso
I have not (haven’t) finished.
You have not (haven’t) finished.
He has not (hasn’t) finished.
She has not (hasn’t) finished.
It has not (hasn’t) finished.
We have not (haven’t) finished.
You have not (haven’t) finished.
They have not (haven’t) finished.
La forma affermativa del Present perfect si ottiene usando il presente dell’ausiliare have
(avere) seguito dal participio passato del verbo.
They’ve bought a new pair of shoes. Hanno comprato un nuovo paio di scarpe.
?
forma interrogativa
Il Present perfect si usa per parlare di:
•u
n evento di cui non si specifica la durata o il momento in cui è avvenuto e che ha di solito
ancora conseguenze sul presente
I’ve finished my homework. Ho finito i compiti.
•q
ualcosa che è avvenuto in un passato non specificato (quello che si vuole sottolineare è
l’evento in sé)
He’s done a parachute jump. Ha fatto un lancio con il paracadute.
forma interrogativa
risposte brevi
Il participio passato dei verbi regolari si forma come il Past simple, cioè aggiungendo -ed.
Have I finished?
Yes, you have. / No, you haven’t.
Have you finished?
Yes, I have. / No, I’m haven’t.
Has he finished?
Yes, he has. / No, he hasn’t.
Has she finished?
Yes, she has. / No, she hasn’t.
Has it finished?
Yes, it has. / No, it hasn’t.
Have we finished?
Yes, you have. / No, you haven’t.
Have you finished?
Yes, we have. / No, we haven’t.
Have they finished?
Yes, they have. / No, they haven’t.
Variazioni ortografiche:
•v
erbi che terminano in -e: si aggiunge solo -d. live ➔ lived
•v
erbi monosillabici che terminano in consonante preceduta da vocale: si raddoppia la
consonante finale. stop ➔ stopped
• Alcuni verbi bisillabici che terminano in consonante preceduta da vocale: si raddoppia
consonante finale. (Questo vale per i verbi che terminano in -l o con una sillaba accentata.)
travel ➔ travelled prefer ➔ preferred
•v
erbi che terminano in -y preceduta da consonante: si cambia la -y in -i + si aggiunge -ed.
study ➔ studied.
Il participio passato dei verbi irregolari è diverso per ogni verbo e va studiato a memoria.
Lo troverai nell’elenco dei verbi irregolari a pag. 84.
PHOTOCOPIABLE © Oxford University Press High Five Unit 3 – Grammar Mind Map Present perfect